Bridge Report:(4425)Kudan Fiscal Year ended March 2024
Kudan Inc. (4425) |
 |
Corporate Information
Exchange | TSE Growth |
Industry | Information and communications |
Managing Director & CEO | Daiu Ko |
Address | 2-10-15 Shibuya, Shibuya-ku Tokyo |
Year-end | End of March |
URL |
Stock Information
Share Price | Shares Outstanding (end of term) | Total market cap | ROE Act. | Trading Unit | |
¥2,900 | 10,288,867 shares | ¥29,837 million | -4.9% | 100 shares | |
DPS Est. | Dividend yield Est. | EPS Est. | PER Est. | BPS Act. | PBR Act. |
0.00 | - | - | - | ¥203.15 | 14.3 x |
*The share price is the closing price on May 27. All figures are taken from the financial results for FY 3/24.
Earnings Trend
Fiscal Year | Sales | Operating Income | Ordinary Income | Net Income | EPS | DPS |
Mar. 2021 (Actual) | 127 | -451 | -1,575 | -1,608 | -214.97 | 0.00 |
Mar. 2022 (Actual) | 271 | -433 | -681 | -2,237 | -283.74 | 0.00 |
Mar. 2023 (Actual) | 332 | -598 | -394 | -413 | -49.30 | 0.00 |
Mar. 2024 (Actual) | 490 | -527 | -50 | -69 | -7.88 | 0.00 |
Mar. 2025 (Estimate) | 700 | -430 | - | - | - | 0.00 |
*Unit: yen, million yen. Net income is profit attributable to owners of the parent. Hereinafter the same shall apply. The earnings forecasts are that of the company. The company will not disclose the exact forecast figures of ordinary income and net income due to the difficulty in estimating foreign exchange gain or loss, which have a significant impact on them.
This report briefly describes Kudan Inc., the financial results for the term ended March 2024, and growth progress and initiatives.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1. Company Overview
2. Fiscal Year ended March 2024 Earnings Results
3. Fiscal Year ending March 2025 Earnings Forecasts
4. Growth Progress and Initiatives
5. Conclusions
<Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance>
Key Points
- Kudan Inc. is a company that carries out research and development of deep technology specializing in the algorithms for artificial perception (AP), which corresponds to the “eyes” of machines (computers and robots). Its strengths and characteristics include the capability of flexibly responding to the growth of diverse demand, which is expected in the future, and a group of professionals in AP. The company has secured a firm position based on the alliance with Artisense Corporation, which is led by Professor Daniel Cremers, who has produced globally recognized research results as a pioneer in self-driving technologies.
- In the fiscal year ended March 2024, sales increased 47.5% year on year to 490 million yen, with an operating loss of 527 million yen (a loss of 598 million yen in the previous fiscal year). The company is focusing on “customer commercialization” and “solution development” as the “two pillars of growth,” which are starting to show results. With regard to customer commercialization, the business is progressing due to the growth of projects and the subsequent expansion of product sales. The total number of commercialization by customers has increased to eight, with the scope expanding to drones, autonomous driving, and other areas. Product-related sales reached 270 million yen, 40 times larger than those in the previous year. Regarding the solution development, the company established a business foundation, had discussions and reached an agreement on a policy for introducing a digital twin as a solution with partners.
- Thanks to the two pillars of growth, the company expects a significant increase in sales and a reduction in loss in the fiscal year ending March 2025. Sales are forecast to increase 42.6% year on year to 700 million yen, with an operating loss of 430 million yen (527 million yen in the previous fiscal year). In terms of customer commercialization, the company expects project growth to accelerate thanks to the contributions from product packaging, which will serve as a “trigger.” In terms of solution development, the company will promote ecosystem collaboration and expand its area into robots and autonomous driving. In addition, it will work on the integration of AI and semiconductors to support the two pillars of growth.
- Even after the announcement of financial results on May 15, 2024, there have been a series of releases by customers announcing the start of product sales, such as “A Chinese delivery robot company decided to sell robots equipped with Kudan technology” (May 21, 2024) and “A U.S.-based robot company decided to sell robots equipped with Kudan technology” (May 22, 2024). At present, their impact on business performance is expected to be minor, but one of the two pillars of growth, “customer commercialization,” is making steady progress.
- In the short term, we would like to pay attention to how much the number of cases of commercialization by customers, which has reached 8, will increase in the fiscal year ending March 2025. In the medium term, we would like to pay attention to when customer products will enter the distribution stage, as they aim to achieve sales of 700 million yen.
1. Company Overview
Kudan Inc. is a company that carries out R&D of deep technology (or deep tech), specializing in algorithms for artificial perception (AP) which acts as the eyes of machines, such as computers and robots.
Working in pairs with artificial intelligence (AI), which serves as the brain of machines, to complement each other as deep tech, AP helps machines evolve to function autonomously. The company operates business based on its unique milestone model focused on the deep tech that has an impact on a wide range of industries through highly sophisticated technological innovations.
【1-1 Corporate history】
Mr. Tomohiro Ohno, currently serving as a Managing Director, became convinced of the prospects and growth potential of the AP technology when working at Andersen Consulting (currently Accenture PLC) and set up Kudan Limited in the United Kingdom in January 2011, at which he pursued his own research and development on the Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology that provides a basis for the AP technology.
In November 2014, he established Kudan Inc. intending to extend the administrative department through business expansion while moving further ahead with his research and development. The company started offering evaluation software for demonstration of the Kudan SLAM technology in December 2016 and officially began to provide Kudan SLAM in the term ended in March 2018.
It got listed on the Market of the High-Growth and Emerging Stocks (Mothers) of the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) in December 2018.
In April 2022, the company got listed on the Growth Market of TSE, through market reclassification.
Consisting of four inside directors, Managing Director & CEO Daiu Ko, who joined the company after working for Toyota Motor Corporation and McKinsey & Company, Managing Director Tomohiro Ohno, Kohei Nakayama, a director and CFO, and Tian Hao, COO, Kudan’s management team places a heavy emphasis on swiftness.
【1-2 Corporate philosophy】
Kudan’s corporate philosophy is “to stand alone, and dare to create what is new and different.”
The philosophy guides the company into avoiding following suit and daring to challenge the generally accepted wisdom. Embracing the philosophy, the company aims to expand its business and research and development, raise shareholder interests, and become a one-of-a-kind company in the market by formulating policies that enable them to stand out from all other companies.
While adopting a corporate vision of “Eyes to the All Machines,” Kudan aims to become a player that offers technology essential for full autonomy and automation, goals that all kinds of machines and devices will strive to reach.
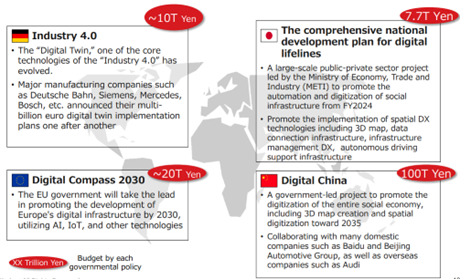
【1-3 Market environment】
In recent years, the increasing need for automation of operations in every industry and advancement of hardware technology, including sensors and semiconductors complementary to algorithms, have been rapidly spreading and practically utilizing the AP algorithms.
In addition, the impact of the spread of COVID-19 has resulted in soaring demand for saving labor and working remotely for operations that require neither human interaction nor group work in all industries. The growth of demand for automation technology, such as robotics, autonomous driving, and drones, is significant particularly in the fields of logistics, manufacturing, construction, retail, etc.
Target technology/device | Economic impact |
IoT | Real GDP boosted by the increase in the use of IoT and AI is estimated at 132 trillion yen in 2030.
The number of people in employment in 2030 when the use of IoT and AI is promoted is facilitated further is estimated to be 63 million, up 7,390,000 compared to the number of people employed when the use of IoT and Ai is not promoted. |
AI | GDP in 2030 is expected to be 9.8% (11.2 trillion dollars) to 14% (15.7 trillion dollars) higher with an impact of AI than without. |
Autonomous driving systems | It is projected that the passenger economy (*) will stand at 800 billion dollars in 2035 and 7 trillion dollars in 2050 globally when autonomous cars are put into practice.
The economic impact is broken down into Mobility as a Service (MaaS) for consumers (3.7 trillion dollars), MaaS for businesses (3.0 trillion dollars), and newly emerging driverless vehicle services (0.2 trillion dollars).
*The passenger economy: economic and social value realized by level-5 fully autonomous cars |
Drones | The market scale of the drone business in Japan is forecasted to be 193.2 billion yen in FY 2020, up 37% from the year before, and reach 642.7 billion yen in FY 2025 (about 3.3 times larger than that of FY 2020).
Drone services were the strongest market in FY 2019 with a 68% year-on-year increase to 60.9 billion yen followed by the drone body market which grew 37% year on year to 47.5 billion yen and the drone peripheral services market which showed a 46% year-on-year rise to 32.6 billion yen.
These three markets are expected to continue booming, with the market scales for FY 2025 are estimated at 442.6 billion yen (about 7.3 times greater than that of FY 2019) for the services market, 122.9 billion yen (about 2.6 times greater than that of FY 2019) for the body market, and 77.1 billion yen (about 2.4 times greater than that of FY 2019) for the peripheral services market, respectively, in descending order. |
*Created concerning “Reference material 2: Case studies for estimating the economic impact of advanced technology” used at the 10th meeting for discussing new governance models for realizing Society 5.0 as posted on METI’s website. The red and bold parts were provided by Investment Bridge Co., Ltd.
In addition to these applications that are already under development, there are many areas where AP (Artificial Perception) technology will be applied and integrated in the future by supporting various advanced technologies, and it is expected that AP (Artificial Perception) technology will be implemented in society at a speed beyond what was previously expected.
【1-4 Business content】
Kudan has issued a license for Kudan SLAM, a software for integrating such algorithms as SLAM, which is the mission-critical technology of AP, into hardware, and grants it to customers.
It is essential to learn about AP (Artificial Perception) and SLAM to understand the business and technological superiority of Kudan.
Below are descriptions of AP and SLAM.
<What is AP?>
Artificial perception (AP) is a technology put forward by Kudan Group that is carrying out research and development thereof.
The evolution of AI (artificial intelligence), a technology that replaces the human brain, is remarkable.
However, the recent evolution of AI is mainly limited to “Internet AI” that does not directly operate in the real (physical) space. At the same time, the demand for “embodied AI” that can directly affect the real space is expected to increase significantly in the future. Machines (computers and robots), which have remained in the Internet space for a long period of time, are heading toward autonomous functions in the real space.
However, autonomous actions and functions of machines cannot be realized by AI alone. It can only be realized by mutually linking and complementing AI (Artificial Intelligence) with the advanced technology AP (Artificial Perception), which is equivalent to the “eyes” for understanding the surroundings. AP (Artificial Perception) is an essential technology that gives machines advanced visual capabilities like human eyes.
With the evolution of AI, the need for AP technology that connects machines and the real world is expected to grow even more in the future.
<What is SLAM?>
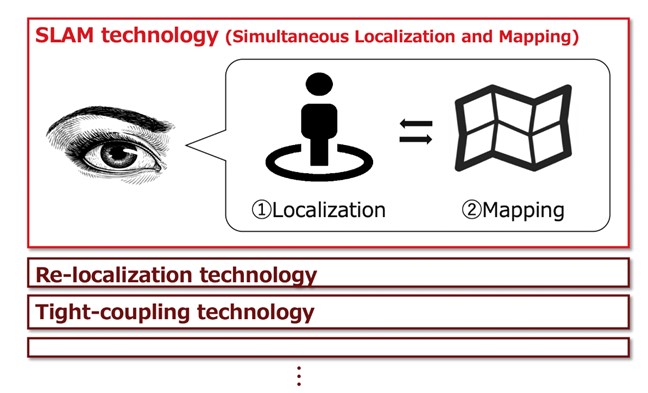
“SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping” plays a key role in enabling the AP (Artificial Perception) to fully demonstrate its required capabilities.
SLAM is a technology for each computer to concurrently “estimate the self-location (localization: checking where you are)” and “produce an environmental map (mapping: checking your surroundings)” in the real environment based on data input from external sensors, such as cameras and lidar.
It is possible to record how you have travelled in a new environment while producing a map (tracking) and recognize where you are based on a previously produced map (re-localization).
Unlike GPS and beacons, which detect the position from external radio waves, it recognizes its own position in a standalone manner. Thus, it can be used in a wider range of environments, situations, and use cases.
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
Taking a car applied with the SLAM technology as an example, the technology localizes the car based on a computer program of mathematically processing the distance that the car has travelled, camera images, and sensor information provided by Lidar, which is a sensor using laser light, and outputting three-dimensional information (such as the direction, distance, and size) and kinesthesia (such as the location and movement) on a real-time and precise basis and, at the same time, makes a three-dimensional map based on data on the surroundings amassed by the sensors.
In the case of cars, SLAM enables drivers to obtain basic information for safe travel by car by using a three-dimensional map drawn from time to time by the technology while driving cars, even if they have no information in advance on road conditions (such as the location of cars driving in the front, back, left, and right of their cars, how fast the cars in all directions drive, the road width, and the number of road lanes).
Differing from GPS, which detects a position with external radio waves, and beacons, it recognizes the self-position in a stand-alone manner, so it can be used in a broader range of environments, situations, and cases.
SLAM is the most critical technology for AP, and what are extremely important are precision and processing speed when it comes to ensuring the safety in autonomous cars. Such technological issues have been pointed out as obstacles to using SLAM for general purposes.
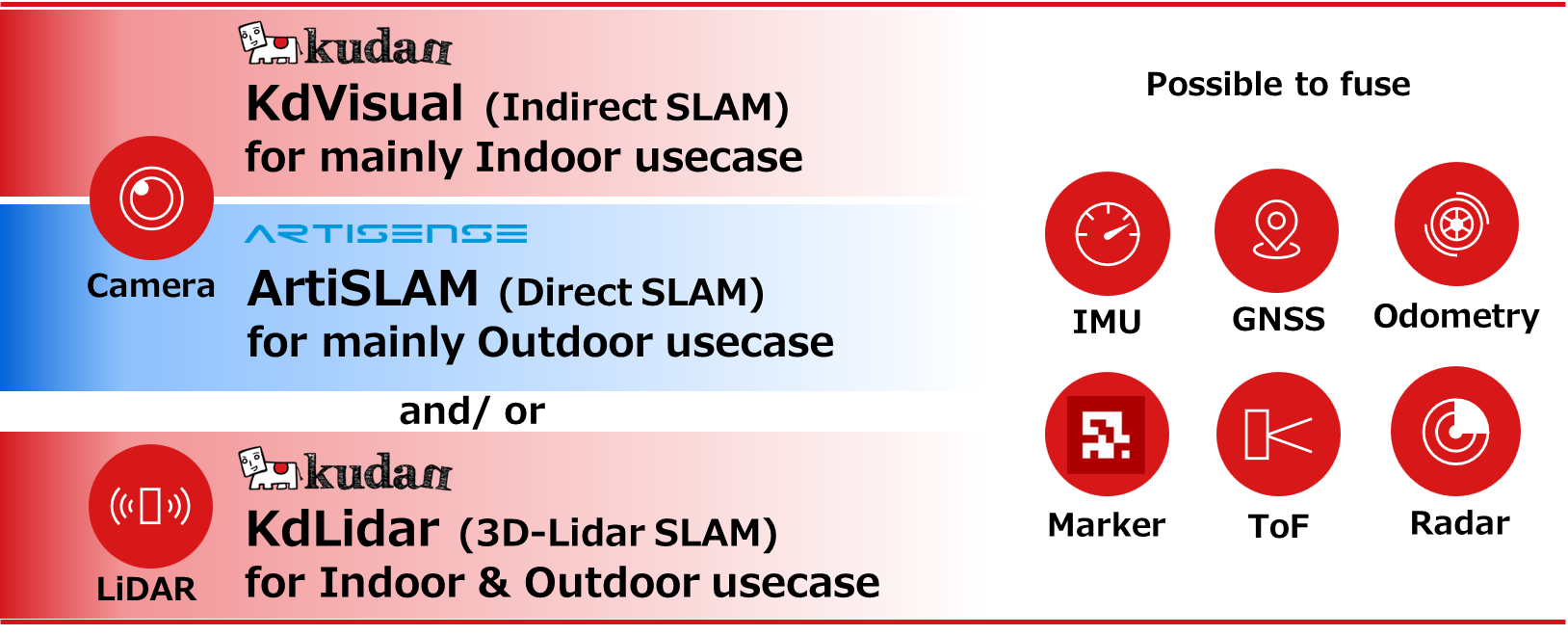
In this regard, GrandSLAM offered by the Kudan Group is comprised of three different SLAM algorithms, each of which has its own unique strengths.
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
Kudan Indirect Visual SLAM, for example, is capable of processing information over 10 times faster with less processing power than the most prominent open-source software of camera-based SLAM technology. Compared to other solutions that can generally give only centimeter-level localization precision, such as 5 cm, the precision of Kudan Indirect Visual SLAM can be as small as millimeters.
By combining these algorithms, etc., the company aims to further improve the function with higher speed and higher precision both indoors and outdoors, using multiple sensors, such as cameras and Lidar, together by integrating the systems through clock synchronization between the sensors (a process called tight coupling).
This technological superiority has been enhanced further by the acquisition of Artisense Corporation as its subsidiary as mentioned later.
Kudan began offering Kudan Indirect Visual SLAM under the name of Kudan SLAM in the term ended March 2018. Then, it started to provide Kudan 3D-Lidar SLAM in March 2020. The company has been striving to broaden the customer base in the following three areas:
Area | Example customers |
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) application area | Optical sensor manufacturers, optical equipment manufacturers, mixed reality (MR) glasses manufacturers, telecommunications equipment manufacturers, electrical equipment manufacturers, e-commerce platforms, computer games producers etc. |
Robotics and IoT area | Optical equipment manufacturers, heavy industrial and industrial robot manufacturers, electrical equipment manufacturers, transportation equipment manufacturers, signal processing internet protocols (IPs), etc. |
Application area targeting cars and maps | Car components manufacturers, digital map companies, spatial information consulting companies, etc. |
Like this, having both Visual SLAM and Lidar SLAM, Direct SLAM and Indirect SLAM in Visual SLAM, and having a hybrid technology combining them is a major strength of the company.
<Growing number of fields in which AP can play roles>
Using one of the existing technologies called computer vision (a set of base technologies of sensor and image processing mainly on a two-dimensional basis) as the foundation after reconstructing it, Kudan has developed its own unique AP technology.
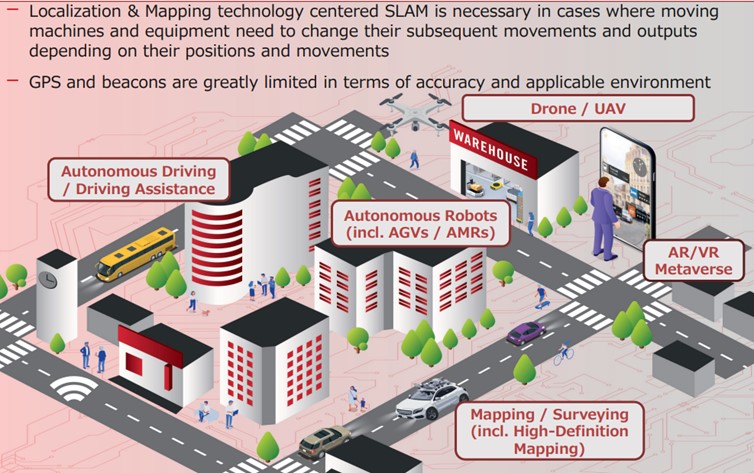
As AP is the base technology necessary for every kind of device that uses cameras and three-dimensional sensors, the company expects that it will be the base technology adopted to diverse next-generation solutions on a cross-cutting basis.
It has been a technology essential for automatic control of all autonomous machines as robotics in a broad sense, including industrial robots, domestic robots, next-generation mobility such as cars, and flying machines such as drones, just to name a few.
It will also be required for spatial perception in AR and VR that will serve as user interfaces of next-generation computers.
In addition, the technology will be applied to an extremely wide range of purposes as the base technology for next-generation digital maps, dynamic maps (a dynamic mapping system that swiftly reflects the conditions of the reality environment), digital twin (information on the virtual space synchronized with the reality environment on a real time basis), and the like.
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
【1-5 The company's vision】
<Technical Strategy and Management Strategy>
◎ Technology Strategy
The company is targeting only achieving full automation. Full automation is difficult to achieve by merely accumulating non-automated and semi-automated technologies. By focusing on this, the company is accumulating technology while achieving full automation in each area in stages, “mapping” → “indoor robot” → “outdoor robot” → “autonomous driving,” in order to realize applied technology with a high degree of difficulty.
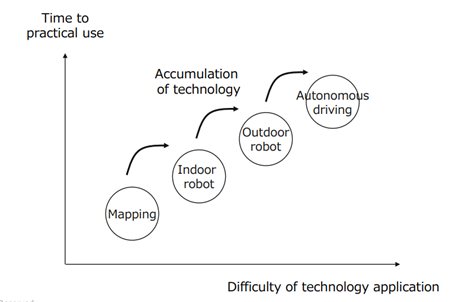 |
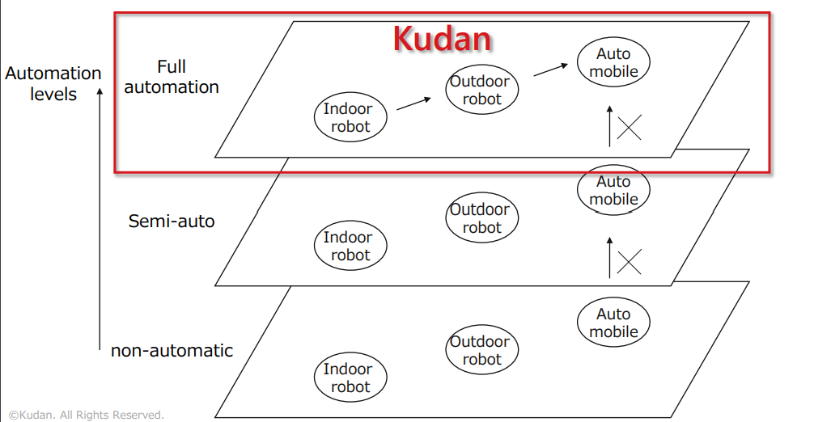 |
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
◎ Management Strategy
Based on the technology strategy, the company is focusing on algorithm research, software development, and licensing in Deep Tech, which is equivalent to the fundamental technology located in the deepest technological layer below solutions, finished products, and applied technology.
With overwhelming technological strength as its weapon, the company is promoting customer acquisition globally and aiming for “maximization of corporate value with a select few employees” and “positioning that is difficult for customers to replace.”
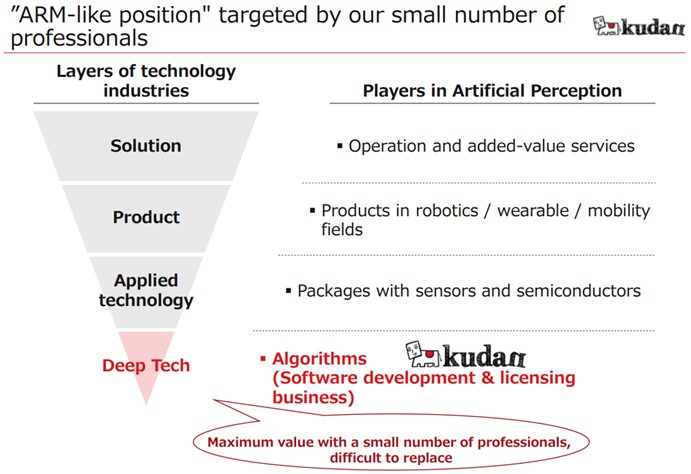
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
【1-6 Competitive superiority】
(1) Technological features
Kudan believes that its AP technology has enormous advantages in taking in not only the existing demand for product development but also demand for research and development on highly novel and complex future technologies, because the AP technology can help the company strategically take in technological demand fueled by continuous advancement and wider applications of the technology in mid-/long-term.
According to the company, the AP technology has the following five features.
Kudan can flexibly fulfill future demand, which is expected to grow and be diverse, by combining their sophisticated and flexible research and development capabilities that they cultivated by focusing on the AP field:
Feature | Overview |
(1) Uniqueness of the algorithms | The Kudan Group possesses diverse families of technologies that consist of uniquely developed algorithms.
Regarding how to perceive image feature points (fairly noticeable local areas in an image) that provide the basis for perceiving three-dimensional geometric structures at an advanced level, for example, the company has developed a unique, high-speed and greatly precise method by integrating and hybridizing a high-speed perception method and a highly precise and stable perception method. Furthermore, the density of feature points perceiving within an image can be adjusted flexibly to optimize the precision of perceiving three-dimensional structure (a set of three-dimensional feature points) and the processing speed, according to the practical application environment. In addition, a wide range of unique mathematical models that guarantee the feasibility of the technology are integrated, including optimized calculation that increases the precision of a group of three-dimensional feature points perceived sequentially in a three-dimensional manner, and a high-speed matching method with already-known, stored data. |
(2) Flexibility and powerful performance | The uniqueness of the algorithms allows high-speed processing (with a light calculation load) as well as realizes great perception precision (which means that deviation from a true value is slight) and robustness (which indicates that the technology performs stably regardless of the environment and conditions in which it is used).
In addition, the AP technology will be able to deliver strong performance that is optimized for a myriad of practical applications as it is designed in a manner that allows users to make detailed adjustments to the perception precision, robustness, processing speed, data size, and other individual functions according to the conditions under which the technology is used and required specifications. |
(3) Flexibility in sensor use | As limiting the number of sensors can narrow the scope of applications of the AP technology, the Kudan Group’s technology is designed to be compatible with various sensors.
Specifically, it can function with a variety of cameras, the technology can be adjusted flexibly according to the number of cameras (such as monocular cameras, binocular cameras, and multiple cameras), and the data read format of optical sensors (such as whether to read data sequentially or simultaneously). Besides cameras, the technology can also be combined with a multitude of sensors, including three-dimensional sensors (such as Lidar and Time of Flight (ToF)), internal sensors (such as inertial measurement unit (IMU) and machine odometry), and position sensors (such as the Global Positioning System (GPS) and Beacon), which will allow advanced application of the technology while taking advantage of the strengths of each sensor. |
(4) Flexibility in arithmetic processing environments | Flexibility in arithmetic processing platforms is also an important factor for applying the AP technology to a wider range of fields.
As the Kudan Group’s technology can work in multifarious arithmetic processing environments, it can be compatible with all kinds of processor designs and thus can speed up calculation processes by optimizing the software according to the kind of processor used (such as a central processing unit (CPU), a digital signal processor (DSP), and a graphics processing unit (GPU)). It can also function in a wide range of system environments through porting a software to major operating systems (such as Linux, Windows, MacOS, iOS, and Android). |
(5) Flexibility in using part of the function | Complex fusion with other technologies is necessary for advanced applications of the AP technology. Parts of the function (software modules) of the Kudan Group’s technology can be selected so that they are flexibly integrated into customers’ existing software.
The degree of dependence on processor designs (the degree of abstraction of software) of each part (software module) of the technology’s function varies, and therefore it can be optimized flexibly either at a semiconductor level (with a lower abstraction degree) or at a software application level (with a higher abstraction degree). |
(2) Global group of experts on AP
Researchers and engineers specializing in SLAM are a handful in the rare computer vision field. Among these, the company has many top-notch personnel with a doctoral degree, and as a group of AP professionals, it has built a strong foundation in both technology and business on a global basis.
Following the establishment of the Kudan Group in the UK in 2011 and the opening of its Tokyo office in 2014, the company invested in Artisense Corporation (Germany) in 2020 and made it a subsidiary in the following year 2021.
The acquisition of Artisense, a world-leading technology company, as a subsidiary and the deepening of the relationship with Professor Daniel Cremers of the Technical University of Munich further strengthens the company's competitiveness in terms of human resource acquisition and technology development.
(Overview of Artisense Corporation)
Artisense Corporation was founded in 2016 jointly by Professor Daniel Cremers, who has delivered the world’s best research results as the leader of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) that has a world-leading research group in AI and computer vision and as a leading expert on the autonomous driving technology, and Mr. Andrej Kulikov, a serial entrepreneur.
With such fields as autonomous driving, robotics, AR and VR, and drones being its application areas, Artisense Corporation provides AP algorithms that perceive the space and location, taking pride in its capability of putting camera-based visual SLAM into practice on a commercial level.
(3) Outstanding business achievements
The number of players in the market is more limited as M&A by major technology companies continues for companies that specialize in SLAM or have SLAM as their core business.
In this environment, the company is far ahead of existing companies in terms of the breadth of technology it offers, its track record of projects, and its recognition.
To date, the company has achieved development and partnerships with many top global companies and has been highly evaluated by the world's leading companies.
【1-7 Business model: Two pillars of growth】
“Customer commercialization” and “Solution development” have been positioned as two pillars of growth.
(1) Acceleration and expansion of customer commercialization
Currently, the majority of projects are in the evaluation and development phase, and the business is in the red due to upfront investment in research and development expenses.
A certain level of profitability and growth is expected for evaluation and development licenses/customer development support, and product-related sales are expected to increase significantly as technology penetrates the market through the spread of customer products. Sales after commercialization by customers are mainly software license income. As a result, additional costs are negligible, and the increase in sales will contribute to profit. Therefore, a dramatic increase in profit can be expected.
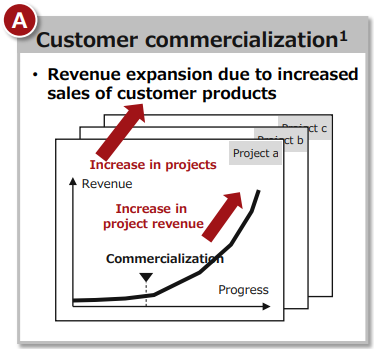
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
(2) Operation of the solution business
In response to growing market demand, the company will collaborate with ecosystem partners to provide solution packages for end customers, such as operations and value-added services, as well as product packages to the market and increase the project size through collaboration.
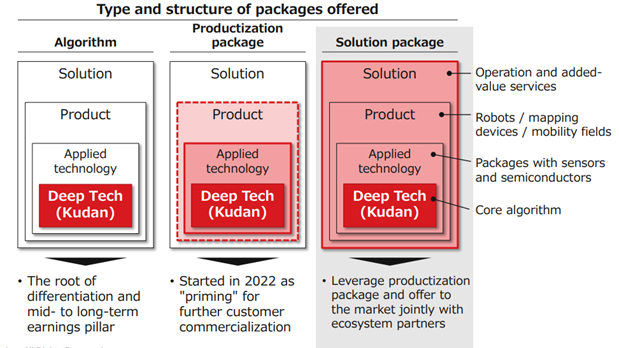 |
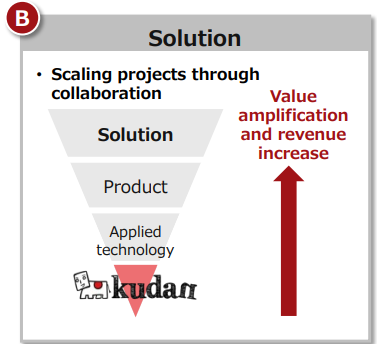 |
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
2. Fiscal Year ended March 2024 Earnings Results
【2-1 Overview of the consolidated results】
| FY 3/23 | Ratio to sales | FY 3/24 | Ratio to sales | YoY | Revised forecasts |
Sales | 332 | 100.0% | 490 | 100.0% | +47.5% | 520 |
Gross Profit | 176 | 53.0% | 439 | 89.4% | +148.7% | - |
SG&A | 775 | 233.0% | 966 | 196.8% | +24.6% | - |
Operating Income | -598 | - | -527 | - | - | -550 |
Ordinary Income | -394 | - | -50 | - | - | -240 |
Net Income | -413 | - | -69 | - | - | -270 |
*Unit: million yen. Net income is profit attributable to owners of the parent. Hereinafter the same shall apply. Revised forecasts are those announced in December 2023.
Sales increased and loss shrunk.
Sales increased 47.5% year on year to 490 million yen, with an operating loss of 527 million yen (a loss of 598 million yen in the previous fiscal year).
The company is focusing on “customer commercialization” and “solution development” as the “two pillars of growth,” which are starting to show results.
With regard to customer commercialization, the business is progressing due to the growth of projects and the subsequent expansion of product sales. The total number of commercialization by customers has increased to eight, with the scope expanding to drones, autonomous driving, and other areas. Product-related sales reached 270 million yen, 40 times larger than those in the previous year.
Regarding the solution development, the company established a business foundation, had discussions and reached an agreement on a policy for introducing a digital twin as a solution with partners.
【2-2 Financial standing and cash flows】
◎ Balance sheet indicating major items
| End of Mar. 2023 | End of Mar. 2024 | Increase/ decrease |
| End of Mar. 2023 | End of Mar. 2024 | Increase/ decrease |
Current Assets | 991 | 1,953 | +962 | Current Liabilities | 241 | 280 | +39 |
Cash and deposits | 852 | 1,719 | +867 | Total Liabilities | 248 | 287 | +39 |
Noncurrent Assets | 16 | 424 | +408 | Net Assets | 759 | 2,090 | +1,331 |
Tangible Assets | 0 | 0 | 0 | Capital | 345 | 740 | +394 |
Investment, Other Assets | 16 | 424 | +408 | Retained Earnings | -332 | 160 | +492 |
Total Assets | 1,008 | 2,378 | +1,370 | Total Liabilities and Net Assets | 1,008 | 2,378 | +1,370 |
*Unit: million yen.
Total assets increased 1,370 million yen from the end of the previous fiscal year to 2,378 million yen due to an increase in cash and deposits associated with the issuance of shares.
Net assets increased 1,331 million yen year on year to 2,090 million yen, mainly due to increased capital stock and retained earnings, despite a higher deficit in foreign currency exchange adjustments.
As a result, equity ratio increased 12.9 points from the end of the previous fiscal year to 87.9%.
◎ Cash Flow
| FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 | Increase/decrease |
Operating Cash Flow | -619 | -490 | +128 |
Investing Cash Flow | -20 | -432 | -412 |
Free Cash Flow | -639 | -923 | -283 |
Financing Cash Flow | 870 | 1,759 | +889 |
Cash and equivalents | 852 | 1,719 | +867 |
*Unit: million yen
The cash inflow from financing activities increased due to higher revenues from the issuance of shares. The cash position increased.
【2-3 Business Topics】
(1)Progress in customer commercialization
Customer commercialization at the commercial level has been progressing steadily.
As a “trigger” for commercialization, product-oriented packages have been introduced for digital twins and subsequently for robotics, with an increase in the number of projects.
In addition to the use of product-oriented packages, the accumulation of cross-sectoral knowledge has reduced development costs and development lead times, resulting in a significant improvement in development efficiency.
In the fiscal year ended March 2024, there were four new projects (a cumulative total of eight), expanding the domain to include drones and autonomous driving.
In the fiscal year ending March 2025, the company expects projects to progress in all areas and a significant increase in new projects.
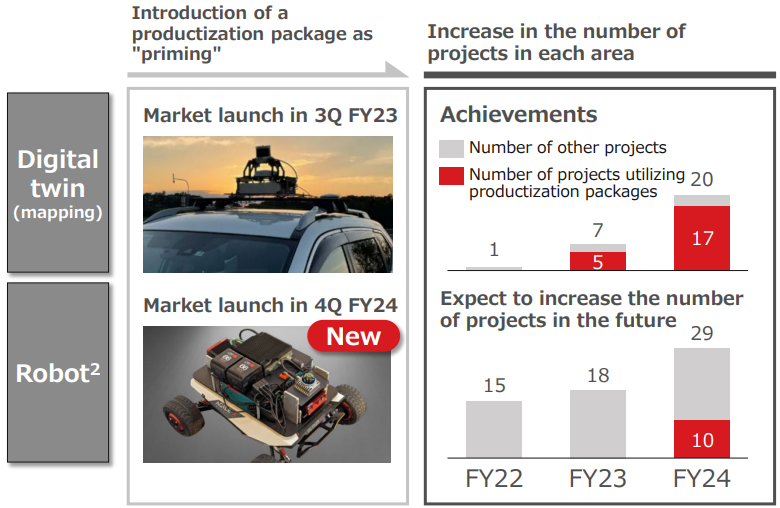 |
 |
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
(2)Solution development
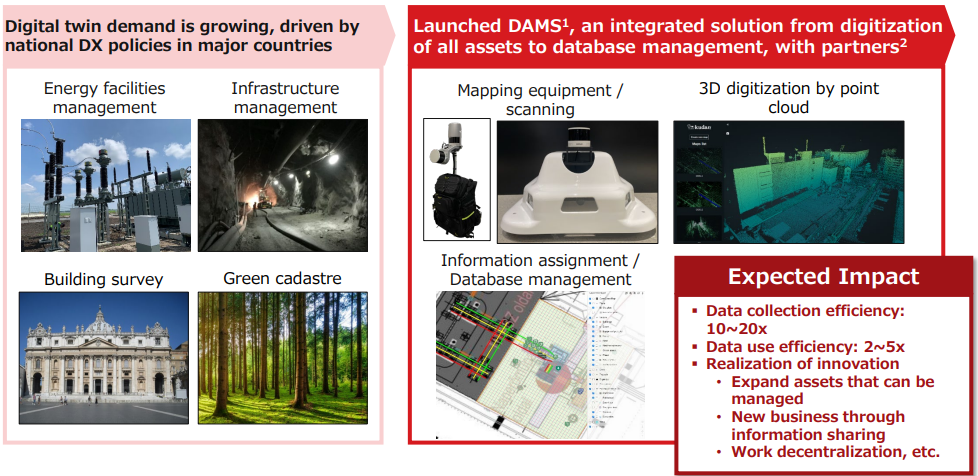
①Solutions for DX of management of facilities and infrastructure
The company expects that the global demand for promoting digital twins and space DX that matches the mapping application of its technology will form a huge market in the future.
First, in response to growing DX demand in Europe for municipalities and public infrastructure (survey and maintenance of infrastructure, surveying for construction, registration of street trees and green spaces, etc.), the company will provide integrated solutions ranging from digitization to database management. The company aims to expand sales to reach the scale of 100 million yen in the short term.
The company signed a basic agreement with STS Group, headquartered in Hungary, to become an ecosystem partner for this purpose, and it plans to jointly develop a solution business for digital asset infrastructure in Europe with STS Group as a strategic business partner.
Founded in 2002, STS Group is a plant engineering and turnkey solution provider for renewable energy. The company designs, constructs, and operates power generation facilities and other lifelines for renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power in Hungary, Germany, Central and Eastern Europe, the Balkans, and the Baltic States.
In Europe, facility management projects for new energy are expected to grow against the backdrop of the acceleration of the shift to decarbonization and quitting of the use of Russian natural gas, and the company has reached an agreement on several digital asset management solution projects related to facility management, operation, and maintenance of major power infrastructure. (However, at present, orders for the agreed projects have not yet been received and the start of project operations has been delayed until the fiscal year ending March 2025 or later.)
 |
 |
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
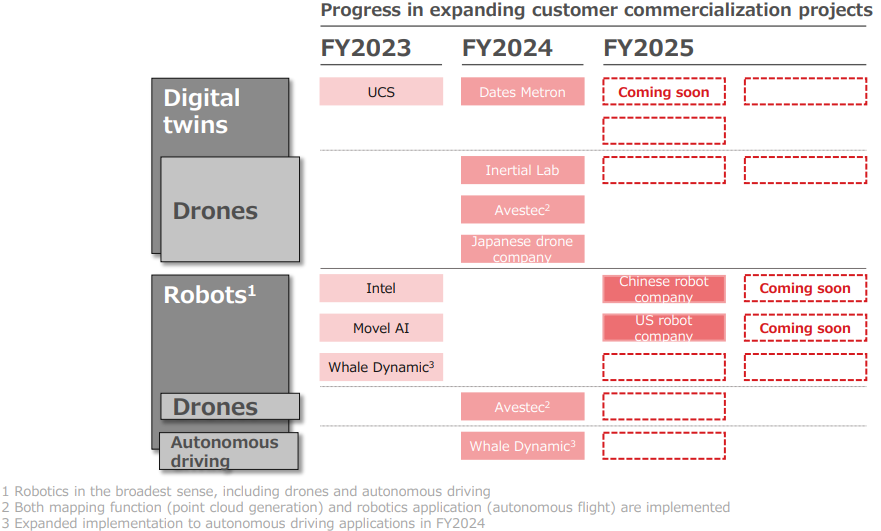
② Initiatives in the field of robotics and autonomous driving
From the fiscal year ending March 2025, the company will also start working on solutions in the field of robots and autonomous driving.
The company is in the process of applying to join “The Autoware Foundation,” the world's first international industry association aiming to set the industry standards for autonomous driving systems, joined by the alliance partner Whale Dynamic. After becoming a member, the company plans to join the ecosystem of 85 partners to collaborate and provide technology.
In addition, collaboration with Japanese autonomous driving companies will start in the fiscal year ending March 2025. The company plans to implement the technology in a wide range of areas, including public projects, and aims to develop solutions for autonomous driving in the broadest sense (outdoor robotics, logistics, mobility, etc.).
3. Fiscal Year ending March 2025 Earnings Forecasts
【Earnings forecasts】
| FY 3/24 | Ratio to sales | FY 3/25 Est. | Ratio to sales | YoY |
Sales | 490 | 100.0% | 700 | 100.0% | +42.6% |
Operating Income | -527 | - | -430 | - | - |
Ordinary Income | -50 | - | - | - | - |
Net Income | -69 | - | - | - | - |
*Unit: million yen. The forecasts were those released by the company. The company will not disclose the exact forecast figures of ordinary income and net income due to the difficulty in estimating foreign exchange gain or loss, which have a significant impact on them.
Thanks to the two pillars of growth, the company expects a significant increase in sales and a reduction in loss
Sales are forecast to increase 42.6% year on year to 700 million yen, with an operating loss of 430 million yen (527 million yen in the previous fiscal year).
The company will keep focusing on “customer commercialization” and “solution development” as the “two pillars of growth” this term and expects a significant increase in sales and a reduction in loss
In terms of customer commercialization, the company expects project growth to accelerate thanks to the contributions from product packaging, which will serve as a “trigger.”
In terms of solution development, the company will promote ecosystem collaboration and expand its area into robots and autonomous driving.
In addition, it will work on the integration of AI and semiconductors (see below) to support the two pillars of growth.
4. Growth Progress and Initiatives
【4-1 Short- and Medium-term Growth】
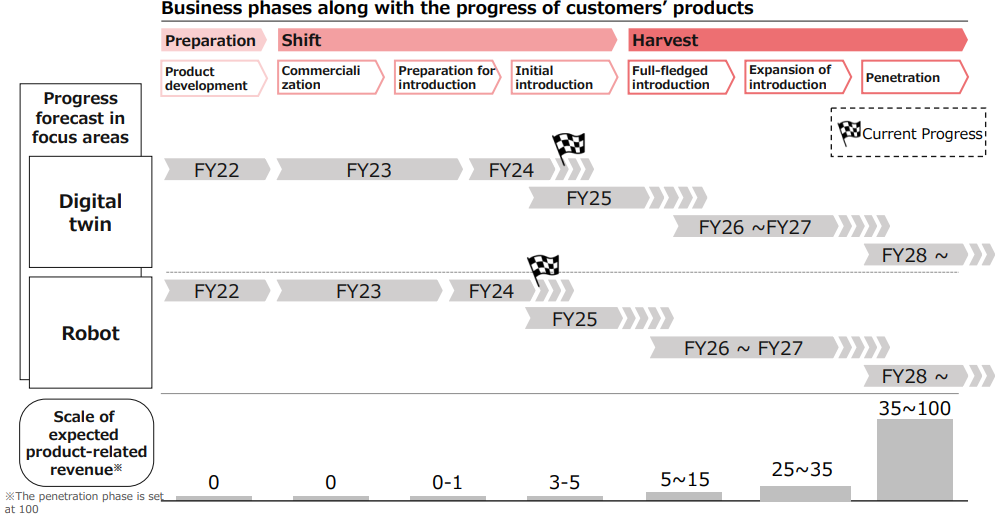
With the aim of expanding product-related sales through the introduction and popularization of customer products, the company will continue to strategically promote measures to accelerate the progress of customer products, using the stage of development of customer products as an index.
Product-related sales for the fiscal year ending March 2025 are expected to grow by up to 50% to 250 million yen to 400 million yen.
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
【4-2 Initiatives to support the two pillars of growth: fusion of AI and semiconductors】
As an initiative to support “customer commercialization” and “solution development,” the company mentions “integration of AI and semiconductors.”
The company is expanding business opportunities through “high added value through the incorporation of AI” and “high efficiency through the incorporation of semiconductors.”
(1)Combining Artificial Perception (AP) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to create innovative value
AI, which is showing rapid evolution, has developed with rich training data in languages, texts, 2D images, and videos and has a significant technological lead. However, it has fallen behind in 3D and spatial data due to the difficulty in acquiring training data.
Artificial perception can generate 3D training data from 2D data, which can significantly solve the challenges of AI processing in 3D and spatial data.
The company believes that these problem-solving abilities of artificial perception can be used in analyzing spatial digital twins with large-scale AI models and generating metaverses with generative AI. It also believes that semantic digital twins (digital twins with AI connotations) will bring disruptive value to all DX solutions related to 3D and spatial information.
(2)Significant improvement in processing efficiency through the incorporation of semiconductors
(The following is a summary taken from the company's website on the fusion of semiconductors and artificial perception.)
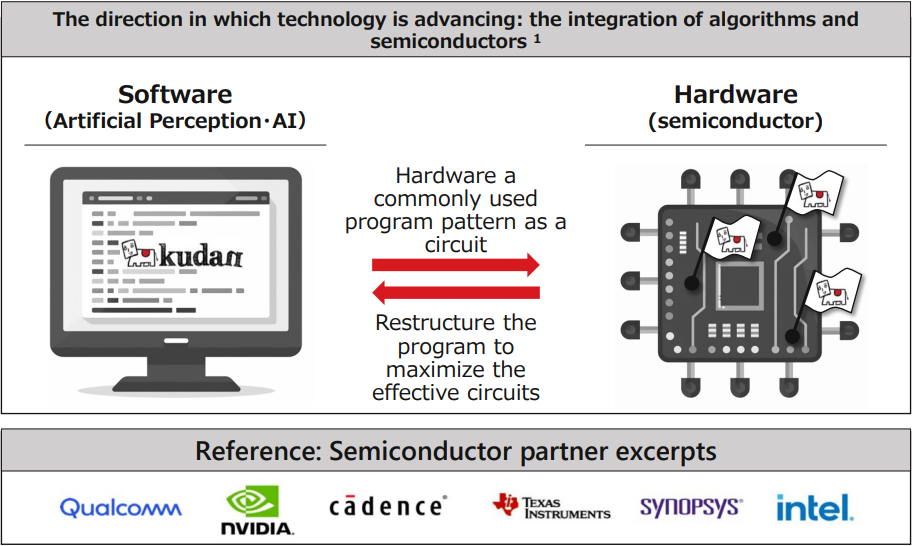
[Interdependence between Software and Hardware]
Demand for semiconductors, known as AI chips, is growing rapidly due to the rise of generative AI (artificial intelligence).
Artificial intelligence is composed of algorithms, which are software, and has no hardware substance. It functions as pure software as a “design document for information processing.”
On the other hand, semiconductors, which are circuits for information processing, efficiently process a huge amount of information as electric signals on highly detailed circuits as hardware.
This combination of software and hardware is superficially a combination of different things, but technically they are closely related, and the two can be mutually optimized and fused together to achieve more efficient processing.
For example, if there is software that calculates 8 x 7 and a semiconductor chip that only has an addition circuit, the answer 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 = 56 is obtained by running the circuit seven times. On the other hand, if a semiconductor chip with a multiplication circuit is used, 8 × 7 can be solved with only 1/7 labor by applying the operation of multiplying 8 by 7 to the circuit only once.
Thus, if the semiconductor chip is prepared with circuits that can more efficiently process the software processing content, the processing capacity will improve exponentially.
If a “design document for information processing” that serves a specific purpose is physically created as a single circuit—in other words, if software is made into hardware and incorporated into a semiconductor chip as a circuit—it will be possible to operate from input to output at once without performing complicated four-digit arithmetic operations.
Conversely, software can also be reshaped and optimized to match the hardware. For example, if a semiconductor already has an efficient circuit, software developers will adjust their information processing methods to maximize the best use of the circuit and try to use it effectively.
Against this technical background, it can be understood that the growing demand for AI chips is supported by the close relationship between software (artificial intelligence) and hardware (semiconductors).
As the amount of information processing is huge, it is important to improve the processing speed of artificial intelligence. Therefore, semiconductor manufacturers improve the processing efficiency of AI by incorporating the patterns of information processing performed by commonly used AI software directly into the hardware as electric circuits of semiconductor chips. This makes it easier to use compatible software with AI semiconductors as they become more widely used.
Importantly, in the process of technology diffusion, hardware and software approach and influence each other. This is a very common phenomenon for deep technologies in the algorithmic layer, and in a sense, it is the royal road for technology diffusion. Furthermore, Kudan's artificial perception (SLAM), which is similar to but different from artificial intelligence, but is also in the algorithm layer, will also merge with semiconductors.
[Potential for deeper and broader integration with semiconductors than artificial intelligence]
If Kudan's artificial perception technology (SLAM) becomes widespread, it is inevitable that Kudan's technology will be incorporated and integrated into semiconductor chips as long as there is demand, but in some ways, it differs from modern AI chips.
The first is that artificial perception (SLAM) is much more complex software than artificial intelligence. This makes artificial perception (SLAM) more deeply integrated with semiconductors. For example, the algorithms at the heart of artificial intelligence itself are typically hundreds of lines long, but the algorithm of artificial perception (SLAM) can comprise hundreds of thousands of lines. Therefore, in the area of software optimization of artificial perception (SLAM) and hardware implementation of software, the integration with semiconductors will deepen, and the benefits of higher speed will be significant.
Second, SLAM can be integrated with a wider variety of semiconductors than artificial intelligence. For example, since it is important for artificial intelligence to process a large amount of relatively simple programs, it is mainly optimized together with semiconductors specialized for parallel processing circuits (circuits suitable for heavy information processing) called GPUs, which are suitable for processing relatively simple programs, to form the so-called AI chip.
On the other hand, artificial perception (SLAM) has information processing patterns of various characteristics in a relatively complex program and can be combined and integrated with semiconductors of different characteristics in a balanced manner. For example, the semiconductor product packages seen in recent years are composed of multiple processors, such as CPUs as a control tower for information processing, GPUs specialized for heavy information processing, DSPs and VPUs with characteristics in between, FPGAs that can be programmed according to niche demand, and ISPs attached to cameras. Elements of artificial perception (SLAM) can be integrated according to the characteristics of each semiconductor. If it can be widely integrated with semiconductors in this way, it will be possible to enjoy the advantages of dramatically improved performance.
[Collaboration with the semiconductor industry]
Kudan has been working on artificial perception (SLAM) for a while and has worked extensively with semiconductor companies, including the world's first commercial SLAM package on Intel's platform. In the future, Kudan's role will be to contribute to the semiconductor industry by deepening the integration of semiconductors and software through artificial perception (SLAM) technology to realize efficient information processing.
Compared to artificial intelligence, artificial perception (SLAM) is still on the eve of widespread adoption, but what the company is looking ahead to is exactly the path that artificial intelligence has taken, and for this reason, Kudan's initiatives will be crucial for the semiconductor industry.
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
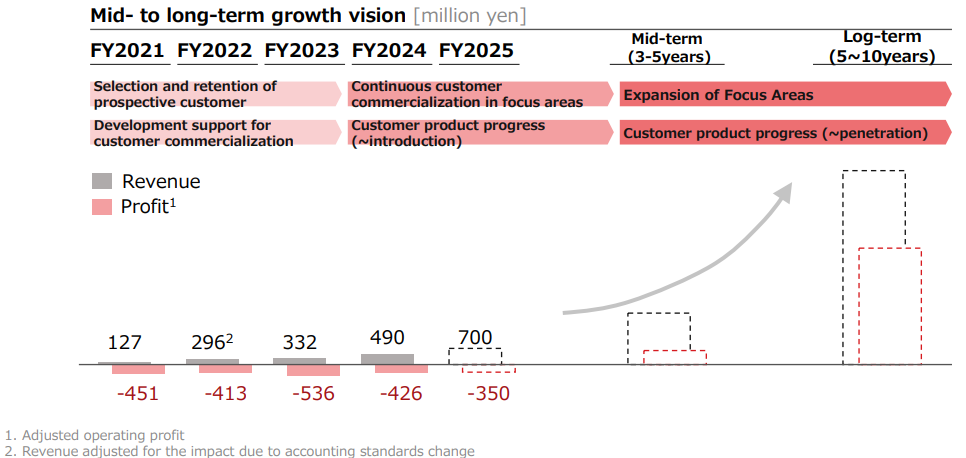
【4-3 Medium/long-term growth】
The company aims to transform its profit structure as soon as possible through the continuous commercialization of its technologies by customers and promoting the progress of customer products.
It also aspires to dramatically increase profits by building up product-related sales significantly through the expansion of focus areas and market penetration of technologies by popularizing customer products.
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
5. Conclusions
Even after the announcement of financial results on May 15, 2024, there have been a series of releases by customers announcing the start of product sales, such as “A Chinese delivery robot company decided to sell robots equipped with Kudan technology” (May 21, 2024) and “A U.S.-based robot company decided to sell robots equipped with Kudan technology” (May 22, 2024).
At present, their impact on business performance is expected to be minor, but one of the two pillars of growth, “customer commercialization,” is making steady progress.
In the short term, we would like to pay attention to how much the number of cases of commercialization by customers, which has reached 8, will increase in the fiscal year ending March 2025. In the medium term, we would like to pay attention to when customer products will enter the distribution stage, as they aim to achieve sales of 700 million yen.
<Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance>
◎ Organizational form and compositions of directors and auditors
Organizational form | Company with audit and supervisory committee |
Directors | 8 directors, including 4 outside ones |
Audit & Supervisory Board Member | 3, including 3 outside the company |
◎ Corporate Governance Report
Last updated in June 23, 2023
<Basic Policy> Our company recognizes that it is indispensable to establish corporate governance, in order to improve our corporate value, maximize the profits of shareholders, and foster good relationships with stakeholders.Under this recognition, the Managing Directors, other Directors, and employees of our company will strive to tighten corporate governance by understanding their respective roles and developing and operating internal control systems.
<Reasons for not following the principles of the corporate governance code>We follow all the basic principles of the corporate governance code.
| This report is not intended for soliciting or promoting investment activities or offering any advice on investment or the like, but for providing information only. The information included in this report was taken from sources considered reliable by our company. Our company will not guarantee the accuracy, integrity, or appropriateness of information or opinions in this report. Our company will not assume any responsibility for expenses, damages, or the like arising out of the use of this report or information obtained from this report. All kinds of rights related to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. The contents, etc. of this report may be revised without notice. Please make an investment decision on your own judgment. Copyright(C) Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |



