Bridge Report:(7776)CellSeed The Fiscal Year ended December 2024
 Setsuko Hashimoto, President | CellSeed Inc. (7776) |
 |
Company Information
Market | TSE Growth Market |
Industry | Precision Instrument (Manufacturing) |
President | Setsuko Hashimoto |
HQ Address | Telecom Center Building, Aomi 2-5-10, Koto-ku, Tokyo |
Year-end | December |
Homepage |
Stock Information
Share Price | Number of shares issued (End of the Term) | Total market cap | ROE Act. | Trading Unit | |
¥398 | 34,666,419 shares | ¥13,797 million | -40.0% | 100 shares | |
DPS Est. | Dividend yield Est. | EPS Est. | PER Est, | BPS Act. | PBR Act. |
¥0.00 | - | ¥-30.58 | - | ¥62.10 | 8.1 x |
*Stock price as of closing on February 25, 2025. Each number is taken from the financial results of Fiscal Year ended December 2024.
Consolidated Earnings Trend
Fiscal Year | Sales | Operating Profit | Current Profit | Net Profit | EPS | DPS |
December 2021 | 161 | -864 | -887 | -914 | -53.18 | 0.00 |
December 2022 | 126 | -743 | -754 | -759 | -36.31 | 0.00 |
December 2023 | 190 | -697 | -710 | -846 | -29.43 | 0.00 |
December 2024 | 193 | -846 | -847 | -859 | -25.72 | 0.00 |
December 2025 Est. | 195 | -1,010 | -1,010 | -1,060 | -30.58 | 0.00 |
* The estimates were provided by the company. Units: million yen. Net profit is net income attributable to parent company shareholders until the Fiscal Year ended December 2021. Consolidated until the Fiscal Year ended December 2021. Unconsolidated from the Fiscal Year ended December 2022.
This Bridge Report presents CellSeed Inc.’s earnings results for the Fiscal Year ended December 2024 and other financial details.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1. Company Overview
2. Fiscal Year ended December 2024 Earnings Results
3. Fiscal Year ending December 2025 Earnings Forecasts
4. Conclusions
<Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance>
Key Points
- In the fiscal year ended December 2024, sales grew and loss augmented, but exceeded the forecast. Sales increased 3 million yen year on year to 193 million yen. In the regenerative medicine supporting business, the sales of cell cultureware business hit a record high successively. Tokai University entrusted them with the production of autologous cartilage cell sheets for 2 cases, and National Center for Child Health and Development entrusted them with the production of pediatric esophageal sheets for 1 case. Namely, they undertook the production of products for a total of 3 cases, and recorded sales. Operating loss was 846 million yen, up 148 million yen year on year. SG&A expenses, mainly R&D costs, augmented 151 million yen year on year.
- The sales of cell cultureware business in overseas markets increased significantly year on year. Both sales and profit exceeded the forecasts, because expenses fell below the initial forecast due to the reduction of costs for outsourcing development and maintaining cell culturing facilities, the delay in the start of clinical trials for allogeneic cartilage cell sheets, etc.
- For the fiscal year ending December 2025, sales are expected to rise 1 million yen year on year to 195 million yen and operating loss is projected to augment 163 million yen year on year to 1,010 million yen.
- For the regenerative medicine supporting business, they will make continuous efforts to expand the sale of devices mainly outside Japan, with the aim of increasing sales of existing products. They will also concentrate on the research and development of new products, to increase new clients. Regarding the regenerative medicine contract manufacturing services business, which supports regenerative medicine by utilizing a cell culturing center, they will keep concentrating on the activities for receiving orders from medical institutions. The sales in this segment are expected to be 195 million yen (192 million yen in the previous fiscal year).
- In the cell sheet regenerative medicine business, the creation of allogeneic cartilage cell sheets was promoted. For the third-phase clinical trial, after going through the Institutional Review Board (IRB), a contract has been concluded with each trial site. They are establishing a system in which surgery can be performed at each trial site.
- They are negotiating with Tokai University about milestone payments, which depend of the progress of clinical trials, but there remains a gap between the amount assumed by CellSeed and the amount assumed by the university, although the total amount of milestone payments has decreased, so they have not yet reached an agreement. In order to start clinical trials, it is necessary to enlist cooperation from Professor Masato Sato of Tokai University School of Medicine Department of Orthopaedics, so they will continue the negotiation to reach an agreement as soon as possible. Accordingly, the third-phase clinical trial has not been started.
- The “expansion of the business of cell cultureware,” which is one of growth strategies, has progressed steadily. With proteolytic enzymes, which are commonly used for collecting cells, cells are collected in a damaged state, and it is difficult to completely maintain the original functions and components of the cells. On the other hand, the company's product will make it possible to collect cells intact. Therefore, it is expected to significantly contribute to the improvement of industrial efficiency and effectiveness. The sales of this business hit a record high, as they met demand steadily and sales grew considerably in overseas markets in the fiscal year ended December 2024. The sales increased 3.5 times in the past 8 years. Profit has recovered, so they have almost posted profit in the second half of the fiscal year ended December 2024.
- Regarding clinical trials for allogeneic cartilage cell sheets, they have not reached an agreement with Tokai University regarding milestone payments, so the start of the third-phase clinical trial is delayed. There is concern about it, but we would like to pay attention to how much sales and profit will increase based on the regenerative medicine supporting business, which mainly handles cell cultureware business.
1. Company Overview
[1-1 Management philosophy]
The management philosophy of CellSeed is “CellSeed has formulated new ‘Mission and Vision’ in 2016, and is committed to contribute to the development of regenerate medicines.”
Mission | We take the initiative of contributing to global health care in the valuable and innovative field of regenerative medicine. |
Vision | We establish a cell sheet business platform and provide excellent regenerative medicine products around the world. |
[1-2 Regenerative medicine of CellSeed]
Regenerative medicine is a new kind of medicine for regenerating and curing lost, damaged or deteriorated organs.
CellSeed uses the fundamental technologies of the world's first “cell sheet engineering” developed in Japan by Professor Teruo Okano of the Tokyo Women’s Medical University in its “cell sheet regenerative medicine” that employs “cell sheets” for the cell regenerative medicine business, and the regenerative medicine support business, where temperature responsive cell cultureware used to fabricate cell sheets are developed and sold and the regenerative medicine consignment services, which support for research and development and commercialization of regenerative medicine, is provided.
“Cell sheet engineering” – Basic Technologies for Regenerative Medicine
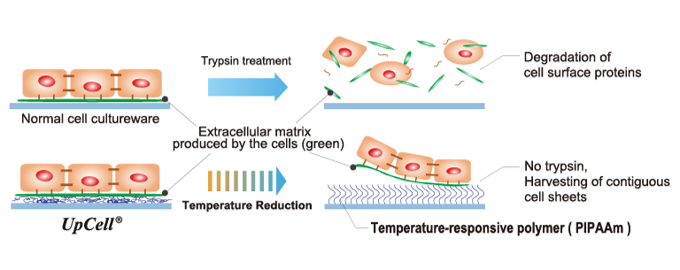
(From the company material)
"Cell sheet engineering" is a platform technology originating in Japan and the first of its kind in the world, which was invented by Mr. Teruo Okano, a professor emeritus of Tokyo Women's Medical University. Cells are cultured in “UpCell®,” a cell culture dish whose surface is processed with a temperature-responsive polymer that changes its molecular structure with temperature. The surface of a cell culture dish becomes moderately hydrophobic (water-repellent) at 37 °C, at which cells can attach, and hydrophilic (water-absorbent) at 20 °C, at which cells cannot attach. Therefore, by simply changing temperature, the organically bound "cell sheet" which retains the extracellular matrix (adhesion protein) can be recovered from the culture dish.
In general, cells secrete an extracellular matrix and grow by fixing themselves. In other words, cells cannot grow unless they are fixed somewhere while secreting adhesion proteins. However, in the conventional culture method, adhesion proteins are decomposed and recovered from cultured cells using proteolytic enzymes such as trypsin (there was no method for recovering cultured cells other than by decomposing adhesion proteins).
Huge Regenerative Medicine Market
The market size of regenerative medicine is expected to reach 2.5 trillion yen in Japan and 38 trillion yen worldwide in 2050, and a significant economic effect is expected.
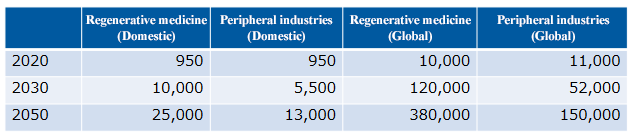
(From the company material, Unit: hundred million yen)
Expanding cell cultureware market
In recent years, along with progress in regenerative medicine research, there have been active efforts to manufacture biopharmaceuticals using substantial amounts of cultured cells, develop immunotherapy using cells, and solve food and environmental problems.
Currently, when using proteolytic enzymes, which is a commonly used cell collection technique, cells are collected in a damaged state, and it is difficult to completely maintain the original functions and components of cells. Introducing the company's temperature-responsive cell cultureware products makes it possible to collect cells without damage.
As a result, it is possible to use cells while maintaining all the functions and components that cells originally had. Thus, the company's products are attracting growing attention for their potential to significantly improve industrial efficiency and effectiveness in new markets.
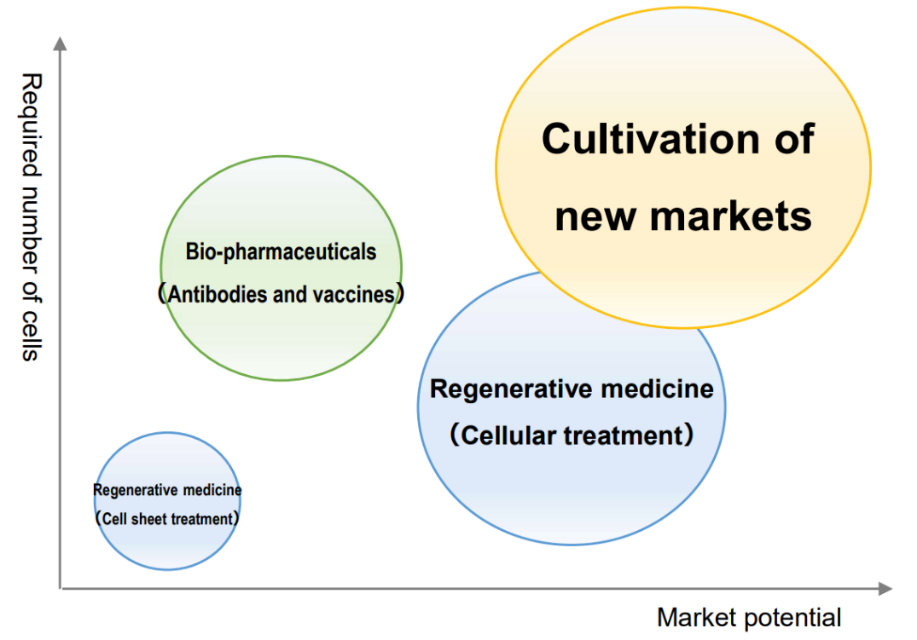
(From the company material)
[1-3 Business model of CellSeed]
Using the outcomes of research into cell sheets conducted at universities as seeds, the company performs clinical trials, transforms them into regenerative medicine products, and provides products to patients.
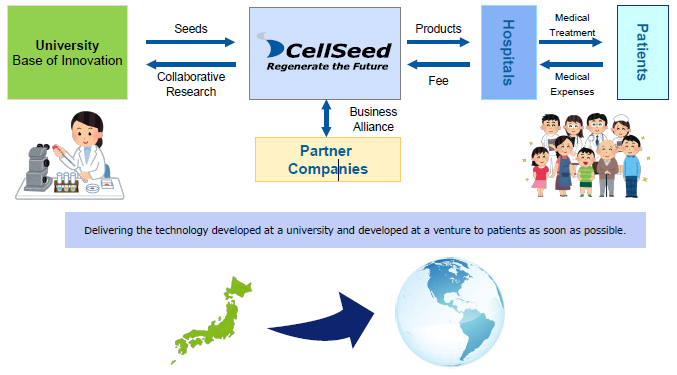
(From the company material)
[1-4 Business Description]
(1) Cell sheet regenerative medicine business
Although treatments based on the fundamental technology of "cell sheet engineering" is being developed in various areas, the company is focusing on "allogeneic cartilage cell sheet" for knee cartilage, and also conducting joint research with Hokkaido University on new treatments for central nerve injury-related diseases.
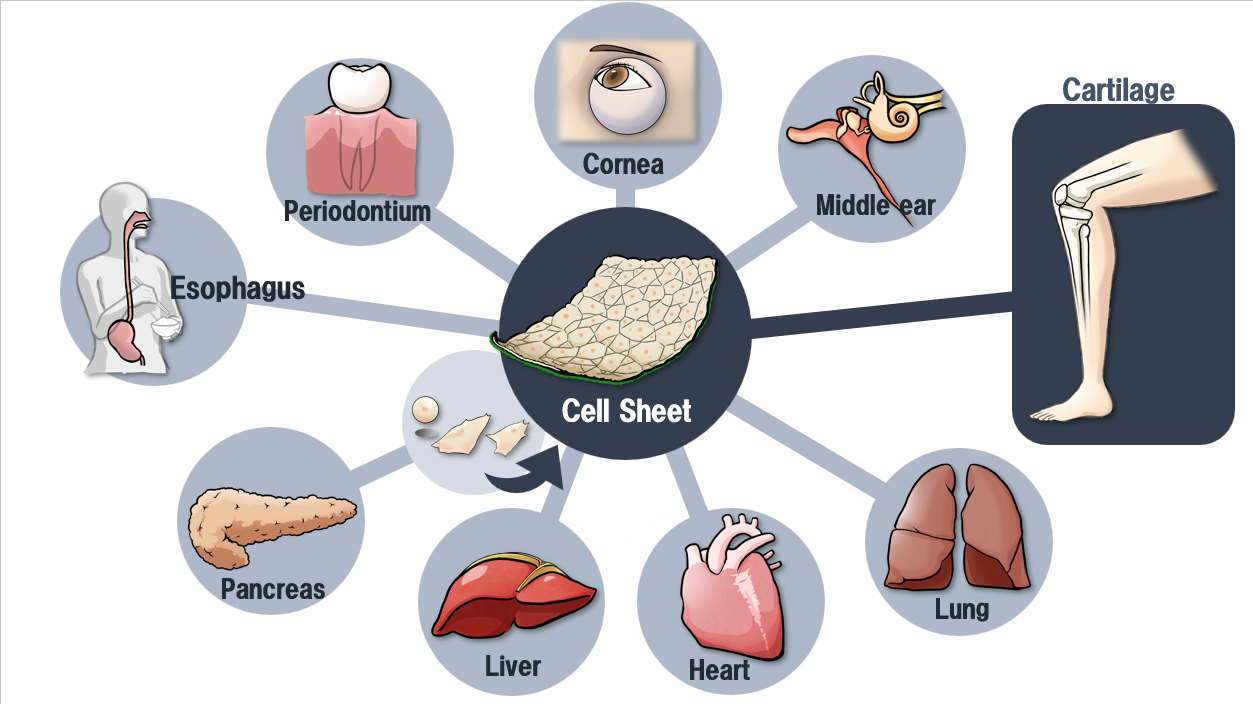
(From the company material)
“Allogeneic cartilage cell sheet”
“Allogeneic cartilage cell sheets,” which are cell sheets based on the cells of a person other than a patient, was developed by Professor Masato Sato of Tokai University School of Medicine Department of Orthopaedics, and CellSeed is developing them as products for regenerative medicine, etc. to treat osteoarthritis.
Knee osteoarthritis is slowly progressing, intractable degeneration of articular cartilage with no fundamental treatment. The number of potential patients in Japan is estimated to be about 30 million, of which about 10 million patients are thought to have subjective symptoms. Furthermore, population aging in Japan is expected to raise the number of patients diagnosed with the illness, making it a disease that needs to be dealt with immediately from the perspective of citizens’ healthy life expectancy and costs of long-term care and medical services. As of now, there are no methods to cure the injury completely, but the “allogeneic cartilage cell sheet” is aimed at regenerating the cartilage surface radically. The cartilage of the knee is called hyaline cartilage, which is hard and excellent in cushioning and abrasion resistance properties, differing from the cartilages of the ear, nose, etc., and it is difficult to regenerate. However, it was confirmed in clinical research in the Tokai University that the “allogeneic cartilage cell sheet” can regenerate the cartilage of the knee as hyaline cartilage.
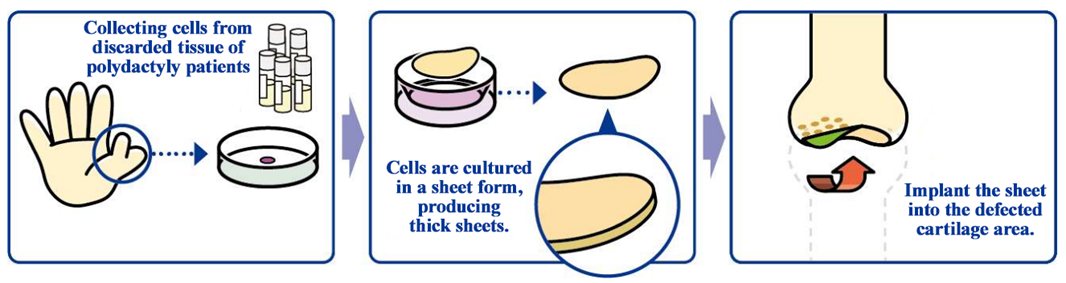
(From the company material)
Professor Masato Sato performed the world's first implant surgery in 2017, and 10 patients underwent implant surgery in the three years from 2017 to 2019. The treatment with allogeneic cartilage sheets has been adopted in the project for developing evaluation methods, etc. for the industrialization of regenerative medicine (support for acceleration of development of regenerative medicine seeds) of AMED (project period: Oct. 2018 to Mar. 2021).
For developing cartilage cell sheets with allogeneic cells, the discarded tissue of patients with polydactyly who have six fingers, so it is necessary to solve ethical issues, but in December 2020, the company obtained approval for the provision of cartilage tissue collected from patients with polydactyly from Ethical Committee of National Center for Child Health and Development.
In July 2021, a research and development project proposed by CellSeed was selected by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) for the "Development of Basic Technologies for the Industrialization of Regenerative Medicine and Gene Therapy (Project to Promote the Industrialization of Regenerative/Cell Medicine and Gene Therapy)," which is a subsidy project (project period: August 2021-March 2023).
In August 2022, the company reached an agreement with the center on the basic terms of a contract to establish a system for continuous provision of resected tissue during polydactyly surgery and commercialization for industrial use. Thus, it will be possible to continuously receive human tissue supply for clinical trials to manufacture and sell allogeneic cartilage cell sheets.
In April 2022, a patent was granted and registered in Japan for a "tissue regeneration cultured cell sheet, its manufacturing method, and how to use it."
In January 2023, a research group led by Professor Masato Sato of Tokai University confirmed the safety and efficacy of allogeneic cartilage cell sheets implanted into cartilage defects in the knee joints one year after surgery in all 10 patients in a clinical study of knee osteoarthritis that had been conducted since 2017. Their findings were published in the online journal npj Regenerative Medicine, a sister publication of Nature.
In addition, in March 2023, the company presented the results of the above-mentioned AMED project "Development of Basic Technologies for the Industrialization of Regenerative Medicine and Gene Therapy (Project to Promote the Industrialization of Regenerative/Cell Medicine and Gene Therapy)" at the Conference of the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine and is accumulating evidence of its effectiveness.
Meanwhile, before the start of clinical trials, the company is working to establish a system to ensure quality, by confirming safety as well as efficacy and establishing quality control and transportation methods for the cell sheets.
For cell banks made from tissues, a total of 20 tests, including cell count, viable cell rate, sterility test, endotoxin test, mycoplasma negative test, virus negative test, and other tests have been conducted to confirm its safety, and regarding cell sheets, 10 tests have been conducted including cell morphology, sheet properties, protein expression, virus negative test, and confirmation of the presence of chromosomal abnormalities.
Based on these results, the company submitted a notification of a clinical trial on September 2023. Then, PMDA finished the 30-day examination for the clinical trial.
They concluded contracts with facilities for conducting clinical trials, and developed a system for carrying out operations at the facilities, but it takes more time to register cases than initially planned, as it was first expected that the registration would be completed in the first half of 2024.
In parallel, they are negotiating with Tokai University about milestone payments, which depend of the progress of clinical trials, but there remains a gap between the amount assumed by CellSeed and the amount assumed by the university, although the total amount of milestone payments has decreased, so they have not yet reached an agreement. In order to start clinical trials, it is necessary to enlist cooperation from Professor Masato Sato of Tokai University School of Medicine Department of Orthopaedics, so they will continue the negotiation to reach an agreement as soon as possible. Accordingly, the third-phase clinical trial has not been started.
(Outline of the third-phase clinical trial)
* Test design: collaboration with multiple facilities, single-blinded, randomized, parallel-group trial
* Target number of cases: 96
* Subject patients: those who have knee osteoarthritis and are subject to proximal tibial osteotomy
* Major evaluation items: reports from patients (Patients evaluate their symptoms and QOL by themselves without help from medical doctors or others.)
* Facilities for conducting the test: a total of 5 facilities, including Tokai University Hospital (planned)
The company is also promoting the patent strategy. The U.S. patent application on “tissue regeneration culture cell sheets, manufacturing methods, and utilization methods thereof” related allogeneic cartilage cell sheets was accepted, and the patent will be granted. This is the outcome of joint research on allogeneic cartilage cell sheets carried out with Tokai University.
(2) Regenerative Medicine Consignment Services
The regenerative medicine support business consists of the regenerative medicine contract manufacturing business, which conducts the development of manufacturing methods, contract manufacturing, facility management, application support, and consulting for cell sheet products, and the cell cultureware business, which develops, manufactures, and sells cell cultureware such as UpCell®, RepCell®, and HydroCell®.
① Description of each business
*Regenerative medicine contract manufacturing business
The company is mainly engaged in contract development and manufacturing of cell sheets for pharmaceutical companies and research institutions. The company employs clinical culturists certified by the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine, and its staff with extensive culture experience develop manufacturing methods for regenerative medicine and other products and manufacture them at its cell culture center, which is licensed to manufacture specified cell processed products and regenerative medicine products.
The company obtained the permit for manufacturing specific processed cells (facility numbe FA3160008) in March 2017 and the permit for manufacturing products for regenerative medicine, etc. in October 2018.
In addition, the company provides support for preparing applications for regulatory approval, obtaining manufacturing and marketing licenses, and training engineers for all stages, from product development to manufacturing and marketing.
The company's main regenerative medicine contract manufacturing services include periodontal ligament cell sheets, autologous cartilage cell sheets, pediatric autologous epithelial cell sheets, and cell sheet culture and detachment training.
Autologous cartilage cell sheets were approved in January 2019 as Advanced Medical Treatment B under the Law for Ensuring Regenerative Medicine Safety. Tokai University started Advanced Medical Treatment B in 2020. CellSeed started undertaking the production of autologous cartilage cell sheets, and had continuously undertaken it until 2024.
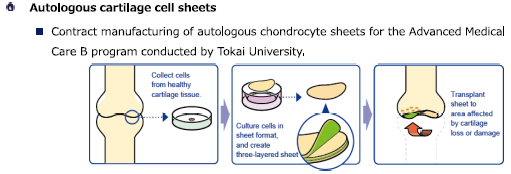
(From the company material)
The periodontal ligament cell sheet is the first case of contract manufacturing of cell sheets for use in investigator-initiated clinical trials.
Pediatric autologous epithelial cell sheets are intended for children after surgery for congenital esophageal atresia.
In May 2023, the company announced a new contract with Ikegami General Hospital to manufacture cell sheets for implantation of autologous cartilage cell sheets for knee joint cartilage damage.
As part of its regenerative medicine and other new medical treatment initiatives, Ikegami General Hospital will provide regenerative medicine to patients with damaged knee joint cartilage due to trauma or osteoarthritis by culturing their cartilage cells in sheet form and applying them to damaged cartilages in the knee joints to improve pain and joint function. Regenerative medicine treatment is provided at the expense of patients who are not eligible for the advanced medical treatment (cartilage regeneration therapy using autologous cell sheets) provided by Tokai University Hospital, as well as patients from overseas.
Ikegami General Hospital has submitted the provision plan necessary for the implementation of regenerative medicine to the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, which has been accepted, and it is now preparing the patient acceptance system.
CellSeed also expects to expand its contract manufacturing business by undertaking the manufacturing of cell sheets to be used in self-funded medical treatments.
Regarding regenerative medicine, in accordance with the law for promotion of regenerative medicine, the government enforced “the act for securing the safety of regenerative medicine, etc.,” which facilitates the R&D in academia with clinical research, advanced medicine, and medical treatments at patients’ own expense, and “the act for pharmaceutical products and medical devices, etc.,” which specifies the procedures for acquiring the approval for manufacturing and sale after non-clinical tests and clinical trials. In reality, there exists a significant gap between the R&D in academia and the approval for manufacturing and sale.
The company aims to bridge this gap by solving the problems with academia through regenerative medicine services and help offer regenerative medicine to patients.
* Cell cultureware business
The temperature-responsive cell cultureware invented by Professor Okano of Tokyo Women's Medical University in 1989 can detach cells simply by lowering the temperature, making it possible to collect intact cell sheets for the first time in the world.
Temperature-responsive cell cultureware is sold worldwide, and research and development of treatment methods using cell sheets are being actively pursued by many researchers.
Until now, the company has developed and supplied various equipment products according to user needs such as universities, research institutes, and pharmaceutical companies, and in September 2022, the company starts to sell new products, UpCell® flasks.
UpCell® is a device that can collect intact cells in a sheet without using enzymes that damage cells by fixing a temperature-responsive polymer to the surface of the device.
The UpCell® flask type has a larger culture area than the conventional UpCell® dish, enabling the collection of larger amounts of undamaged cells, which will be optimal in research related to immunology and cell therapy. It is possible to recover cell sheets that maintain a higher level of biological functions through cell culturing that is close to the biological environment, such as co-culturing using the UpCell® 6-well cell culture inserts.
The company expects to meet new demand for the mass cultivation of cells for research purposes to develop preventive and therapeutic methods for various infectious diseases and cancer diseases and anticipates medium/long-term business growth.
In December 2022, the temperature-responsive cell culture device product "UpCell® ADVANCE" was registered in the Master Files for Devices (MAF) of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
MAF is a system under which a supply manufacturer registers its corporate information, manufacturing know-how, and other trade secrets and various data as MAF with the FDA in advance. This enables drug and medical device manufacturers to apply for marketing approval from the FDA simply by quoting the MAF number.
Although the completion of MAF registration does not necessarily mean that the FDA has finished confirming or evaluating the quality and safety of the product, the MAF registration is expected to contribute to the promotion of "UpCell® ADVANCE" because it will no longer be necessary for drug and medical device manufacturers to request from CellSeed to submit confidential information when they file applications with the FDA for products using "UpCell® ADVANCE."
The company also concentrate on the education of engineers in cell culture. In Aomi Cell Culture Innovation Center, they hold training for users of UpCell®, giving lectures on how to produce cell sheets and exfoliate cells.
② Main facilities and equipment
Cell Culture Center
The cell sheets used for advanced medicine are cultivated at the cell culture center of CellSeed on commission.
With a floor space of about 763 square meters, the Cell Culture Center is equipped with an automated monitoring system that controls the cleanliness, room pressure, temperature and humidity, and operational status of equipment (such as incubators and reagent stockers), and a surveillance camera system throughout the entire facility. Besides, the facility is only twenty-minute drive from Haneda International Airport, making it possible and easy to transport products by air.

(From the company material)
Aomi Cell Culture Innovation Center
The full-scale operation started in September 2021. The company develops and manufactures cell culture equipment, including laboratory flask products, etc.
[1-5 Growth Strategy]
The company's two main growth strategies are “Business expansion of cell culture equipment” and “Promotion of business cooperation for global development.”
(1) Business expansion of cell culture equipment
In 1989, Professor Okano of Tokyo Women's Medical University invented temperature-responsive cell culture equipment that can exfoliate cells simply by lowering temperature as described above, making it possible to recover intact cell sheets for the first time, leading to the advancement of research and development of treatment methods using the cell sheet by many researchers.
In 2020, the company’s equipment business exceeded 100 million yen in sales for the first time. In September 2021, the company established a new development and manufacturing facility exclusively for cell culture equipment products, and also agreed to extend the sales contract with Thermo Fisher Scientific of the United States, an alliance partner for expanding sales of equipment products overseas, until 2025.
In recent years, many efforts have been made to manufacture biopharmaceuticals using cells cultured in large quantities, perform immunotherapy using the cells themselves, and solve food and environmental problems.
However, with proteolytic enzymes, that is, a commonly used cell recovery technique, cells are recovered in a damaged state, and it is difficult to completely maintain the original functions and components of the cells. On the other hand, by adopting this product, it is possible to recover cells without damage, and it is expected to greatly contribute to improvement of industrial efficiency and effectiveness in the new market, because all functions and components of cells are maintained.
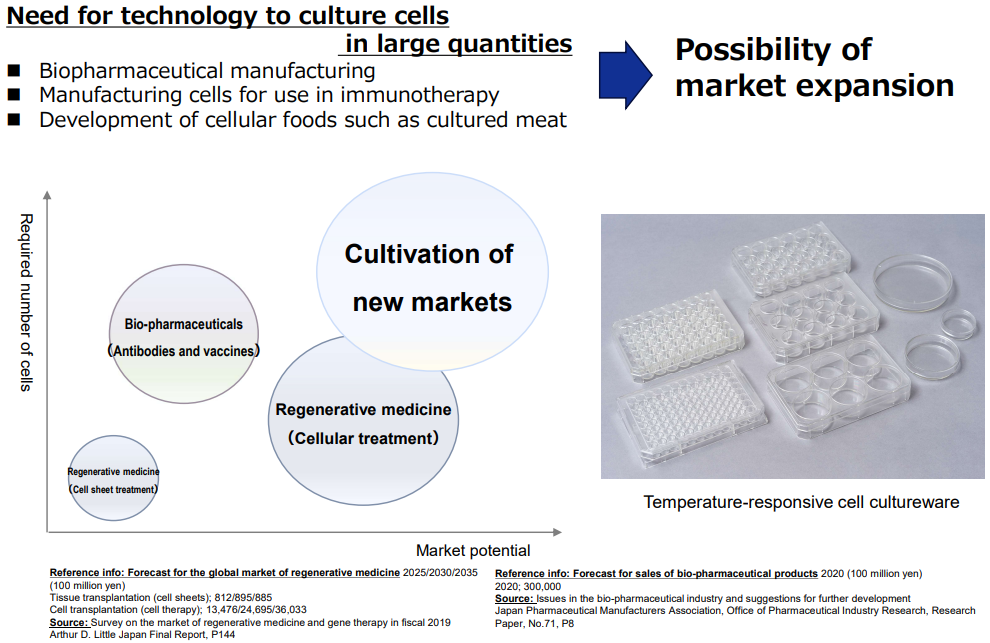
(From the company material)
They met such demand steadily, and the sales of this business increased 3.5 times between 2016 and 2024. The sales of cell cultureware business hit a record high in fiscal year ended December 2024 like in fiscal year ended December 2023, because overseas sales rose considerably.
(2) Promotion of business cooperation for global development
In parallel with the steady expansion of product sales for the research and development phase aimed at application to regenerative medicine, product sales for new applications aimed at mass culturing of cells for research are increasing, mainly overseas is rapidly expanding, and overseas sales currently account for about 80%.
For this reason, the company is focusing not only on product development in the conventional regenerative medicine market, but also on product development to provide solutions that meet the needs of new markets, such as developing new cell culture equipment products and establishing new manufacturing facilities.
In December 2022, “UpCell® ADVANCE,” temperature-responsive cell cultureware, was registered in the Master Files (MAF) for Devices of Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
They released “UpCell Flask,” a product suited for the mass culture and collection of cells, in 2022, and plan to sell it outside Japan, too.
The company is also strengthening the sales structure to further expand the overseas sales channels. As mentioned above, The company has extended the sales contract with Thermo Fisher Scientific, the alliance partner for expanding sales of equipment products overseas, to further strengthen collaboration, provide consistent quality and service, and further enhance customer satisfaction. In order to achieve this goal, the company has built a quality management system and obtained ISO9001:2015 certification, an international standard, in January 2020.
In addition, aiming for global expansion, the company has been promoting business alliances by participating in exhibitions held not only in Japan but also in other Asian countries and Europe, such as a presentation at “Translate! 2021 – Metrics and Milestones of Success” held in Berlin in January 2021. The company aims to find business partners by participating in exhibitions held in various regions.
2. Fiscal Year ended December 2024 Earnings Results
[2-1 Non-Consolidated Earnings]
| FY 12/23 | FY 12/24 | YoY | Forecast Ratio |
Sales | 190 | 193 | +3 | +23 |
Gross Income | 107 | 110 | +2 | - |
SG&A | 804 | 956 | +151 | - |
R&D | 456 | 573 | +116 |
|
Operating Profit | -697 | -846 | -148 | +73 |
Ordinary Profit | -710 | -847 | -137 | +72 |
Net Income | -846 | -859 | -13 | +80 |
* Unit: million yen.
Exceeded forecasts despite an augmentation of sales and loss.
Sales increased 3 million yen year on year to 193 million yen.
In the regenerative medicine supporting business, the sales of cell cultureware business exceeded the sales of the previous fiscal year, hit a record high successively.
Tokai University entrusted them with the production of autologous cartilage cell sheets for 2 cases, and National Center for Child Health and Development entrusted them with the production of pediatric esophageal sheets for 1 case. Namely, they undertook the production of products for a total of 3 cases, and recorded sales.
Operating loss was 846 million yen, up 148 million yen year on year. SG&A expenses, mainly R&D costs, augmented 151 million yen year on year.
The sales of cell cultureware business in overseas markets increased significantly year on year. Both sales and profit exceeded the forecasts, because expenses fell below the initial forecast due to the reduction of costs for outsourcing development and maintaining cell culturing facilities, the delay in the start of clinical trials for allogeneic cartilage cell sheets, etc.
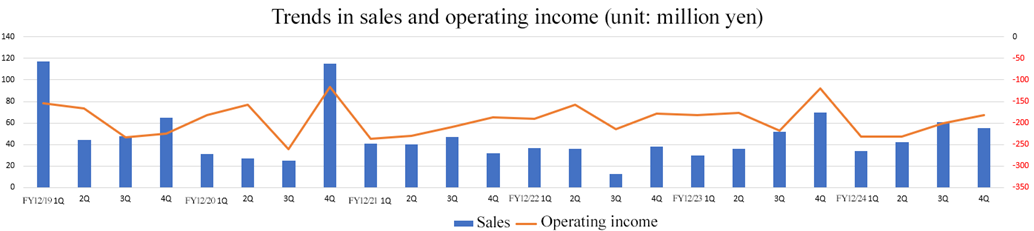
[2-2 Segment trends]
| FY 12/23 | FY 12/24 | YoY |
Regenerative medicine supporting business | 182 | 192 | +9 |
Cell sheet regenerative medicine business | 7 | 1 | -6 |
Consolidated sales | 190 | 193 | +3 |
Regenerative medicine supporting business | -32 | -20 | +11 |
Cell sheet regenerative medicine business | -468 | -595 | -126 |
Adjustments | -196 | -230 | -33 |
Consolidated operating Income | -697 | -846 | -148 |
* Unit: million yen.
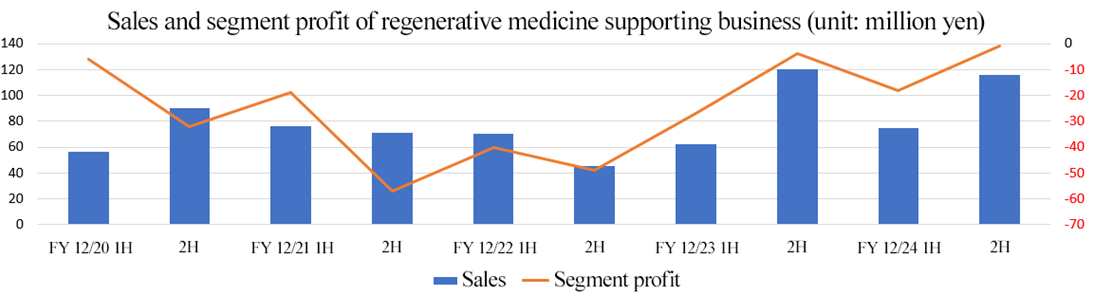
Regenerative medicine supporting business
Sales were 192 million yen, and operating loss was 20 million yen (Sales were 182 million yen, and operating loss was 32 million yen in the previous fiscal year).
For the cell cultureware business, they cemented the cooperation with existing distributors and gave presentations about the results of R&D and set up their corporate booth at several academic conferences, to promote sales. Outside Japan, sales increased significantly year on year, hitting a record high. The sales of this business grew 3.5 times in the past 8 years.
In the regenerative medicine contract manufacturing business, which supports regenerative medicine by utilizing a cell culturing center, National Center for Child Health and Development entrusted them with the production of pediatric esophageal sheets for 1 case, and Tokai University entrusted them with the production of autologous cartilage cell sheets for 2 cases. Namely, they undertook the production of products for a total of 3 cases, and recorded sales. (1 case in the 1st quarter, 0 cases in the 2nd quarter, 1 case in the 3rd quarter, and 1 case in the 4th quarter)
Cell sheet regenerative medicine business
Sales were 1 million yen, and operating loss was 595 million yen (Sales were 7 million yen, and operating loss was 468 million yen in the previous fiscal year).
For allogeneic cartilage cell sheets, a clinical trial plan for the third-phase clinical trial of the allogeneic cartilage cell sheet (CLS2901C) was submitted to the PMDA on September 20, 2023. After going through the Institutional Review Board (IRB), a contract has been concluded with each trial site. They are establishing a system in which surgery can be performed at each trial site. However, it takes more time to register cases than initially planned. In parallel, they are negotiating with Tokai University about milestone payments, which depend of the progress of clinical trials, but there remains a gap between the amount assumed by CellSeed and the amount assumed by the university, although the total amount of milestone payments has decreased, so they have not yet reached an agreement. In order to start clinical trials, it is necessary to enlist cooperation from Professor Masato Sato of Tokai University School of Medicine Department of Orthopaedics, so they will continue the negotiation to reach an agreement as soon as possible. Accordingly, the third-phase clinical trial has not been started.
Regarding business alliances, the company engages in activities for forming business alliances and concluding collaborative research contracts with multiple companies, for accelerating commercialization and the sale of allogeneic cartilage cell sheets.
[2-3 Financial Condition and Cash Flows (CF)]
◎ Summary of BS
| December 2023 | December 2024 | Increase/ decrease |
| December 2023 | December 2024 | Increase/ decrease |
Current Assets | 2,351 | 2,312 | -39 | Current Liabilities | 123 | 103 | -20 |
Cash | 2,163 | 2,134 | -28 | ST Borrowings | 7 | 10 | +3 |
Receivables | 51 | 37 | -14 | Fixed Liabilities | 177 | 166 | -10 |
Inventories | 46 | 45 | +0 | LT Borrowings | 143 | 132 | -10 |
Fixed assets | 113 | 120 | +6 | Total Liabilities | 301 | 269 | -31 |
Total Assets | 2,465 | 2,433 | -32 | Net Assets | 2,164 | 2,163 | -1 |
* Unit: million yen |
|
|
| Total Liabilities and Net Assets | 2,465 | 2,433 | -32 |
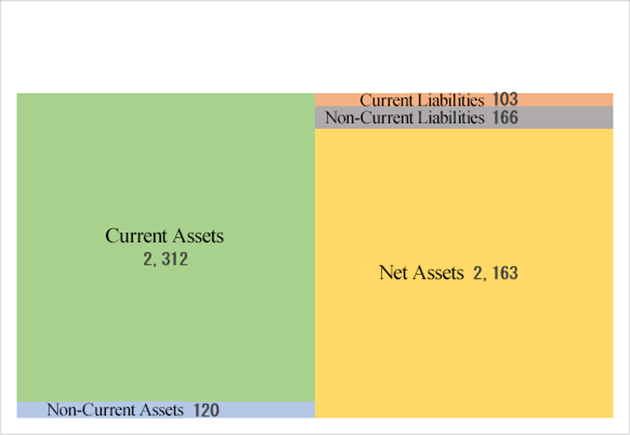
*This figure is created by Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. Based on disclosed materials.
Total assets decreased 32 million yen from the end of the previous fiscal year to 2,433 million yen, mainly due to the decrease of cash and deposit.
Net assets stood at 2,163 million yen, almost unchanged from the end of the previous fiscal year, as the deficit of retained earnings augmented while capital stock and capital surplus increased.
The capital adequacy ratio increased 1.6 percentage points from the end of the previous fiscal year to 88.5%.
◎ CF
| FY 12/23 | FY 12/24 | Increase/decrease |
Operating Cash Flow | -779 | -866 | -86 |
Investing Cash Flow | 56 | -18 | -74 |
Free Cash Flow | -723 | -884 | -161 |
Financing Cash Flow | 1,814 | 855 | -958 |
Cash and Equivalents | 2,163 | 2,134 | -28 |
* Unit: million yen.
The cash inflow from financial activities shrunk due to the decrease in revenues caused by the issuance of shares through the exercise of share acquisition rights.
The cash position remained almost unchanged.
[2-4 Topics]
◎ Display of products, presentation about research, etc. at academic conferences
In December 2024, too, they actively exhibited their products and gave presentations about research at academic conferences, such as “the General Meeting of the Japan Society for Regenerative Medicine,” “Regenerative Medicine EXPO,” and “Regenerative Medicine JAPAN.”

|
 |
 |
◎ 4th Cell Sheet Engineering Innovation Forum is scheduled to be held
In November 2025, they plan to hold “the 4th Cell Sheet Engineering Innovation Forum.”
 |
3. Fiscal Year ending December 2025 Earnings Forecasts
[3-1 Earnings forecasts]
| FY 12/24 Act. | FY 12/25 Est. | YoY |
Sales | 193 | 195 | +1 |
Operating Income | -846 | -1,010 | -163 |
Ordinary Income | -847 | -1,010 | -162 |
Net Income | -859 | -1,060 | -200 |
* Unit: million yen
Increase in sales, expanding of loss.
Sales are expected to increase 1 million yen year on year to 195 million yen, while operating loss is forecast to augment 163 million yen to 1,010 million yen year on year.
<Regenerative medicine supporting business>
They will make continuous efforts to expand overseas sales of mainly devices, and collect and analyze data on sales provided by major distributors, with the aim of increasing the sales of existing products based on more careful, proactive judgment. They will concentrate on R&D for new products that would meet customer needs and follow the market trend, in order to reel in new clients.
In the regenerative medicine contract manufacturing business, which supports regenerative medicine by utilizing a cell culturing center, they will keep concentrating on the activities for receiving orders from medical institutions. The sales of this segment are projected to be 195 million yen (192 million yen in the previous fiscal year).
<Cell sheet regenerative medicine business>
The creation of allogeneic cartilage cell sheets was promoted. This development is expected to require further R&D costs. Regarding the third-phase clinical trial, they will make efforts to start it as soon as possible.
They will actively negotiate with candidate licensees of technologies for pipelines for new business.
[3-2 Significant Events Related to Going Concern]
The balance of cash on hand (cash and deposits) as of the end of December 2024 was 2,134 million yen, due to the procurement of funds through the exercise of stock acquisition rights, and the financial base has been stable. On the business side, however, the company has not yet been able to show the path to the early commercialization of its first cell sheet regenerative medicine product, which is a significant issue in the cell sheet regenerative medicine business.
Based on the above, the company has determined that, as of the end of December 2024, there continue to be circumstances that raise substantial doubt on the going concern assumption.
The company will proceed with the development of allogeneic cartilage cell sheets and try to seize earning opportunities by commercializing the first product for cell sheet-based regenerative medicine as soon as possible and finding business alliance partners, to improve the above situation.
4. Conclusions
The “expansion of the business of cell cultureware,” which is one of growth strategies, has progressed steadily. With proteolytic enzymes, which are commonly used for collecting cells, cells are collected in a damaged state, and it is difficult to completely maintain the original functions and components of the cells. On the other hand, the company's product will make it possible to collect cells intact. Therefore, it is expected to significantly contribute to the improvement of industrial efficiency and effectiveness. The sales of this business hit a record high, as they met demand steadily and sales grew considerably in overseas markets in the fiscal year ended December 2024. The sales increased 3.5 times in the past 8 years. Profit has recovered, so they have almost posted profit in the second half of the fiscal year ended December 2024.
Regarding clinical trials for allogeneic cartilage cell sheets, they have not reached an agreement with Tokai University regarding milestone payments, so the start of the third-phase clinical trial is delayed. There is concern about it, but we would like to pay attention to how much sales and profit will increase based on the regenerative medicine supporting business, which mainly handles cell cultureware business.
<Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance>
◎ Organization type, and the composition of executive directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with audit and supervisory committee |
Directors (excluding audit and supervisory committee members) | 4 directors, including 3 external ones(including an independent one) |
Auditors and supervisory committee members | 3 committee members, including 3 external ones (including an independent one) |
◎ Corporate Governance Report (Latest Update:April 5, 2024)
Basic Policy
With the missions to introduce technological innovations, to exert creativity and to contribute to people’s health and welfare by providing high-quality products and services, we are enhancing corporate governance to raise quality in all of our corporate activities. We will implement timely and appropriate information disclosure to ensure the transparency of decision-making and to enhance accountability. We will also improve our business management and auditing systems and strengthen our management checking functions.
<Reasons for Non-compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
CellSeed has stated, “Our company implements all the basic principles stipulated in the Corporate Governance Code as a TES Growth listed company.”
This report is not intended for soliciting or promoting investment activities or offering any advice on investment or the like, but for providing information only. The information included in this report was taken from sources considered reliable by our company. Our company will not guarantee the accuracy, integrity, or appropriateness of information or opinions in this report. Our company will not assume any responsibility for expenses, damages or the like arising out of the use of this report or information obtained from this report. All kinds of rights related to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. The contents, etc. of this report may be revised without notice. Please make an investment decision on your own judgment. Copyright(C) Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |
For back numbers of Bridge Reports on CellSeed Inc. (7776) and Bridge Salon (IR seminar), please go to our website at the following URL. www.bridge-salon.jp/



