Bridge Report:(4205)ZEON The first half of the fiscal year ending March 2025
 Tetsuya Toyoshima President and CEO | ZEON CORPORATION(4205) |
 |
Company Information
Market | TSE Prime Market |
Industry | Chemicals |
President and CEO | Tetsuya Toyoshima |
HQ Address | Marunouchi 1-6-2, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo Shin-Marunouchi Centre Building |
Year-end | March |
HOMEPAGE |
Stock Information
Share Price | Shares Outstanding (including treasury shares) | Total market cap | ROE Act. | Trading Unit | |
¥1,408.0 | 229,513,656 shares | ¥323,155 million | 8.9% | 100 shares | |
DPS Est. | Dividend yield Est. | EPS Est. | PER Est. | BPS Act. | PBR Act. |
¥70.00 | 5.0% | ¥92.10 | 15.3x | ¥1,714.88 | 0.8x |
* Share price as of closing on December 5. The number of outstanding shares, DPS, and EPS were taken from the brief report on financial results in the second quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2025. ROE and BPS are the values in the previous fiscal year.
Earnings Trend
Fiscal Year | Sales | Operating Income | Ordinary Income | Net Income | EPS | DPS |
Mar. 2021 | 301,961 | 33,408 | 38,668 | 27,716 | 126.74 | 22.00 |
Mar. 2022 | 361,730 | 44,432 | 49,468 | 33,413 | 153.22 | 28.00 |
Mar. 2023 | 388,614 | 27,179 | 31,393 | 10,569 | 49.94 | 36.00 |
Mar. 2024 | 382,279 | 20,500 | 26,906 | 31,101 | 147.19 | 45.00 |
Mar. 2025 Est. | 415,000 | 23,500 | 24,500 | 19,000 | 92.10 | 70.00 |
*Unit: million yen, yen. Estimates are those of the company. Effective from the beginning of March 2022, the "Accounting Standard for Revenue Recognition" (ASBJ Statement No. 29) and others are applied. Net income is net income attributable to owners of the parent company. The same applies hereinafter.
This Bridge Report presents ZEON CORPORATION’s earnings results for the first half of the fiscal year ending March 2025.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1. Company Overview
2. First half of the Fiscal Year ending March 2025 Earnings Results
3. Fiscal Year ending March 2025 Earnings Forecasts
4. Medium-term Management Plan
5. Conclusions
<Reference:Regarding Corporate Governance>
<Appendix:Fact Sheet>
Key Points
- In the first half of the fiscal year ending March 2025, sales increased 15.0% year on year to 213.3 billion yen, and operating income rose 77.6% year on year to 16.8 billion yen. Both sales and profit increased in the Specialty Materials and Elastomer Business. In the specialty plastics segment, demand for cyclo olefin polymer (COP) and optical films for mobile terminals recovered, and the shipment of COP for semiconductor containers increased as the semiconductor market recovered. In the synthetic rubber segment, operations at major overseas plants remained at a high level, and sales were steady, especially for spot sales for overseas markets. The interim dividend will be 35.0 yen/share, up 15.0 yen/share year on year, far exceeding the company's forecast of 23.0 yen/share.
- For the full year of fiscal year ending March 2025, the company forecasts an 8.6% year-on-year increase in sales to 415 billion yen and a 14.6% increase in operating income to 23.5 billion yen. The forecast was revised due to a defect that occurred in one of the four production lines at Mizushima Plant. To resolve the problem, the company suspended the operation of the production line in question in October. In addition, the Elastomer Business division experienced production issues with a raw materials supplier. These factors, along with a revision of the assumed exchange rate and raw material assumptions, led to the forecast revision. The company carefully examined the recent business situation and found that there are both upward and downward revisions for individual products. Net income has been revised due to the booking of a gain on the sale of investment securities (extraordinary profit). For the second half of the fiscal year, the company forecasts the following exchange rates: 1 U.S. dollar = 145 yen (previously 155 yen), 1 euro = 155 yen (previously 165 yen), domestic naphtha = 68,200 yen/kl (previously 76,000 yen/kl), and Asian butadiene = 1,400 U.S. dollar/ton (previously 1,100 U.S. dollar/ton). The year-end dividend forecast has been revised upwardly from 24.0 yen/share to 35.0 yen/share. The company expects a dividend increase of 25.0 yen to 70.0 yen/share for the full year. This marks the 15th consecutive year of dividend increases since the fiscal year 2010. The expected dividend payout ratio is 76.0%.
- The first half of the fiscal year saw double-digit growth in sales and a significant increase in profit. While there was a rebound from the significant decline in the same period of the previous year due to factors such as customer inventory adjustments and the startup of a new optical film production line, the results were generally in line with the company’s expectations. The full-year forecast has been revised to reflect changes in underlying exchange rates and the trouble at one production line at Mizushima Plant, but the impact on the medium-term plan is expected to be minor. Therefore, Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. believes that the revised forecast remains conservative. As discussed in our previous report, we are concerned that the market for battery materials for EVs remains uncertain due to the sluggish market. The company is taking various actions, but the excess EV production capacity in China has become a detriment to global competition, and demand is stagnant in the U.S. and Europe. We will continue to monitor the future of the market and the company's response. The most noteworthy aspect of this earnings announcement is the return of profit to shareholders. By setting DOE as the yardstick for dividends, the company is able to ensure a stable and high dividend level without being affected by a single year's performance or market conditions. The company has also strengthened its share buyback program and is now close to achieving a P/B ratio of 1.
1. Company Overview
The company handles synthetic rubber used for automobile parts and tires, synthetic latex used in surgery-use gloves, and other products, and highly functional materials produced based on the technologies for manufacturing synthetic rubber and latex. It is a petrochemical manufacturer that handles a lot of products with a high global market share, although they target niche markets. The Company’s strengths include its creative technology development function, R&D structure, and high earnings generation capability.
Many of the products and materials manufactured by Zeon are used in a wide variety of products including automobile parts and tires, rubber gloves, disposable diapers, cell phones, LCD televisions, perfumes and other products commonly used in everyday life.
The Zeon Group is comprised of the parent company, 59 subsidiaries and 8 affiliated companies. Zeon also has manufacturing and marketing facilities in 18 countries around the world.
 |
 |
(Source: the company)
[1-1 Company Name and Management Vision]
The company name “Zeon” is derived from the Greek word for earth “geo” (phonetically pronounced “zeo” in Japanese) and the English word reflecting eternity “eon,” and reflects the Company’s principle of “deriving raw materials from the earth and perpetually contributing to human prosperity” through the development and application of creative technologies. (Zeon’s original name “Geon,” used at the time of its establishment, was derived from the trademark acquired for the vinyl chloride plastics “Geon” from B.F. Goodrich chemical Company in the United States, with which it had capital and collaborative technological agreements. The company name was changed to “Zeon” when the capital agreement was dissolved in 1970.)
[1-2 Corporate History]
Zeon was established as a joint venture company formed by the Furukawa Group of companies: Nippon Light Metal Co., Ltd., Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd., and Yokohama Rubber Co., Ltd. in April 1950 to acquire and use the vinyl chloride resins technology from B.F. Goodrich Chemicals Co.
In 1951, Goodrich acquired 35% of the shares of Zeon for full-scale technological and capital partnership, and in 1952 mass production of vinyl chloride resins began in Japan for the first time.
In 1959, Goodrich transferred synthetic rubber manufacturing technologies to Zeon, which, in turn, started Japan’s first mass production of synthetic rubber. Manufacturing facilities were also expanded to match the growing demand for automobile parts.
In 1965, use of the Company’s unique technology called Geon Process of Butadiene (GPB) for the efficient manufacture of butadiene (main raw material of synthetic rubber) from C4 fraction was operational.
Goodrich transferred its specialty synthetic rubber business to Zeon along with the shift in its main business focus toward vinyl chloride resins. Capital ties were dissolved in 1970. Along with these changes, the Company name was changed from Geon to Zeon in 1971.
Also, in 1971, Zeon developed a unique technology called Geon Process of Isoprene (GPI) and began using it to manufacture raw materials including high-purity isoprene, petroleum plastics, and synthetic perfume ingredients from C5 fraction.
After entering the 1980s, Zeon aggressively launched new businesses in various fields including photoresists and other information materials, synthetic fragrance, and medical-related applications in addition to its main synthetic rubber business.
In 1984, production of hydrogenated nitrile rubber Zetpol®, which currently has top share of the worldwide market, began at the Takaoka Plant.
In 1990, manufacture of cyclo olefin polymer (COP) ZEONEX®, which is the main product of the specialty materials business using the GPI method to extract and synthesize products, was started at the Mizushima Plant.
In 1993, Zeon entered China with its electronics materials business.
In 1999, Zeon Chemicals L.P. (Consolidated subsidiary in the United States) acquired the specialty rubber business of Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company of the United States to become the world’s top manufacturer of specialty rubber.
In 2000, Zeon discontinued production of vinyl chloride resins at the Mizushima Plant, and thus withdrew from the Company’s founding business.
Since the 21st century came, the company has been operating business actively. For example, by releasing ZeonorFilm®, an optical film for LCD, strengthening global production and sales systems, starting the commercial operation of solution-polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber(S-SBR) in Singapore, upgrading the equipment for optical films for LCD in Himi-shi, Toyama Prefecture, starting the operation of the world’s first mass-production factory for super-growth carbon nanotubes, and establishing a joint venture for manufacturing and selling S-SBR in cooperation with Sumitomo Chemical.
[1-3 Business Description]
Zeon’s main products use various extracted from naphtha, which is extracted by distillation of crude oil.
When the naphtha is heated, carbon monoxide gas (C1), ethylene (C2), and propylene (C3) are extracted in sequence.
Zeon uses butadiene extracted in the GPB method developed in-house from C4 fraction, isoprene monomer, piperylene, dicyclopentadiene, and 2-butyne extracted from C5 fraction using the GPI method, as raw materials to be processed into synthetic rubber, synthetic latex and various other materials.
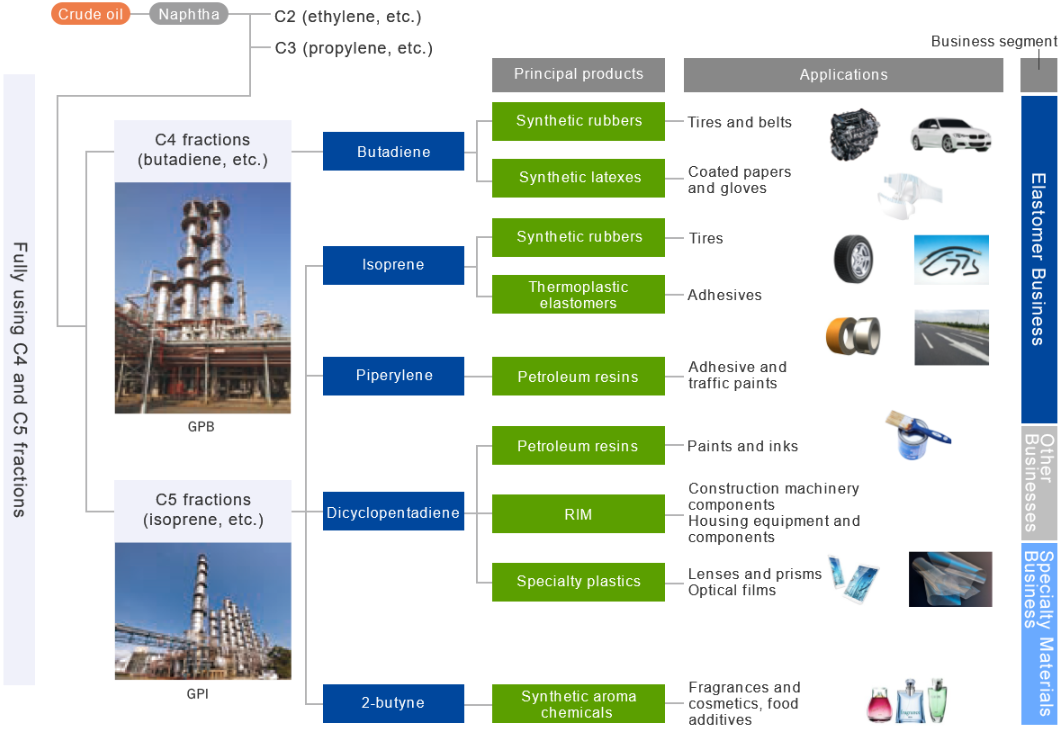
GPB Process … A technology for efficiently manufacturing highly pure butadiene
GPI Process … A technology for economically manufacturing highly pure isoprene, petroleum resins, synthetic aroma chemicals, and other useful components.
(Source: the company’s website)
Zeon has three business segments: 1) the Specialty Materials Business, where basic materials are submitted to primary processing for sale to customers as processed materials, 2) the Elastomer Business, where basic materials are sold to customers, and 3) the other business.
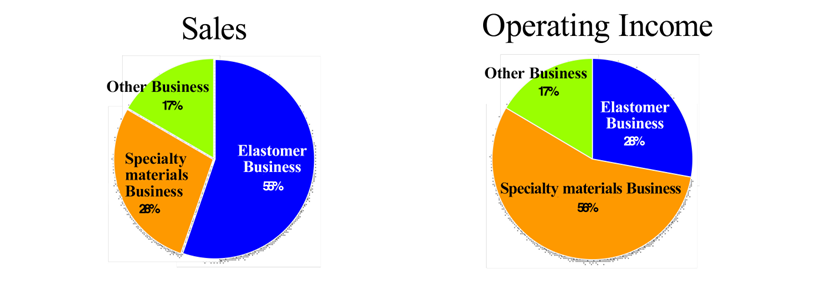
*Both are results for the fiscal year ended March 2024. Composition ratio is before elimination and company-wide.
Specialty Materials Business
Zeon deals in high value-added materials and parts that are created using its unique technologies including polymer design and processing technologies.
This is composed of the specialty plastics business, including cyclo olefin polymer (COP) and optical films, the specialty chemicals business, including battery materials, chemicals, electronic materials and polymerized toners, and the medical devices business.
1) Specialty Plastics Business
◎ Cyclo olefin polymer (COP) and optical films
Cyclo olefin polymer (COP) is thermoplastic polymer developed using raw material extracted from C5 fraction using GPI methods and synthesized with Zeon’s own unique technologies. The commercial products are ZEONEX® and ZEONOR®.
ZEONEX® leverages its high transparency, low water absorption, low absorptive and chemical resistance properties for use in camera and projector lenses and other optical applications and in medical use containers including syringes and vials.
ZEONOR® leverages its high transparency, transferability, and heat resistance properties for use as transparent general use engineering plastics used in light guide plates, automobile parts, semiconductor containers and a wide range of other product applications.
ZeonorFilm® is the world's first optical film by the melt extrusion method from the cyclo olefin polymer (COP). It is excellent in optical properties, low water absorption / low moisture permeability, high heat resistance, low outgassing, and dimensional stability. It is used in a wide range of applications such as displays for LCD TV, smartphones, tablets, and OLED displays.

(Source: the company)
“Diagonally-stretched optical film” is also Zeon’s world first development.
The OELD application as anti-reflection film is progressing, and demand for small- to medium-sized flat panel display applications is growing. The company’s optical films are produced in 3 bases: Takaoka city, Toyama prefecture, Himi city, Toyama prefecture, and Tsuruga city, Fukui prefecture.
ZEOCOAT® is organic insulation material used in electronic devices such as cellphones, smartphones, and LCD televisions.
ZEOCOAT® was successful in improving both the picture quality and reliability of displays because of its high transparency, extremely low water absorption and low gas generation properties.
Zeon will aggressively expand its marketing efforts for OELDs, which will be thinner displays than LCD, thin-film transistors using new semiconductors, and flexible displays.
2) High Performance Chemicals Business
◎ Battery Materials
Zeon provides materials for Li-ion battery in this segment; anode / cathode binders, binder for functional layer (heat resistant separator), and sealant. Currently, Li-ion batteries are widely used as a power source for mobile devices such as smartphone and notebook computers and there is a steady demand for batteries with higher capacity.
Adoption for electric vehicles, including hybrid and plug-in hybrid cars, and industrial power sources (such as smart grids, etc.) is expanding, since it is lightweight and compact and can store a lot of energy. On the other hand, there was a problem that lifetime tends to decrease under high temperature usage.
The company has advanced the function of Li-ion battery binder and succeeded in developing an aqueous cathode binder, which greatly contributes to longer battery life. In addition, Zeon succeeded in commercializing anode binder, which can raise the storage capacity of Li-ion battery by 5% to 15%. Furthermore, as part of its efforts to expand the product lineup while paying attention to environmental burdens, the company embarked on full-scale development of adhesive slurry for separator coating designed as an aqueous product.
The company believes that its binders and sealants for the cathode, anode, and functional layer (heat-resistant separator) will contribute to the improvement of the five major performance parameters of lithium-ion batteries: durability, capacity, productivity, safety, and quick charge, and thus contribute to the popularization of electric vehicles. In addition, their products are PFAS-free, that is, they do not include fluorine, as a characteristic. Their contribution to the reduction of environmental burdens is attracting attention.
Recognizing the potential of lithium-ion batteries and working on them earlier than any other company, ZEON continuously proposes specialty materials for further generalizing new material functions and developing new batteries that meet needs in automobile applications, such as quick charging, as the top innovator in the market of lithium-ion battery binders.
Binder for Battery
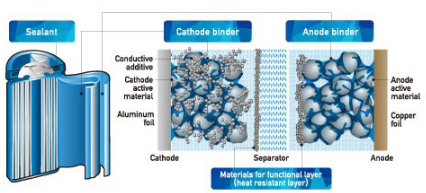
(Source: the company’s website)
◎ Specialty Chemicals
Zeon deals in specialty chemicals that use derivatives from C5 fraction, such as synthesized fragrances for cosmetics and flavor used in foods, characteristic solvents, and plant growth regulator.
The Company holds the world’s top share of the synthesized fragrances in green note. They provide a wide range of specialty products including ingredients for intermediary bodies used in medical and agricultural chemicals, alternative solvents to CFCs, cleaning agents, urethane expanding agent, and functional ether agents.
3) Medical Devices Business
The medical device market is relatively well insulated from fluctuations in the economy and is anticipated to grow with the aging society in Japan and expansion in developing countries. Furthermore, medical device companies are subject to strict laws and regulations, and they need to submit approval applications to regulatory bodies. In addition, the need to develop relationships with healthcare professionals is critical and the subsequent high barriers to entry makes this a highly attractive market.Along with the start of development of artificial kidneys in 1974, Zeon aggressively promoted its medical device business. In 1989, a subsidiary Zeon Medical Inc. was established to conduct development, manufacturing, sales, and all other functions of the medical field for the Zeon Group.
“The Offset Balloon Catheter” as a means of differentiation in the gallstone removal process and with Japan’s first biliary covered stent “Zeostent Covered in the area of gastroenterology products, and the world’s smallest diameter “XEMEX IABP Balloon PLUS” as a device to aid the heartbeat at times of acute myocardial infarction in the area of cardiovascular products.
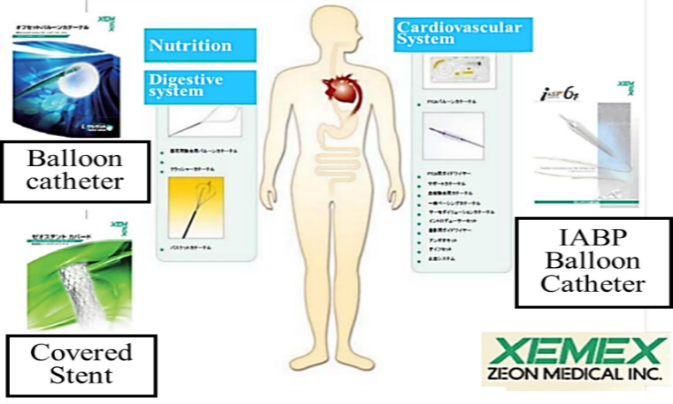
Currently Zeon is focusing efforts in the development of the biliary stone removal devices that eliminate pain. Zeon has a lineup of products for extracting biliary stones ranging from extremely large stones to sludge and sand with products such as XEMEX Crusher Catheter, XEMEX Basket Catheter NT, Extraction Balloon Catheter, and is aiming at a 50% share of the gallstone removal market. In March 2016, the Company launched the world’s first optical sensor FFR device as a type of guide wire. Because it uses an optical fiber sensor, mistaken readings of blood pressure measurements rarely occur. The operability as a guide wire has also gained a high evaluation.
* FFR: fractional flow reserve ratio for quantitatively evaluating the severity of lesions and determining treatment strategies in diagnosing and treating coronary arteries.
【New Specialty Materials Development: ~Carbon Nano Tube (CNT)~ 】
Aggressive R&D activities have allowed Zeon to launch various new materials into the market, and particularly high expectation is in the development of “single-wall carbon nanotubes (CNT)”.
1) What is Single-Walled CNT?
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) are cylindrical nanostructure formed by hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms. In 1993, Sumio Iijima, Ph.D., head of the Applied Nanotube Research Center of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), discovered this structure for the first time in the world and named Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs). CNTs are categorized into single-walled and multiple-walled CNTs. Multiple-walled CNT is relatively easy to manufacture and the developments for commercial applications already started.
At the same time, single-walled CNT exhibits the following properties and is superior to multiple-walled CNT:
- 20 times stronger than steel
- 10 times more heat conductive than copper
- Half as dense as aluminum
- 10 times the electron mobility of silicon
- lightweight but highly flexible
- has extremely high electric-and heat-conductivity properties
Possible CNT applications are electrical conductivity assistance agent in Li-ion batteries, transparent conductive film used in electronic paper and ultra-thin touch panel because of its high elasticity and strength, and as a thermal interface material. Because of its ability to absorb a wide spectrum of light, practical applications of single-walled CNT are being promoted in the area of electromagnetic wave absorbing materials for use in a wide range of fields including energy, electronics, structural materials, and other specialty materials.
Conventional single-walled CNT has several major issues including high levels of impurities, low levels of productivity and high manufacturing costs, which are about several tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of yen per gram.
2) Zeon’s Efforts and Position
Against this backdrop, the company aims at establishing technologies that are necessary for the commercialization of new products using single-walled CNT developed in Japan with its numerous superior qualities in response to the worldwide social demands to realize a low-carbon society.
3) Future Endeavors
Having established the mass production technology based on the super growth method, Zeon completed the CNT production facility and started mass production, the first in the world in November 2015 in its Tokuyama plant at Shunan-city, Yamaguchi Prefecture. Zeon is the only company in the world that has established mass production technologies for single-wall CNT. Companies around the world request for its product samples. Consequently, shipments of samples have already begun. Zeon has also begun to propose practical applications of this product. Developing a technology for suppressing lithium dendrites with the sheets based on carbon nanotubes is expected to contribute to significant improvement in the life of lithium metal electrodes (negative electrodes) and to accelerating the practical application of high energy density and large capacity lithium metal electrodes (negative electrodes) (from the company's press release on January 25, 2022).
At the same time, single-wall CNT is a type of nanomaterial that is extremely small and fiber shape. Therefore, there is a concern that it may have some impact upon biological processes depending upon its size and shape.
Currently, the AIST is conducting standardization of the evaluation process, and activities for the OECD endpoint measurement are being conducted, with global standardization and legal and regulatory aspects being considered.
Elastomer Business
Elastomers are “high molecular compounds that have rubber-like elastic properties,” an example of which is synthetic rubber. As described in the corporate history section of this report, in 1959 Zeon became the first company in Japan to mass-produce synthetic rubber, which became the foundation underlying all of Zeon’s businesses. This business includes the segments of synthetic rubbers, synthetic latices, and chemicals products (Petroleum resins, thermoplastic elastomers) businesses.
1) Synthetic Rubbers Business
<Example of final product: Tires>
Zeon provides the world’s leading tire manufacturers with the world’s highest-quality synthetic rubber for use in tires. Among the various types of synthetic rubber manufactured are styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which promotes superior abrasion resistance, aging resistance and mechanical strength properties, butadiene rubber (BR), which includes a superior balance between elasticity, wear and low-temperature properties, and isoprene rubber (IR), which features similar properties as natural rubber but with higher quality stability.
It is expected that the demand for S-SBR for fuel-efficient tires, which was developed by improving the characteristics of SBR, will grow rapidly. In order to increase the supplying capacity for coping with it, the first line of Singapore Plant started operation in September 2013, and the second line in April 2016. The supplying capacity of Singapore Plant is now 70,000 tons.
<Example of product: Automobile Parts>
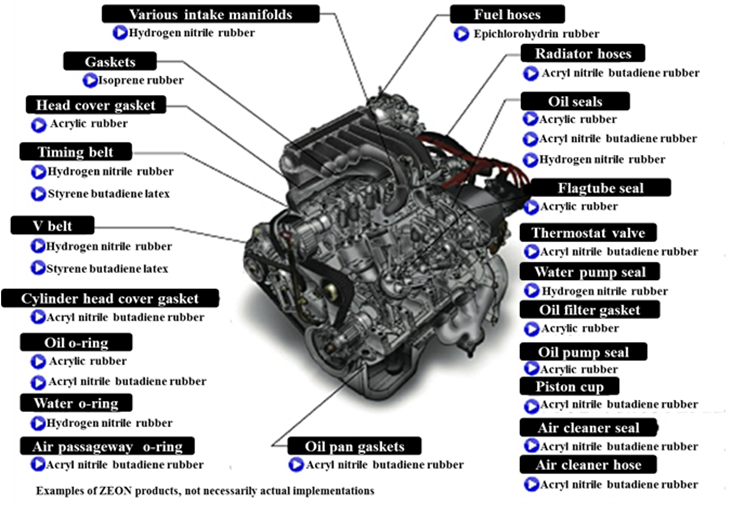
(Source: the company)
Radiator hoses, fuel hoses, timing belts, oil seals, and various other car engine parts use specialty synthetic rubber that has superior oil resistance and heat deterioration-resistant qualities.
Zeon is the world’s number one manufacturer of specialty synthetic rubber and features high quality levels and high market share of specialty synthetic rubber automobile parts. In particular, Zeon’s Zetpol® hydrogenated nitrile rubber, used for timing belts, displays superior heat and oil resistance and mechanical strength characteristic and claims high share of the worldwide market.
Furthermore, a new grade of Zetpol® has vastly improved the performance of products using the original versions of Zetpol®. Products using the new grade of Zetpol® are heat resistant at temperatures that exceed the limits for the original version of Zetpol® by 10 degrees centigrade, thereby extending the life of seals and gaskets, and are in steady demand for use in next generation bio-fuel engines. The new grade of Zetpol® is well suited to extrusion processing which is being leveraged to expand its usage in various hoses. Products using Zetpol® have also been well received by customers and are being used increasingly as a replacement material for more expensive competitive rubber in Japan, Asia, Europe, and North America.
2) Synthetic Latices Business
Synthetic latex is liquid rubber that synthetic rubber dispersed in water. It is used to manufacture gloves, paper coating, textile processing, adhesives, paints, and cosmetic puffs, etc. Zeon has high share of NBR latex used in cosmetic puffs in the world.
3) Chemicals Business
Zeon produces C5 fraction by its unique in-house GPI method, and turn it into materials for adhesive tapes and hot melt adhesive traffic paint binder and a wide variety of other products.
Other Business
The combination liquid for Reaction Injection Molding (RIM) using the ingredient dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) as a raw material.
[1-4 ROE Analysis]
| FY 3/17 | FY 3/18 | FY 3/19 | FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
ROE (%) | 10.3 | 5.3 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 10.0 | 10.9 | 3.2 | 8.9 |
Net income margin (%) | 8.05 | 3.92 | 5.47 | 6.27 | 9.18 | 9.24 | 2.72 | 8.14 |
Total asset turnover (times) | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.72 |
Leverage (x) | 1.77 | 1.71 | 1.66 | 1.62 | 1.55 | 1.52 | 1.54 | 1.51 |
ROE exceeded 10% in the fiscal years ended March 2021 and March 2022. In the fiscal year ended March 2023, however, the demand environment deteriorated, so net income margin shrank and ROE was at a low level. Although the fiscal year ended March 2024 showed a numerical recovery due to the posting of extraordinary income, the actual situation was unchanged from the fiscal year ended March 2023. In addition to recovery of demand and profitability improvement in the future, we would like to expect medium- and long-term increase in profitability based mainly on growth in the Specialty Materials segment.
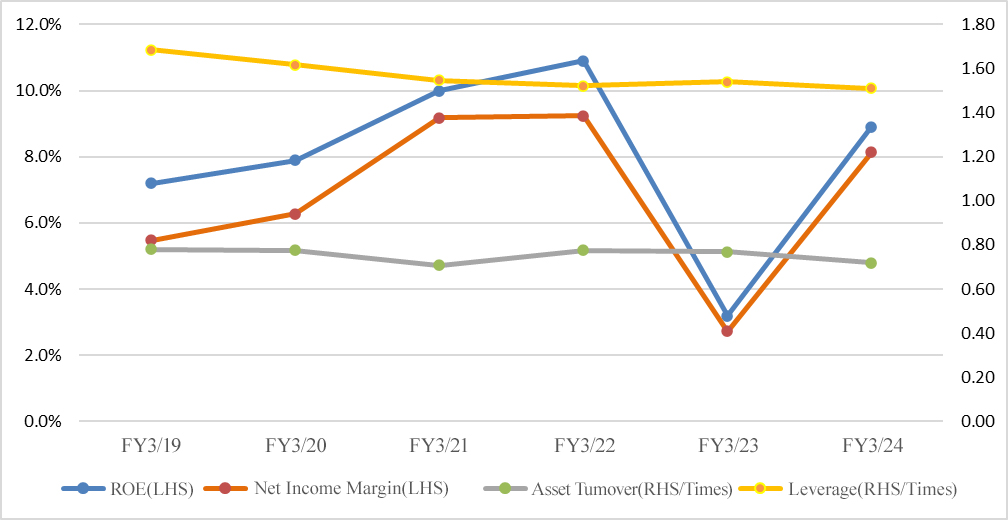
*Prepared by Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. based on the disclosed material.
[1-5 Characteristics and Strengths]
1. World’s Leading Creative Technology Development Capability
The GPB method used to manufacture butadiene from C4 fraction is the most important development in Japan’s postwar history of chemicals and is licensed to 49 plants in 19 countries around the world.
In addition, the Mizushima Plant is the world’s only plant with GPI method to extract high-purity isoprene and other effective substances from C5 fraction. This Zeon’s GPI method is a completely unique technology, which is not provided to other companies.
These two technologies represent the creative technological capabilities that are among the strengths of Zeon. They also are highly regarded and have received numerous awards in the global markets. Regarding technologies, Zeon has received 54 awards since 1960 including the GPB and GPI methods, in addition to 28 awards since 1982 for its environment conservation and safety efforts.
2. High Worldwide Share
Zetpol®, ZEONEX®, and ZEONOR® are representative of the products born from Zeon’s highly creative technologies, which have allowed it to acquire high shares of worldwide markets. In addition, their Leaf alcohol for in cosmetics and food flavorings and NBR latex for cosmetic puffs have the world’s top share.
3. R&D Structure that Continues to Yield Creative Technologies
Zeon seeks to conduct R&D activities based upon its basic corporate philosophy of "contributing to society by continuously creating the world's No.1 products and businesses based on innovative and original technologies that are unique to ZEON, even in niche markets, in fields in which ZEON excels, and that no one else can imitate, and that are friendly to the earth."
The Company’s main R&D center is in Kawasaki City, Kanagawa Prefecture. Zeon has also established the Precision Optics Laboratory and Medical Laboratory at the Takaoka Plant, the Specialty Chemical Product Research Facility at the Yonezawa Plant, the Toner Research Facility at the Tokuyama Plant and C5 Chemicals Laboratory at the Mizushima Plant for more efficient R&D activities to be conducted closer to the manufacturing sites. The technical support bases are in the U.S., Germany, Singapore, and China. New research and development initiatives have also been launched, including the establishment of the Emergence Promotion Center, which specializes in new businesses and technologies, and is taking on the challenge of sustainable research and development, including efforts to address the SDGs, which are to be attained by 2030.
2. First Half of the Fiscal Year ending March 2025 Earnings Results
[2-1 Consolidated Earnings]
| FY 3/24 1H | Ratio to sales | FY 3/25 1H | Ratio to sales | YoY | The company’s forecast | Compared with forecast |
Sales | 185,442 | 100.0% | 213,350 | 100.0% | +15.0% | 210,000 | +1.6% |
Gross Profit | 49,928 | 26.9% | 61,144 | 28.7% | +22.5% | - | - |
SG&A | 40,467 | 21.8% | 44,341 | 20.8% | +9.6% | - | - |
Operating Income | 9,461 | 5.1% | 16,802 | 7.9% | +77.6% | 15,000 | +12.0% |
Ordinary Income | 13,034 | 7.0% | 18,587 | 8.7% | +42.6% | 19,000 | -2.2% |
Quarterly Net Income | 10,359 | 5.6% | 12,300 | 5.8% | +18.7% | 12,000 | +2.5% |
*Unit: million yen.
Double-digit year-on-year growth in sales and profit
Sales increased 15.0% year on year to 213.3 billion yen, and operating income rose 77.6% year on year to 16.8 billion yen.
Both sales and profit grew in the Specialty Materials Business. In the specialty plastics segment, demand for cyclo olefin polymer (COP) and optical films for mobile devices recovered, and demand for optical films for large TVs was also steady. In addition, the shipment of COP for semiconductor containers increased due to the recovery of the semiconductor market, resulting in higher sales and profits. In the battery material segment, sales increased due to a recovery in demand for mobile terminals as well as steady demand for ESS applications. On the other hand, profit decreased due to inventory adjustments caused by a sharp drop in EV sales, especially in Europe, and intensified price competition in the Chinese market. In the chemicals segment, sales increased year on year due to the regular inspection conducted in the same period of the previous year. However, operating income decreased due to factors such as a decline in shipment volume and lower market prices for synthetic fragrances caused by a supply-demand imbalance. In the electronic materials segment, sales increased as the semiconductor market gradually recovered. However, operating income declined due to rising raw material prices and logistics costs. In the toner segment, sales grew due to the robust printer market, but operating income remained flat year on year due to rising raw material prices.
The Elastomer Business saw increases in both sales and profit. While the synthetic rubber segment was affected by production trouble at raw material suppliers and reduced production due to regular inspection at major domestic plants, sales remained steady, particularly for spot sales for overseas, as major overseas plants maintained high levels of operation. Furthermore, price increases to offset rising raw material costs contributed to the increase in sales and profit. In the synthetic latex segment, while market prices remained low and price increases to offset rising raw material costs were insufficient, sales increased due to the completion of inventory adjustments for hygiene gloves overseas. In the chemical products business, sales increased due to a recovery in demand for adhesive tape and labels and an increase in shipments mainly to overseas markets as a result of aggressive sales expansion policies. Still, profit declined because the company was unable to pass on higher raw material prices to selling prices due to weak market prices.
The interim dividend will be 35.0 yen/share, up 15.0 yen/share year on year, far exceeding the company's forecast of 23.0 yen/share.
[2-2 Trends by Business Segments]
◎Full year
| FY 3/24 1H | Composition ratio | FY 3/25 1H | Composition ratio | YoY |
Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 51,409 | 27.7% | 61,566 | 28.9% | +19.8% |
Elastomer Business | 104,731 | 56.5% | 120,651 | 56.6% | +15.2% |
Other Business | 31,463 | 17.0% | 33,760 | 15.8% | +7.3% |
Adjustment | -2,160 | - | -2,627 | - | - |
Total | 185,442 | 100.0% | 213,350 | 100.0% | +15.0% |
Operating Income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 6,592 | 12.8% | 10,801 | 17.5% | +63.9% |
Elastomer Business | 3,644 | 3.5% | 6,014 | 5.0% | +65.0% |
Other Business | 1,399 | 4.4% | 1,473 | 4.4% | +5.3% |
Adjustment | -2,174 | - | -1,485 | - | - |
Total | 9,461 | 5.1% | 16,802 | 7.9% | +77.6% |
*Unit: million yen. Composition of operating profit as % of operating profit on sales.
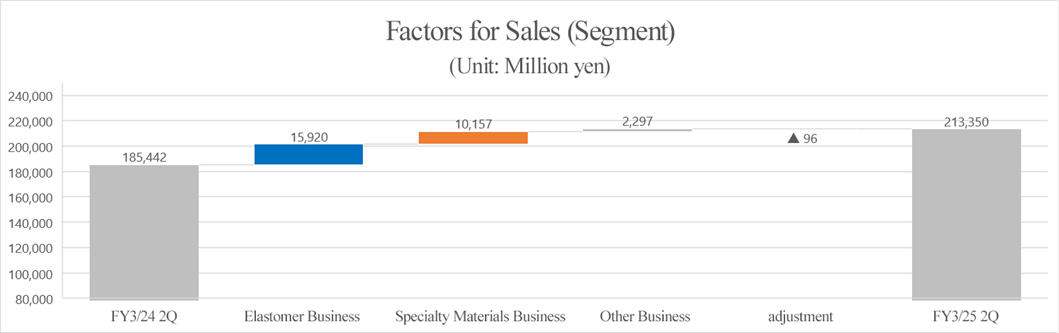
*Prepared by Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. based on the disclosed material.
[2-3 Quarterly Trends]
| 1Q FY 3/24 | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q | 1Q FY 3/25 | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q |
Sales | 91,927 | 93,515 | 98,364 | 98,473 | 106,105 | 107,245 |
|
|
Operating Income | 6,114 | 3,347 | 6,525 | 4,514 | 9,041 | 7,761 |
|
|
*Unit: million yen.
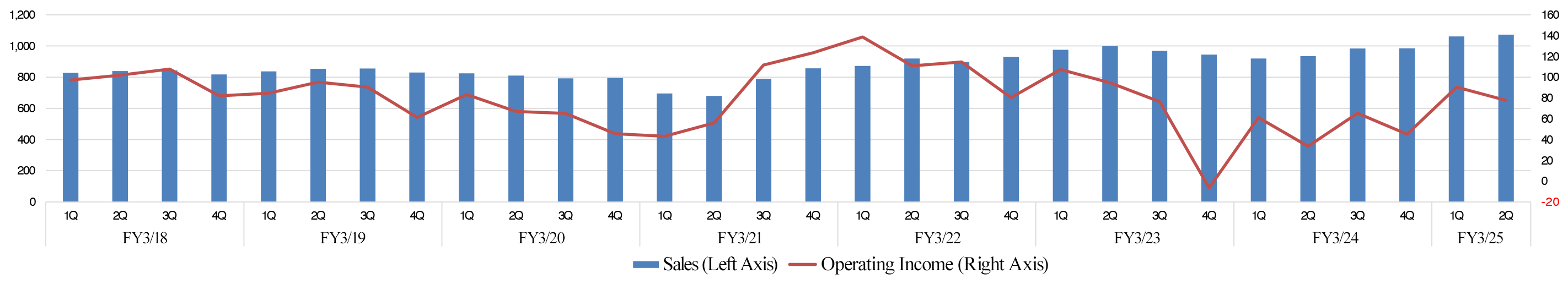
From the previous quarter (the first quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2025), sales grew 1.1%, but profit shrank 14.2%.
◎Segment
| 1Q FY 3/24 | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q | 1Q FY 3/25 | 2Q | 3Q | 4Q |
Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 25,196 | 26,213 | 27,664 | 28,300 | 30,322 | 31,244 |
|
|
Elastomer Business | 52,218 | 52,513 | 54,951 | 55,604 | 60,248 | 60,403 |
|
|
Other Business | 15,374 | 16,089 | 17,122 | 15,754 | 16,782 | 16,978 |
|
|
Operating Income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 3,998 | 2,594 | 3,600 | 3,049 | 5,269 | 5,532 |
|
|
Elastomer Business | 2,464 | 1,180 | 2,520 | 471 | 3,773 | 2,241 |
|
|
Other Business | 637 | 762 | 1,341 | 1,187 | 770 | 703 |
|
|
*Unit: million yen.
【Specialty Materials】
Sales and profit grew quarter on quarter.
The sales and profits of both specialty plastics and chemicals increased.
*Specialty plastics
As the shipments of COP and optical films increased, sales and profit grew year on year and quarter on quarter.
*Specialty chemicals
As the markets of printers and semiconductors were healthy, the shipments of toner and electronic materials increased, and sales grew year on year and quarter and quarter. Operating income declined year on year and quarter on quarter, due to the decreases in shipments of synthetic flavoring agents and battery materials and the drop in market prices.
◎Trends in shipment volume by item
* Battery materials
In 2Q (Jul-Sep), non-consolidated shipment decreased 23% year on year and 1% quarter on quarter.
The shipment of products for EVs decreased 40% year on year and 9% quarter on quarter, due to the inventory adjustment caused by the rapid decrease in the sales quantity of EVs in Europe, etc.
The shipment of products for consumers increased 75% year on year and 19% quarter on quarter, thanks to the growth of sales of products for an electricity storage system (ESS) in addition to the continuous recovery of sales of products for mobile terminals.
* Cyclo olefin polymer (COP)
In 2Q (Jul-Sep), non-consolidated shipment increased 34% year on year and 14% quarter on quarter.
The shipment of products for optical use grew 27% year on year and 2% quarter and quarter. The demand for products for smartphones and printers remained healthy.
The shipment of products for medical use, etc. rose 37% year on year and 20% quarter on quarter, thanks to the rebound from the transitional period in 1Q and the recovery of the market of products for semiconductor containers.
* Optical films
In 2Q (Jul-Sep), non-consolidated shipment grew 21% year on year, but declined 3% quarter on quarter.
The shipment of products for small and medium-sized displays increased 35% year on year and 4% quarter on quarter, thanks to the advanced shipment of products for smartphones and the healthy sales of products for tablet PCs.
The shipment of products for large-sized displays increased 18% year on year, but decreased 5% quarter on quarter. It decreased quarter on quarter due to the production adjustment by panel makers from late 2Q, but increased year on year, as they met the demand related to the new line whose operation started in September 2023.
【Elastomers】
Quarter-on-quarter increase in sales but decrease in profit.
Sales and profit grew year on year, as they revised the price of synthetic rubber, etc. Profit declined quarter on quarter, as shipment decreased due to the trouble with production in suppliers of raw materials and the regular inspection of major factories in Japan.
* Synthetic Rubber
The shipment from production bases decreased 7% year on year and 8% quarter on quarter.
The shipment of special rubber decreased 10% year on year and 4% quarter on quarter. Shipment adjustment was carried out for regular inspection at Tokuyama and Takaoka Factories. Demand was sluggish, due to the partial suspension of manufacturing in the automobile industry.
The shipment of versatile rubber declined 6% year on year and 9% quarter on quarter, due to the trouble with supply of raw materials and the shipment adjustment for regular inspection at Tokuyama Plant.
[2-4 Financial standing]
◎Main Balance Sheet
| End of Mar. 2024 | End of Sep. 2024 | Increase/ decrease |
| End of Mar. 2024 | End of Sep. 2024 | Increase/ decrease |
Current Assets | 300,982 | 301,195 | +213 | Current liabilities | 143,561 | 138,156 | -5,405 |
Cash | 42,784 | 31,984 | -10,800 | Payables | 86,754 | 68,927 | -17,827 |
Receivables | 87,446 | 89,243 | +1,797 | ST Interest-Bearing Liabilities | 8,960 | 23,960 | +15,000 |
Inventories | 123,353 | 136,394 | +13,041 | Non-current liabilities | 24,965 | 22,742 | -2,223 |
Non-current Assets | 231,272 | 233,221 | +1,949 | LT Interest-Bearing Liabilities | - | - | - |
Tangible Assets | 130,672 | 135,415 | +4,743 | Total Liabilities | 168,525 | 160,899 | -7,626 |
Intangible Assets | 5,432 | 5,754 | +322 | Net Asset | 363,729 | 373,517 | +9,788 |
Investment, Others | 95,168 | 92,053 | -3,115 | Capital | 362,380 | 372,721 | +10,341 |
Total assets | 532,254 | 534,416 | +2,162 | Total Liabilities and Net Assets | 532,254 | 534,416 | +2,162 |
*Unit: million yen. Receivables include electronically booked receivables; likewise, payables include electronically booked payables.
Total assets grew 2.1 billion yen from the end of the previous fiscal year, as trade and other accounts receivable decreased, but inventory assets increased due to the accumulation of inventory for regular inspection at Tokuyama and Takaoka Factories.
Total liabilities decreased 7.6 billion yen from the end of the previous term due to decreases in payables.
Net assets increased 9.7 billion yen from the end of the previous term due to increases in retained earnings and foreign currency translation adjustments.
As a result, the equity ratio increased by 1.6 points from the end of the previous fiscal year to 69.7%, and the D/E ratio was 0.06, up 0.04 from the end of the previous period.
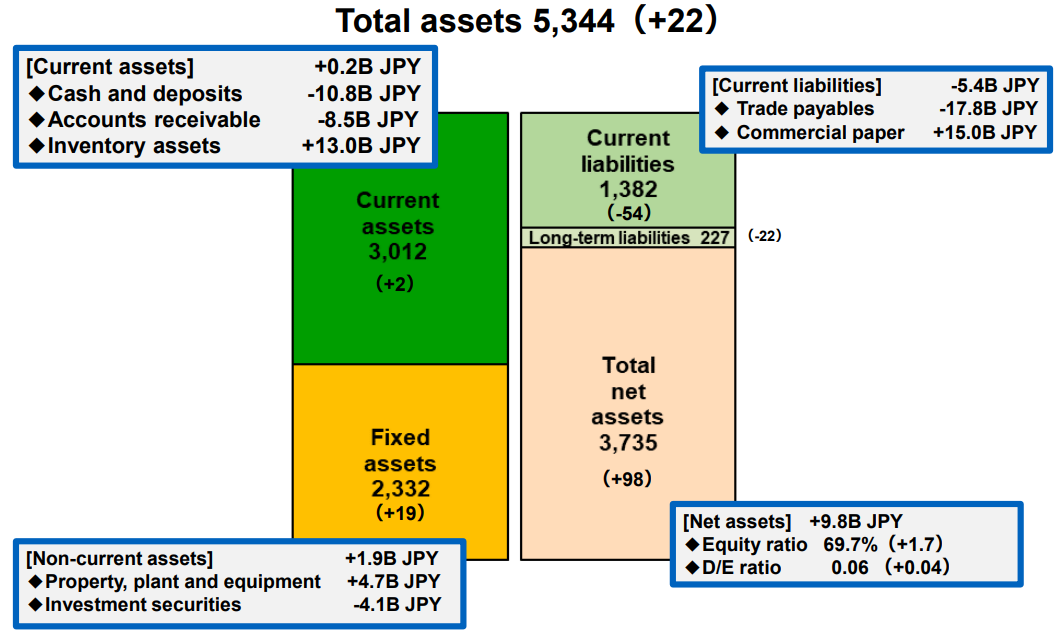
(Source: the company)
3. Fiscal Year ending March 2025 Earnings Forecasts
[3-1 Earnings Forecast]
| FY 3/24 | Ratio to Sales | FY 3/25 (Est) | Ratio to Sales | YoY | Initial Forecast |
Sales | 382,279 | 100.0% | 415,000 | 100.0% | +8.6% | 397,000 |
Operating Income | 20,500 | 5.4% | 23,500 | 5.7% | +14.6% | 26,500 |
Ordinary Income | 26,906 | 7.0% | 24,500 | 5.9% | -8.9% | 27,500 |
Net Income | 31,101 | 8.1% | 19,000 | 4.6% | -38.9% | 17,500 |
*Unit: million yen.
Revised Full-Year Forecasts: Sales to Increase 8.6% and Operating Profit to Rise 14.6%
The company has revised its full-year forecasts as shown in the table above, projecting an 8.6% year-on-year increase in sales to 415 billion yen and a 14.6% year-on-year increase in operating income to 23.5 billion yen for the fiscal year ending March 2025. The forecast was revised due to a defect that occurred in one of the four production lines at Mizushima Plant. To resolve the problem, the company suspended the operation of the production line in question in October. It is expected to take about three months to resume operations. Although the impact on overall performance is expected to be minimal as the company is managing customer product shipments by utilizing existing inventory, operating income and ordinary income for the Specialty Materials Business segment are expected to fall below the previous forecasts. This is primarily due to fixed costs incurred during the production line shutdown and expenses related to equipment restoration. In addition, the Elastomer Business division experienced production issues with a raw materials supplier. These factors, along with a revision of the assumed exchange rate and raw material assumptions, led to the forecast revision. The company carefully examined the recent business situation and found that there are both upward and downward revisions for individual products. Net income has been revised due to the booking of a gain on the sale of investment securities (extraordinary profit).
For the second half of the fiscal year, the company forecasts the following exchange rates: 1 U.S. dollar = 145 yen (previously 155 yen), 1 euro = 155 yen (previously 165 yen), domestic naphtha = 68,200 yen/kl (previously 76,000 yen/kl), and Asian butadiene = 1,400 U.S. dollar/ton (previously 1,100 U.S. dollar/ton).
The year-end dividend forecast has been revised upwardly from 24.0 yen/share to 35.0 yen/share. The company expects a dividend increase of 25.0 yen to 70.0 yen/share for the full year. This marks the 15th consecutive year of dividend increases since the fiscal year 2010. The expected dividend payout ratio is 76.0%.
[3-2 Trends by Business Segments]
| FY 3/24 | FY 3/25 (Est) | YoY | Previous forecast |
Sales |
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 107,373 | 115,500 | +7.6% | 110,500 |
Elastomer Business | 215,286 | 238,000 | +10.6% | 225,000 |
Sales Total | 382,279 | 415,000 | +8.6% | 397,000 |
Operating Income |
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 13,241 | 14,000 | +5.7% | 17,000 |
Elastomer Business | 6,635 | 9,000 | +35.6% | 9,000 |
Operating Income Total | 20,500 | 23,500 | +14.6% | 26,500 |
*Unit: million yen.
Revision in each segment
(1) Specialty Materials
For the first half of the fiscal year, it was forecast that sales would be 60 billion yen and operating income would be 9 billion yen, while actual sales were 61.6 billion yen and actual operating income was 10.8 billion yen.
For the second half, they have revised the forecast sales from 50.5 billion yen to 53.9 billion yen and the forecast operating income from 8 billion yen to 3.2 billion yen.
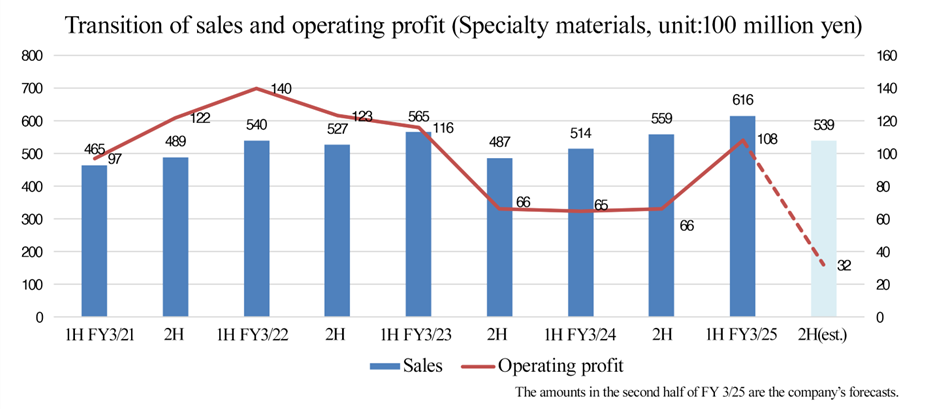
(2) Elastomer
For the first half of the fiscal year, it was forecast that sales would be 120 billion yen and operating income would be 6 billion yen, while actual sales were 120.7 billion yen and actual operating income was 6 billion yen.
For the second half, they have revised the forecast sales from 105 billion yen to 117.3 billion yen while leaving the forecast operating income of 3 billion yen unchanged.
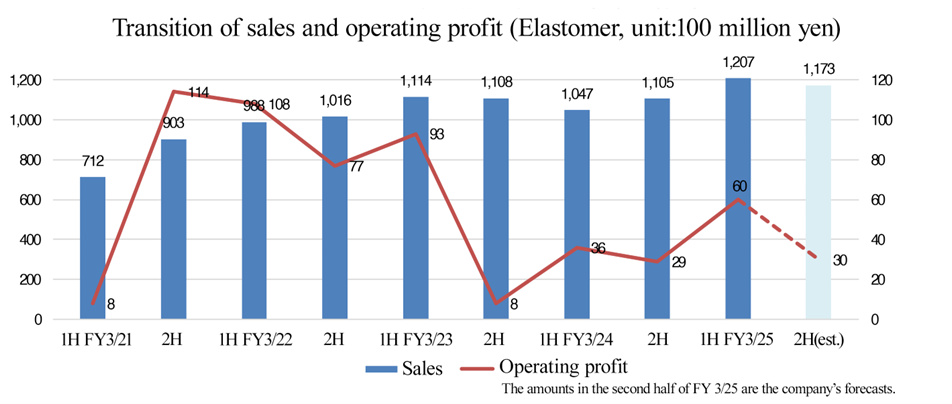
4. Medium-term Management Plan
The company is promoting its Medium-term Management Plan, “STAGE 30,” which began in the fiscal year ended March 2022. Having completed “Phase 1” of the plan in the fiscal year ended March 2023, the company has entered “Phase 2” of the business plan, which will end in the fiscal year ending March 2027. They will proceed with the plan in a flexible manner while revising it partially.
[1-1 Overview of the New Medium-term Management Plan]
The corporate philosophy is to contribute to the preservation of the earth and the prosperity of human race.
Zeon’s mission befits the company name’s origin, which is acquiring raw materials from the earth and prospering for eternity. The company’s mission is to contribute to a sustainable planet and a safe and comfortable life for people by providing unique technologies, products, and services.
Based on this mission, the company set its vision for 2030 to be a company that meets the expectations of society and the aspirations of employees.
Furthermore, the company has listed three specific action guidelines for all employees to focus on: “Let’s try first,” “Let’s connect,” and “Let’s polish up.”
Zeon will focus on achieving nine of the SDGs’ target to be a company that meets society’s expectations.

(Source: the company)
[1-2 Overview of the Medium-term Management Plan - Phases and Performance Targets]
The initial plan for fiscal year 2026 was revised in June as described below.
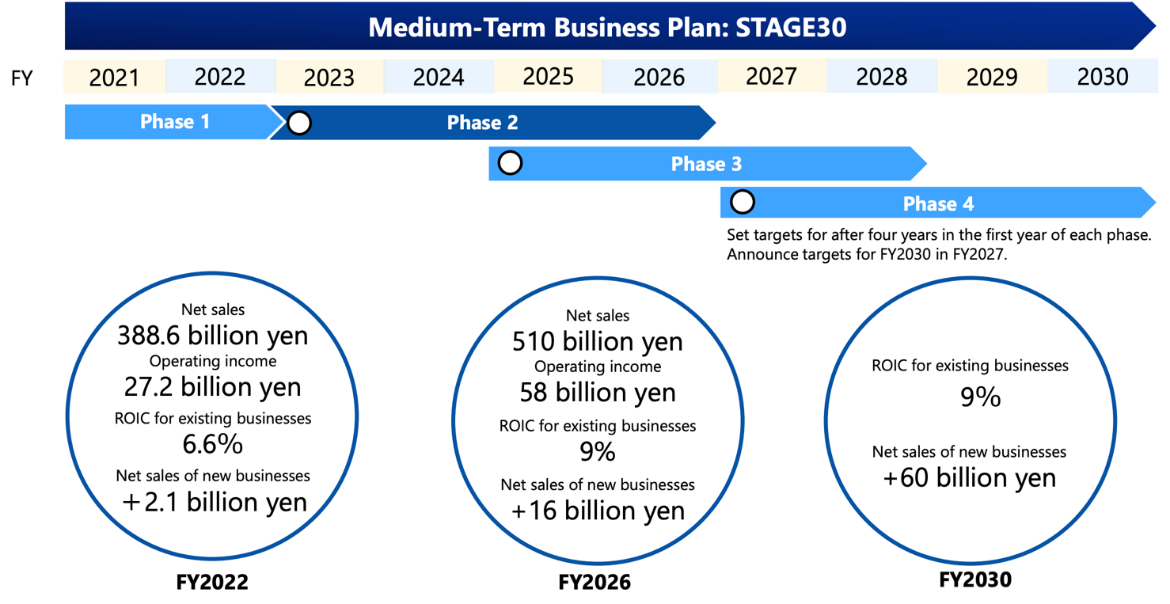
(Source: the company)
[1-3 Progress of Phase 1]
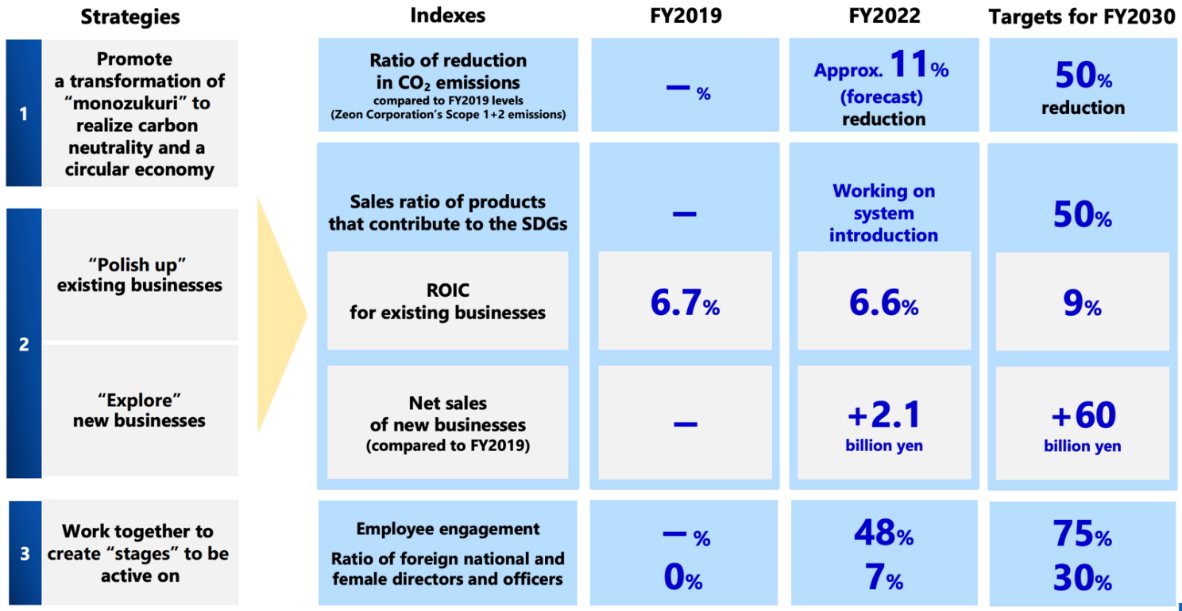
(Source: the company)
[2-1 Overview of Phase 2 of the Medium-term Management Plan]
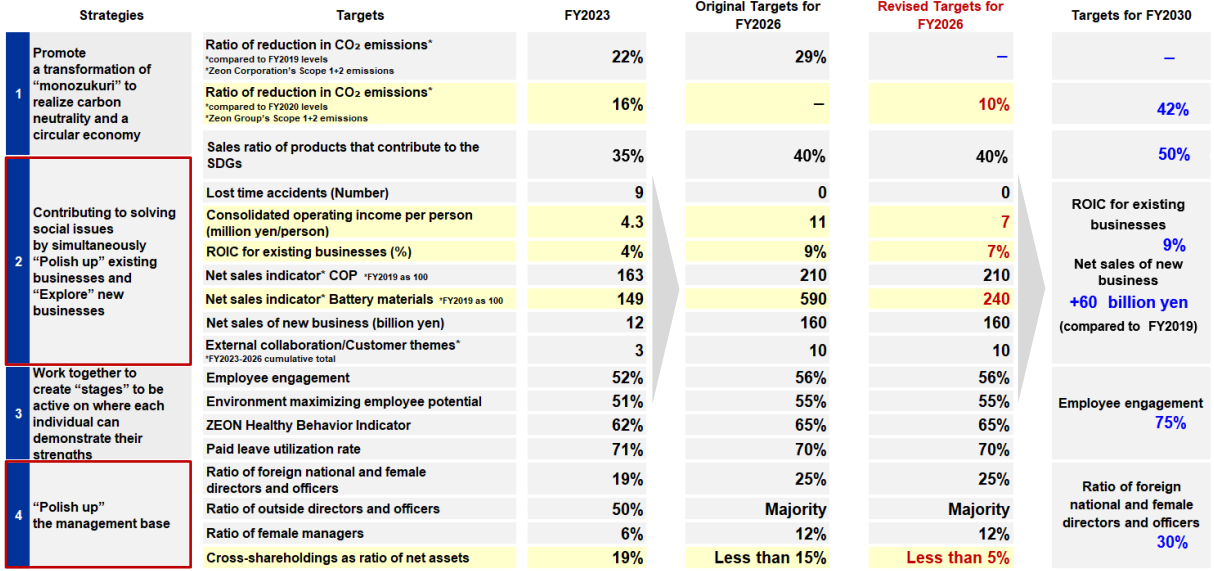
*In calculating a ROIC, we have revised the tax calculation used when calculating NOPAT as follows:
Previously) NOPAT = Operating profit - Tax expense → Revised) NOPAT = Operating profit - Operating profit x (Tax expense ÷ Pretax profit)
(Source: the company)
In Phase 2, without changing the vision for 2030, “A company that lives up to societal expectations and aspirations of employees,” it set performance targets for the fiscal year ending March 2027, with an emphasis on profitability. The company was meticulous about quantifying and defining the target values for the fiscal year 2026, which is the final year of this phase. The company intends to roll out interim targets and measures every two years to achieve the targets for the fiscal year 2030. In fiscal year ended March 2024, they were not supposed to revise their goals, but considering the recent changes in the business environment surrounding EVs, adhesives, etc., they have revised the goals for fiscal year ending March 2027. Additionally, in the overall strategy, the company plans to establish a new “polished management base” from Phase 2, and further enhance governance.
New name for the Medium-Term Plan: “STAGE 30”

(Source: the company)
[2-2 Strategy in Phase 2 of the Medium-term Management Plan]
(1) Promote a Shift to “Manufacturing” to Realize Carbon Neutrality and a Circular Economy
Key Measures
Reduce Scope 1 and Scope 2 CO2 emissions for 2030.
Looking ahead to 2050, to contribute to the reduction of Scope 3 emissions.
As they obtained the SBT certification, they have unified the goals of all group companies based on the GHG protocol.
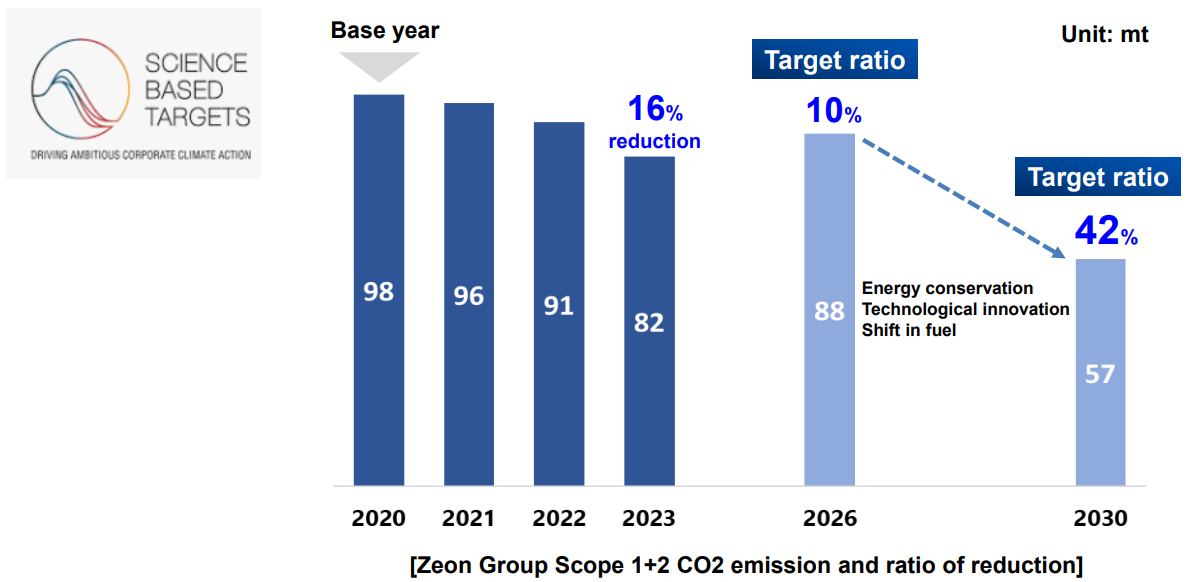
(Source: the company)
(2) Promoting a Shift to “Manufacturing” to Realize Carbon Neutrality and a Circular Economy
+ “Polishing up” existing businesses + “Exploring” new businesses
Key Measures
Achieving safe and stable production and promoting sustainable manufacturing.
These will improve labor productivity.
The amount of investment in human resources increased by 18 billion yen (FY 3/24 to FY 3/27) from the first phase.
① Initiatives for realizing carbon neutrality by 2050
To realize “manufacturing” that will contribute to a recycling-oriented society by reducing GHG emissions

(Source: the company)
② Start of operation of a system for certifying products that would help attain SDGs
39 products have been certified. The ratio of certified products was 35% in fiscal year 2023. They aim to raise it to 40% in fiscal year 2026.
Products are certified after in-house examination based on the degree and range of contribution to the settlement of social issues, the sustainability of business, etc.

(Source: the company)
(3) “Polishing up” existing businesses
They first set the following policies.
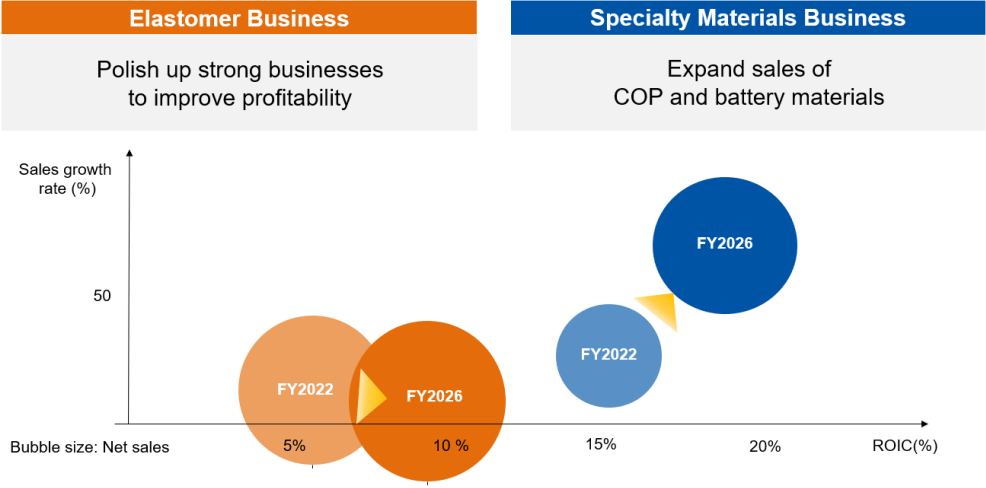
(Source: the company)
①Elastomer at Tokuyama Plant
It is assumed that the manufacturing of the E-SBR1 series and NBR-LX series will be discontinued in fiscal year ending March 2027 and the manufacturing of BR will be discontinued in fiscal year ending March 2029 or later.
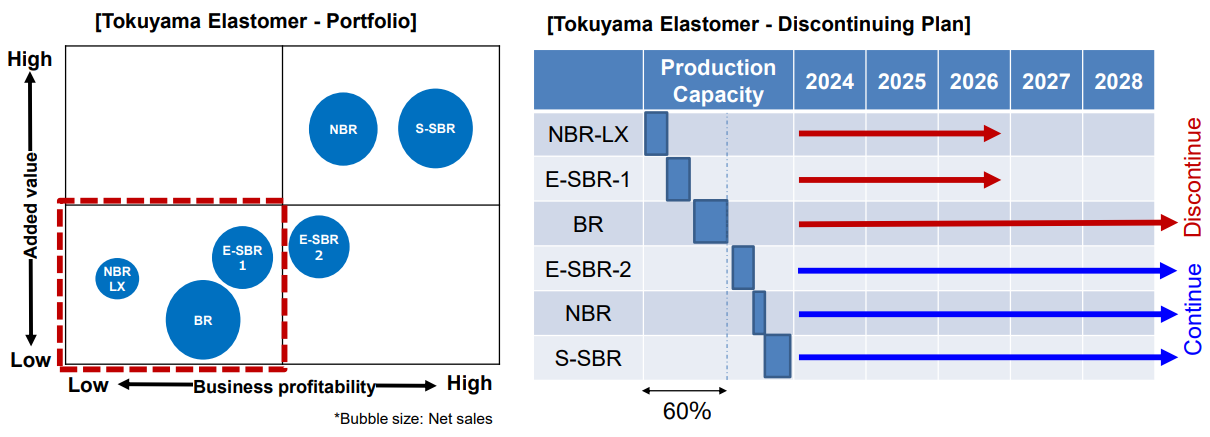
(Source: the company)
They plan to stop the operation of 60% of elastomer manufacturing equipment of Tokuyama Factory.
②Specialty Materials Business
In response to the growth of the cyclo olefin polymer (COP) business, they decided to construct a new plant in the Tokuyama area.
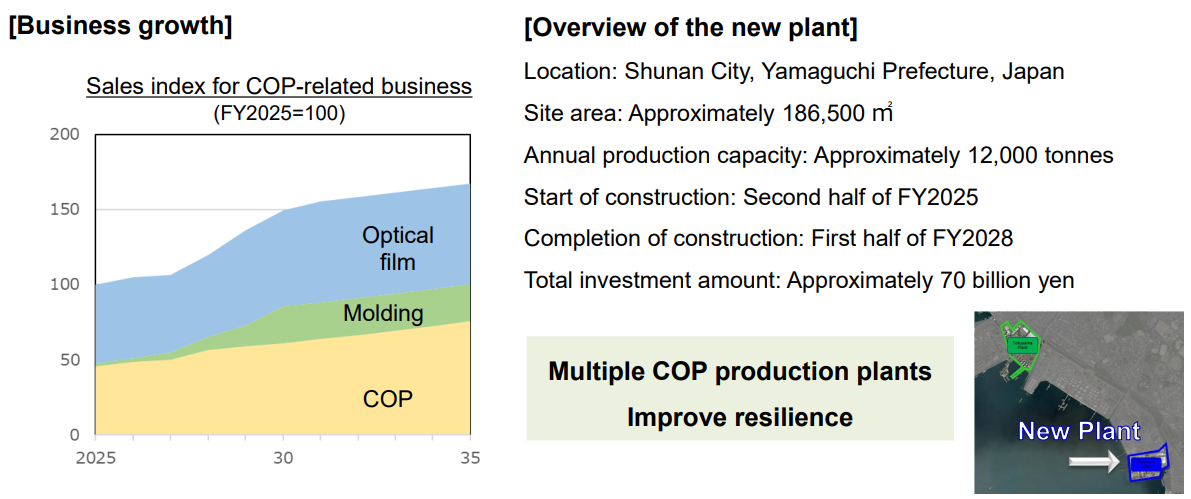
(Source: the company)
Through the modification of the portfolio, profit increased from the time when elastomer was still produced at Tokuyama Plant.
Policy based on human resources, the resilience of COP, and the best owner of rubber
③ Battery material business
Revision to target values
Slowdown in growth, changes in the technological trend, and the delay in product development ⇒ Revision to the goal for fiscal year ending March 2027
They aim to grow their business significantly with several measures for fiscal year ending March 2030.
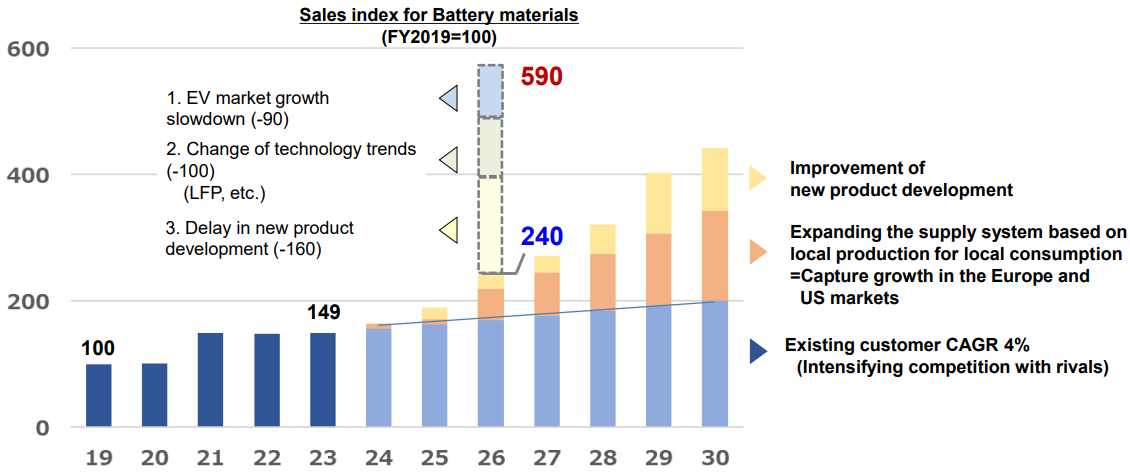
(Source: the company)
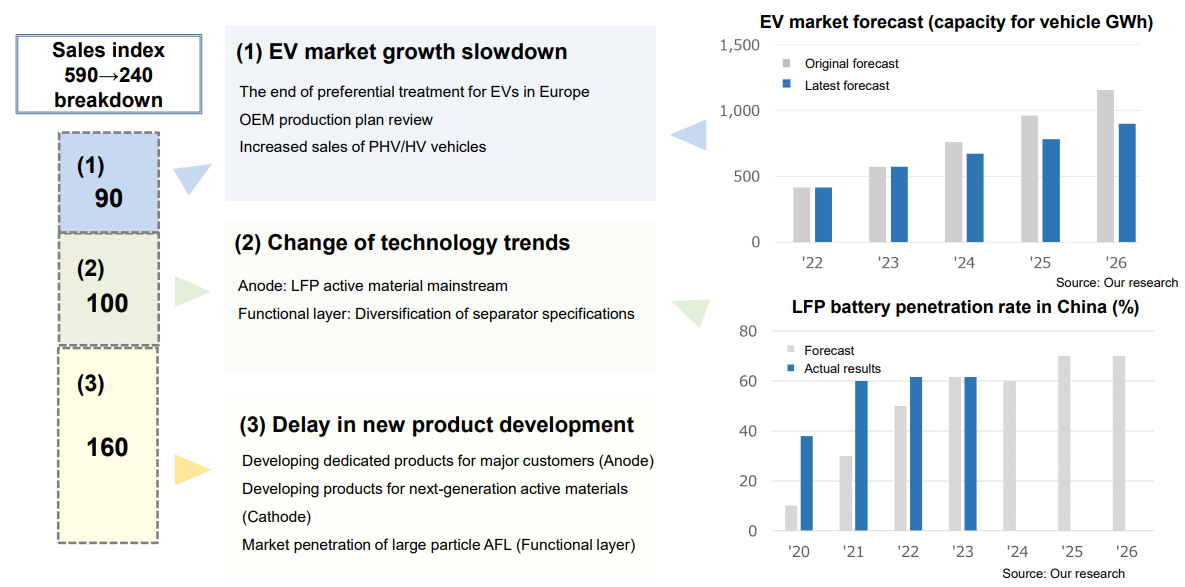
(Source: the company)
Initiatives for the year 2030
To enrich a global supply system to meet the needs for local production and local consumption
④ Chemical products business
The profitability of the chemical products business (PDR and SIS) declined due to the entry of overseas competitors, but this business is an important constituent of their C5-related business.
Acquisition of raw materials for profitable products at low cost ⇒ By-products of raw materials for less profitable products ⇒ It is necessary to continue the chemical products business.
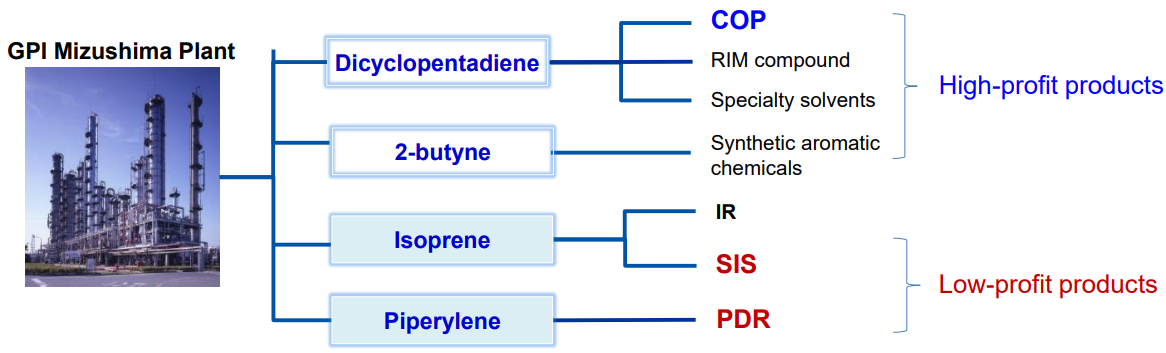
(Source: the company)
To avoid the competition with overseas competitors ⇒ To secure competitive advantages in Japan and North America (coping with customs and cementing the relationships with clients)
⑤ Optical film business
Pulling through the Noto earthquake, they resumed the full-scale operation of all manufacturing lines. ⇒ Improvement in revenue
They are considering the enlargement of factories, in response to the expansion of demand for large-sized displays.
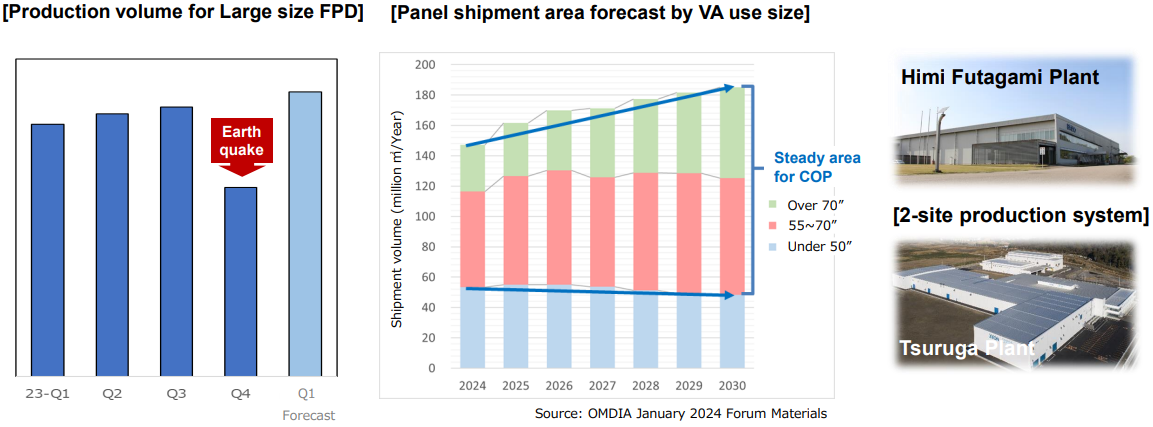
(Source: the company)
⑥ Initiatives for earning sales with new business
1. To release new products in a new market
2. To realize inorganic growth through M&A
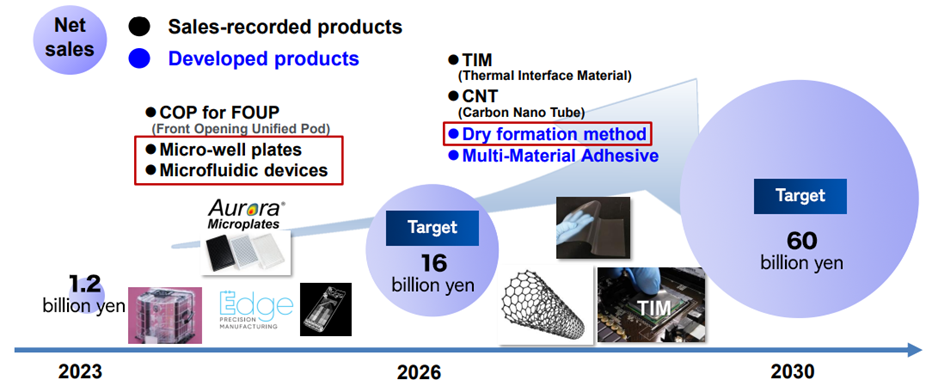
(Source: the company)
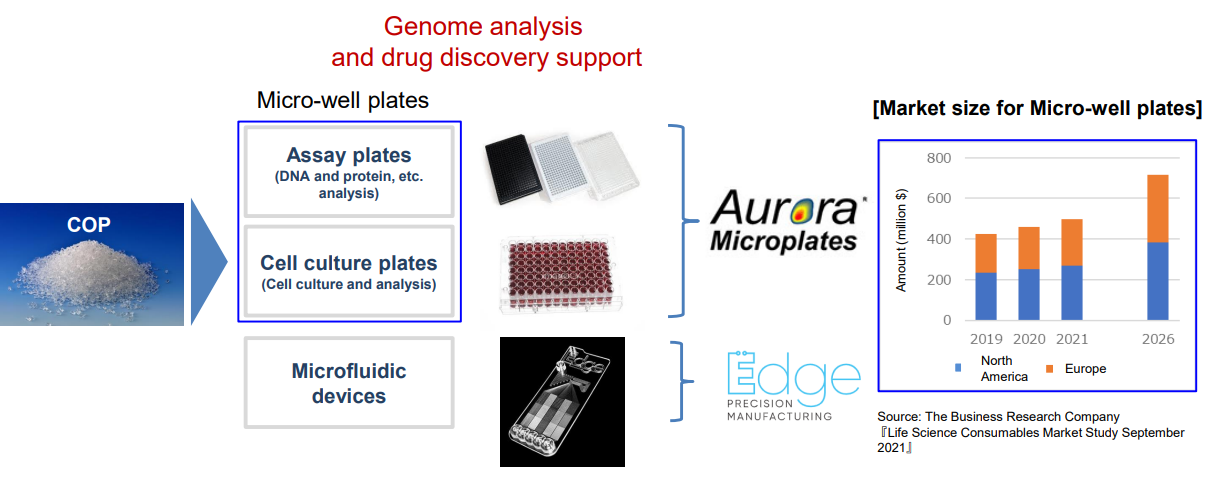
MicroWell plates
Acquisition of two U.S. makers ⇒ Acceleration of the expansion of the life science business
(Source: the company)
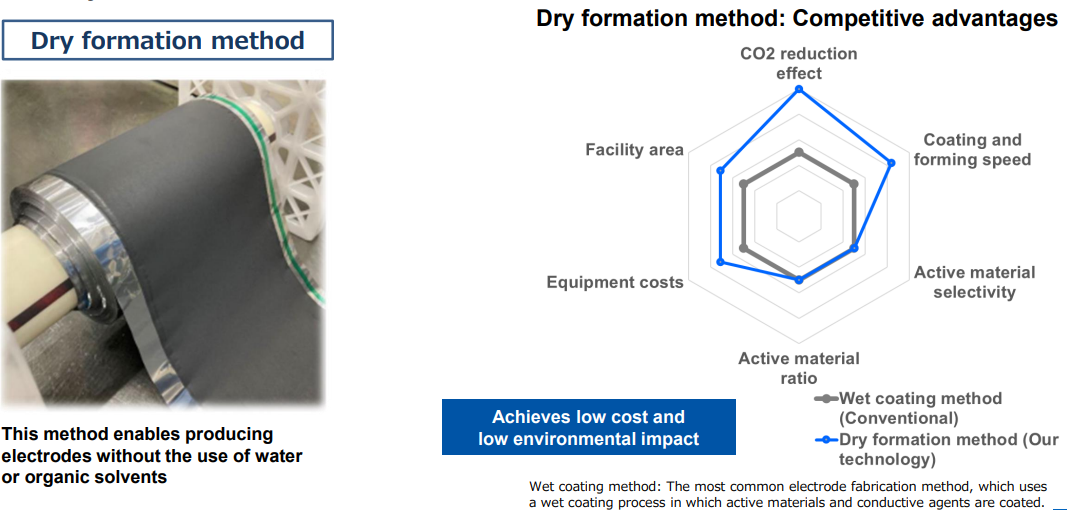
Method for shaping battery materials under dry condition
The company is developing an innovative method for manufacturing electrodes in cooperation with a battery maker.
(Source: the company)
 |
 |
(Source: the company)
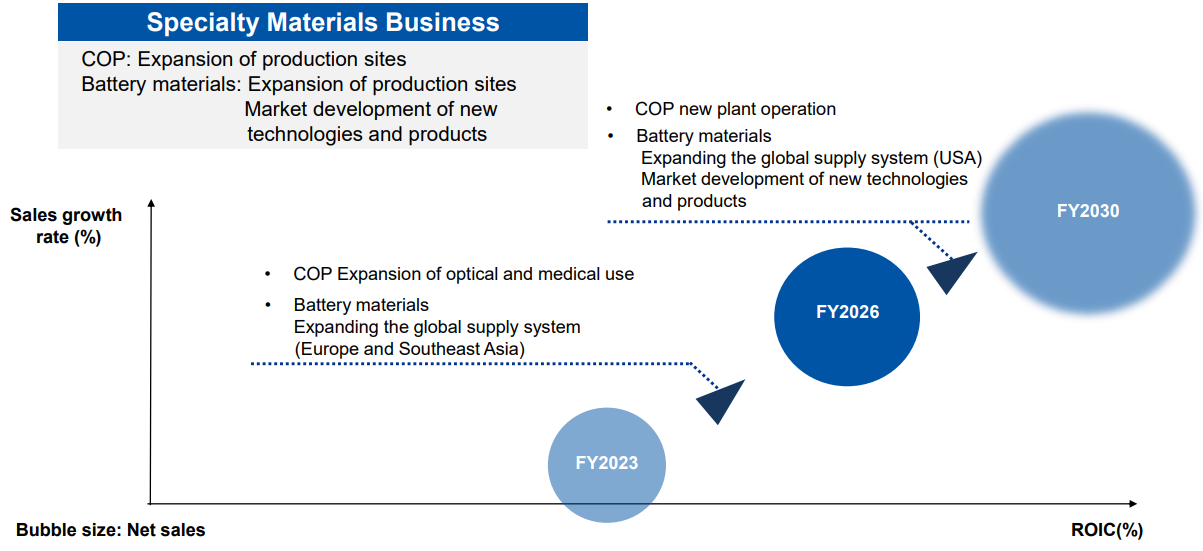
ROIC declined temporarily, due to the discontinuation of production of elastomer at Tokuyama Plant and the investment in COP.
It is expected that group-wide ROIC will show a V-shaped recovery and exceed the value before the large-scale investment during a period from 2030 to 2035.
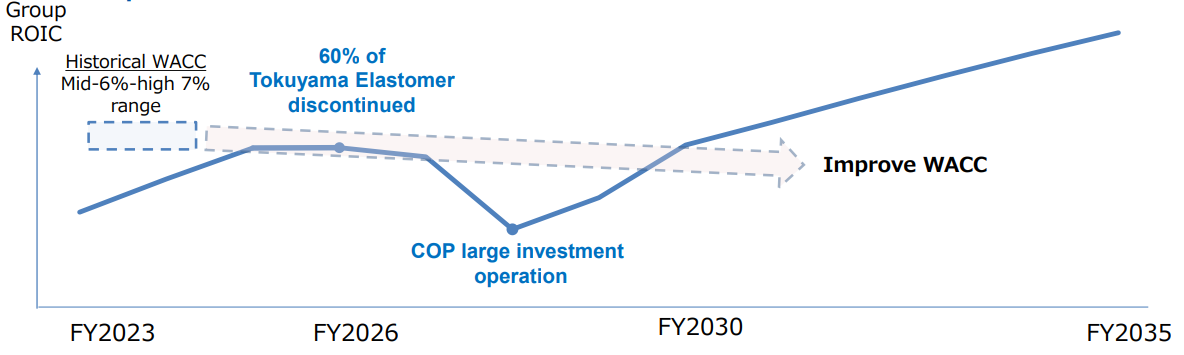
(Source: the company)
(4) Work together to create “stages” to be active on
Creating a working environment where employees can work healthily and enthusiastically.
Promoting initiatives for health-oriented management | ●Efforts to reduce the risk of lifestyle-related diseases through the introduction of the ZEON Healthy Behavior Indicator (*) (*) ZEON Healthy Behavior Indicato Percentage of participants who achieved at least 2 of the 3 actions (BMI baseline maintenance, physical activity habits, and non-smoking) to reduce the risk of lifestyle-related diseases |
Operating a personnel system that allows people to demonstrate their “individuality” | ●Transforming the human resources management system to draw out individual strengths and foster growth ●Adopting and integrating a new personnel system for managerial positions centered around “duties” |
Instilling the DI & B concept | ●Creating an organizational culture that supports the expression of individuality through the promotion of Diversity, Inclusion, and Belonging (DI&B) ●Leadership education that leverages diverse talents |
(5) “Polish” a Management Base
Target values for FY 3/27 |
 |
Results in FY 3/24 |
 |
(Source: the company)
Revision to the target values
They plan to reduce the ratio of strategically held shares to net assets to less than 5% in fiscal year ending March 2027.
“Polishing” Corporate Governance.
Strengthening Governance | ●Strengthening the linkage of executives’ compensation to the medium-term plan ●Appointing diverse and independent executives ●Reducing strategically-held shares |
Developing diverse human resources for future management | ●Starting the operation of the new personnel system for managers ●Promoting the training of managers and candidates for managers ●Diversifying career opportunities |
Polishing up Capital Efficiency | ●Advanced financial management to support aggressive business investment |
[2-3 Phase 2 of the Medium-term Management Plan, Financial Targets]
(1) Performance Target
As they have revised the target sales of battery materials, they have consolidated financial goals.
Original target value for FY 3/27 |
 |
Revised target value for FY 3/27 |
 |
(Source: the company)
At the time of announcement of financial results in the first half of the fiscal year, they announced that they would buy more treasury shares and revised the target ROE to 10%.
Targets in Each Segment
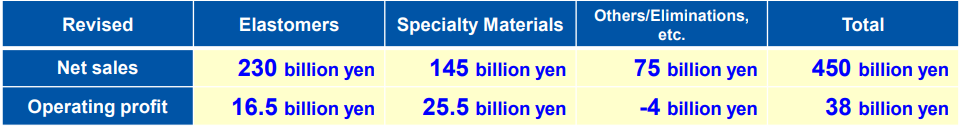
(2) Financial strategy
Measures for realizing business administration conscious of capital cost and stock price
-Revision to the policy for shareholder return
Significantly enhancing the financial strategy from the previous one of aiming to achieve a payout ratio of 30%, they now aim to realize a DOE of 4% while buying more treasury shares.
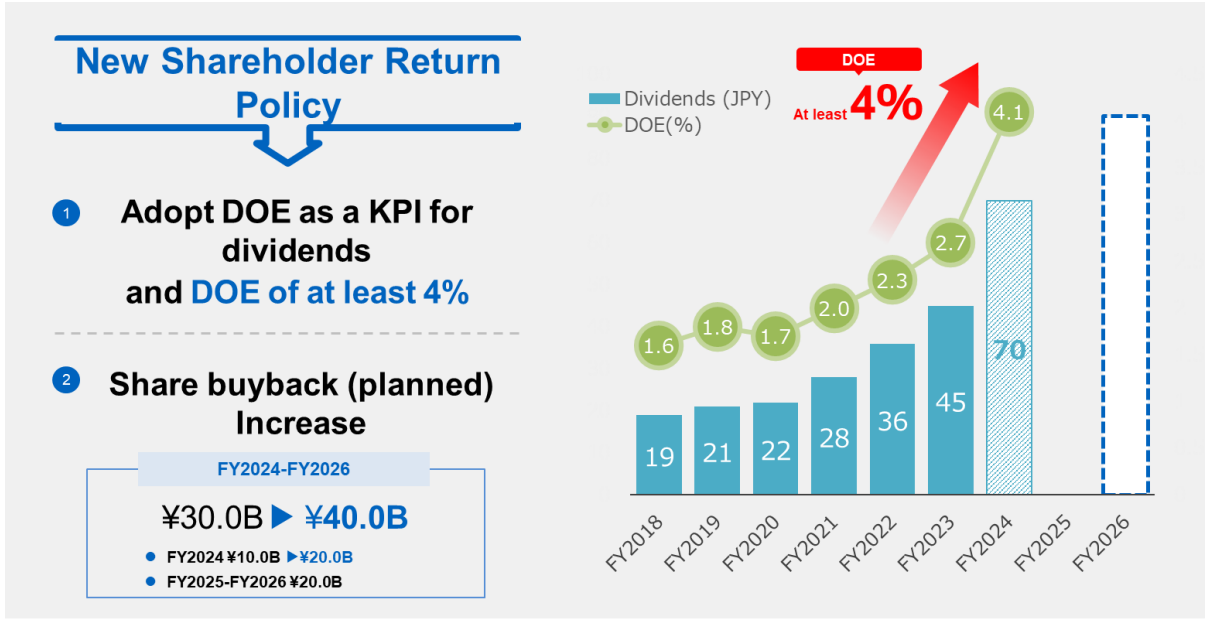
(Source: the company)
Group-wide ROIC is expected to be 6% in fiscal year ending March 2027. We aim to expand spread while improving WACC.
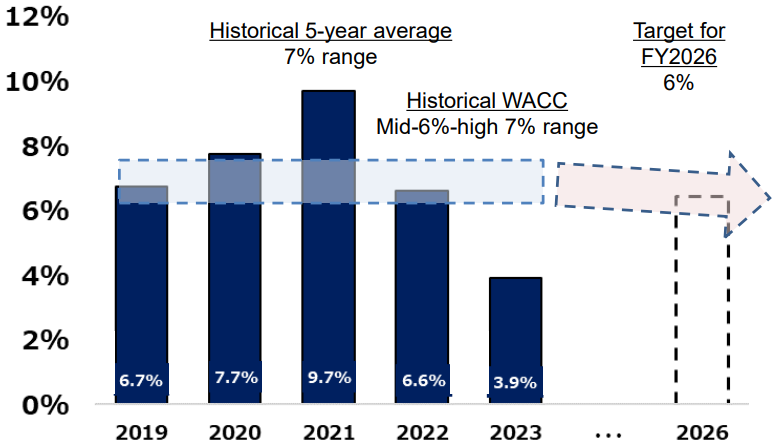
Historical WACC is the company's estimate
(Source: the company)
Cash Flow Allocation
The cash outflow that will augment through the enhancement of shareholder return will be covered by the procurement of more interest-bearing liabilities.

(Source: the company)
(3) Investment Plan
Revision to the investment plan ⇒ Down 20 billion yen from the initial plan
To concentrate investment funds onto highly profitable and new businesses
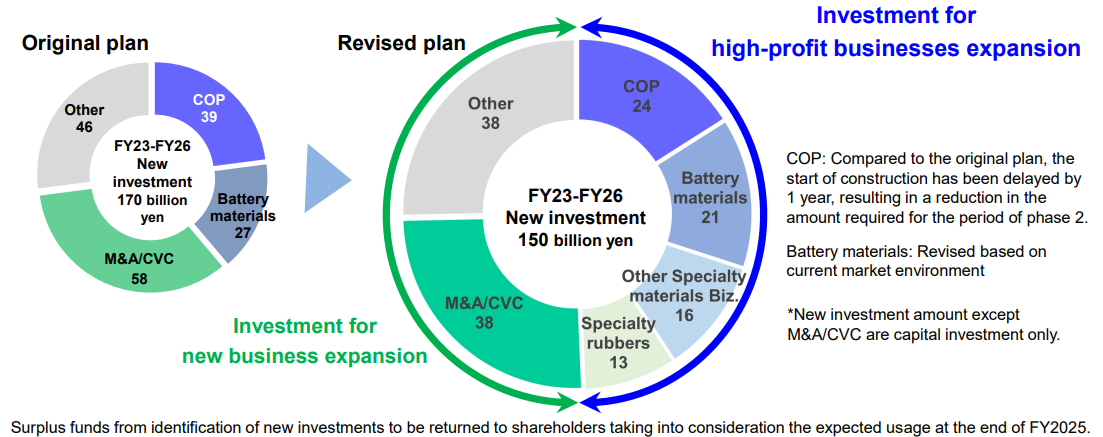
(Source: the company)
(4) Initiatives for securing capital profitability exceeding capital cost
・ Rationalization of the level of cash conversion cycle (CCC): Enhancement of in-house monitoring for inventory
・ Revision of expense plans, etc.: They are reviewing SG&A expenses and fixed costs of factories.
・ Revision to the financial leverage goal: They are examining the outlooks for business and investment.
(5) Capital Structure
They are reducing strategically held shares, with the aim of decreasing the ratio of strategically held shares to net assets to less than 5% by fiscal year ending March 2027.
・Procuring more funds with interest-bearing debt to support aggressive investment and optimize the capital structure
・Controlling financial discipline to a level that keeps the single A rating
・Reducing strategically-held shares and improving asset efficiency
・ To improve D/E ratio by procuring interest-bearing liabilities and enriching shareholder return (keeping it 0.3 or less)
・ To optimize the capital composition and continuously improve corporate value in the medium/long term
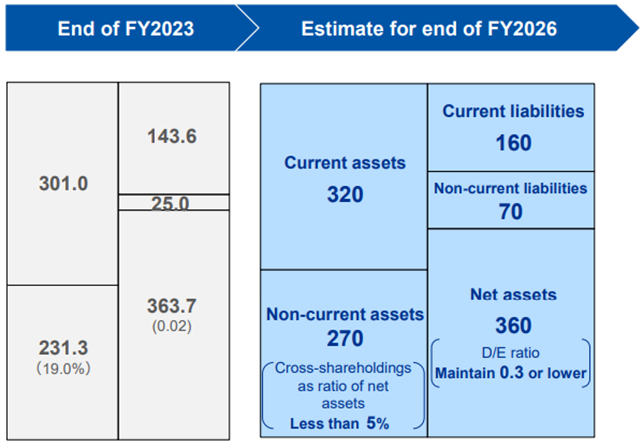
(Source: the company)
5. Conclusions
The company achieved double-digit growth in sales and a significant increase in profit in the first half, generally meeting the company’s expectations, although there was a rebound from the double-digit decline in profit in the same period of the previous year. While the full-year forecast has been adjusted to reflect changes in assumed exchange rates and production issues at Mizushima Plant, their impact on the medium-term plan is expected to be minimal. Therefore, Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. believes that the revised forecast remains conservative. As discussed in our previous report, we are concerned that the market for battery materials for EVs remains uncertain due to the sluggish market. The company is taking various actions, but the excess EV production capacity in China has become a detriment to global competition, and demand is stagnant in the U.S. and Europe. We will continue to monitor the future of the market and the company's response.
The most noteworthy aspect of this earnings announcement is the return of profit to shareholders. By setting DOE as the yardstick for dividends, the company is able to ensure a stable and high dividend level without being affected by a single year's performance or market conditions. The company has also strengthened its share buyback program and is now close to achieving a P/B ratio of 1. If the company achieves the profit level targeted in its medium-term management plan for the fiscal year ending March 2027, EPS is expected to be around 120 yen.
While the company's materials for electric vehicle lithium-ion batteries may face a temporary plateau, the market is expected to grow in the future. Additionally, the outlook for cyclo olefin polymers (COP), which are valued for their optical and medical properties, is also bright. The company is expected to continue investing aggressively, and it will be interesting to see how it balances these investments with its ongoing business operations.
<Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance>
◎ Organization type, and the composition of directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with auditors |
Directors | 11 directors, including 5 external ones |
Auditors | 5 auditors, including 3 external ones |
◎ Corporate Governance Report
Last update date: July 8, 2024
Basic policy
Our company respects the interests of a broad range of stakeholders, including shareholders, and aims to earn revenue and continuously improve our corporate value while adjusting the relations of interests. To do so, we will make continuous efforts to establish a system for realizing efficient, sound business administration through corporate governance.
In addition, we will make decisions and execute business operations swiftly after clarifying the functions and roles of each institution and each in-company organization by developing internal control systems. We will properly monitor and disclose its progress and results and strive to improve the transparency of our business administration.
Reasons for Non-compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)
(All principles are based on the Code revised in June 2021, including the content for the prime market)
Our company follows the principles of the corporate governance code.
Disclosure Based on the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpt)
Principles | Disclosure content | |
[Principle 1-4 The so-called strategically held shares] | ・Before strategically holding shares of any other companies, we consider carefully if the strategically held shares of a company strengthen the relationship between us and our business partners, the society and other stakeholders and will eventually enhance our corporate value in a medium- to long-term perspective. As for shares held based on these considerations, the company will annually verify the appropriateness of holding shares of each company by considering the appropriateness of its holding purpose and whether the benefits, risks, etc. that come along are commensurate with the capital cost. Based on the evaluation of appropriateness in fiscal year 2023, we judged at the meeting of the board of directors held on October 27, 2023, that it was appropriate to hold the shares in all of the companies. ・In the second phase of the medium-term management plan, STAGE30, which was initiated in fiscal year 2023, we hold up “brush up the management base” as one of the company-wide strategies and will raise our corporate value while attaching weight to enhancement of the governance structure. Regarding the financial strategies, we have set a target for fiscal year 2026 which is that the shares we strategically hold account for less than 5% of the consolidated net assets, and plan to sell a portion of our listed securities. As of the end of March 2024, the ratio to consolidated net assets is 19.0%. However, we will continue to work toward further reduction in the future to achieve the target mentioned above. ・We will determine when to exercise our voting right of strategically held shares based on a medium- to long-term viewpoint on enhancement of the corporate value of the company that we invest in. | |
[Supplementary Principle 4-11-1 Concept of Balance, Diversity, and Scale of the Board of Directors] | ・The Board of Directors shall consist of diverse directors with different backgrounds such as knowledge, experience, and expertise. As the scale of the board should be appropriate for sufficient deliberation and prompt and rational decision-making, the number of directors shall be limited to 15 or less based on the provisions of the Articles of Incorporation. ・In order to appropriately reflect the opinions of personnel with abundant experience and insight, such as outside corporate managers and those who possess experience in public administration, in the company’s management policy and to ensure the effectiveness of independent and objective management supervision by the Board of Directors, we will appoint multiple independent outside directors who will not be involved in business execution. -For a list of the skills that the Board of Directors should possess in light of the Company's management strategy and the combination of skills that each Director possesses and that the Company specifically expects him/her to demonstrate (so-called skills matrix), please refer to Reference documents for the General Meeting of Shareholders in the “Notice of Convocation of the Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders” ().https://www.zeon.co.jp/ir/stock/meeting/ | |
Principle 5-1 Policy on constructive dialogue with shareholders | ・In our company, the IR and SR Department is in charge of interacting with our shareholders, and the Director of Administration manages the office. ・The IR and SR Dept. appropriately exchanges information with the related departments within our company and provides precise and unbiased information to our shareholders. ・Our company will continuously strive to enrich methods of dialogue other than individual interviews, such as holding information sessions for investors on a quarterly basis, improving explanatory materials for our financial results disclosed on our website and participating in company information sessions for individual investors. ・The IR and SR Dept. collates and analyzes opinions obtained through interaction with our shareholders when necessary and report them to the Representative Director. ・Our company thoroughly manages unreleased important facts in accordance with the “Insider Trading and Timely Disclosure Management Rules”, and communicates with our shareholders to prevent information leak. ・For detailed information on IR activities, including dialogues with shareholders, please refer to section III-2 (IR Activities) under "Measures for Shareholders and Other Stakeholders.” | |
[Measures for Achieving Management with a Focus on Capital Costs and Stock Price] | Our current PBR (Price-to-Book Ratio) is below 1, and improving this to above 1 is an important management challenge. We are committed to steadily advancing efforts to achieve the goals in the second phase of the medium-term management plan, STAGE30, aiming to improve capital profitability. Our specific initiatives are as follows: ■ To “polish” existing businesses ・To modify the portfolio of the Elastomer Business and the COP business ・To enhance product development in the battery material business, upgrade the supply system for local production and local consumption, and cement the relationships with clients ・To secure competitive advantages of the chemical products business in Japan and North America ・To discuss the enlargement of factories in response to the growth of demand in the optical film business, etc. ■ To “seek” new businesses ・To release new products in a new market ・Inorganic growth through M&A ・To construct facilities for co-creation and innovation, to realize co-creation with business partners around the world and fusion with core technologies of our company ■ Financial strategies ・To concentrate investment funds onto highly profitable and new businesses ・To reduce the ratio of strategically held shares to net assets to less than 5% by fiscal year 2026 ・To enrich shareholder return by increasing the dividend amount according to performance with the minimum payout ratio being 30% and acquiring treasury shares ・Promote dialogue with the capital markets. | |
|
| |
This report is intended solely for information purposes and is not intended as a solicitation for investment. The information and opinions contained within this report are made by our company based on data made publicly available, and the information within this report comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However, we cannot wholly guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness, or validity of said information and opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration. Copyright(C) Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. | ||
For back numbers of Bridge Reports on ZEON CORPORATION(4205)and Bridge Salon (IR seminar), please go to our website at the following URL. www.bridge-salon.jp
<Major Shareholders>
Shareholder | Number of Holding Shares (thousand) | Rate (%) |
The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account) | 25,191 | 11.84 |
Custoday Bank of Japan, Ltd.(Trust Account) | 15,878 | 7.46 |
SSBTC CLIENT OMNIBUS ACCOUNT | 12,652 | 5.95 |
Mizuho Bank, Ltd | 8,370 | 3.93 |
Asahi Mutual Life Insurance Company | 7,679 | 3.61 |
Yokohama Rubber Co., Ltd. | 7,678 | 3.61 |
Asahi Kasei Corporation | 5,043 | 2.37 |
National Mutual Insurance Federation of Agricultural Cooperatives | 4,765 | 2.24 |
The Norinchukin Bank | 4,000 | 1.88 |
Zeon Corporation Client Stock Ownership Association | 3,847 | 1.81 |
| 95,103 | 44.7 |
*Total number of shares issued at the end of the period: Common stock: 229,513,656 shares
As of Mar. 31, 2024
<Selected Financial Data>
(Units: Million Yen)
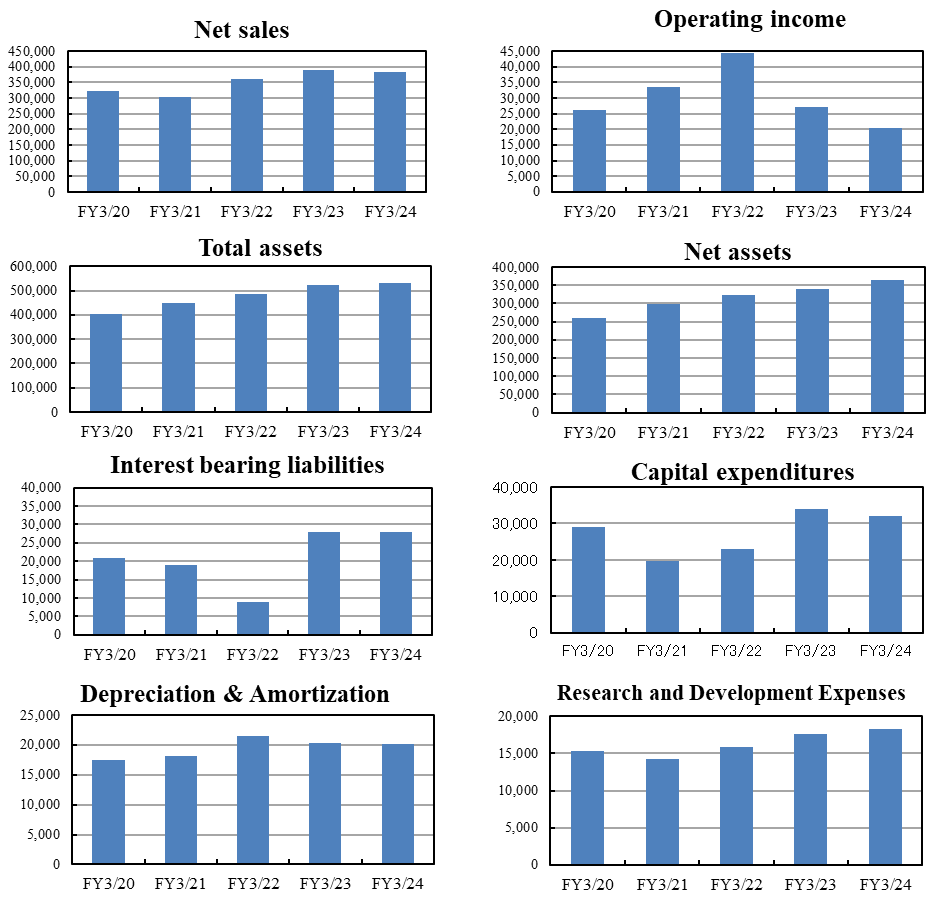
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
Net sales | 321,966 | 301,961 | 361,730 | 388,614 | 382,279 |
Gross profit | 91,911 | 97,552 | 120,358 | 109,643 | 102,510 |
Operating income | 26,104 | 33,408 | 44,432 | 27,179 | 20,500 |
Ordinary income | 28,744 | 38,668 | 49,468 | 31,393 | 26,906 |
Net income | 20,201 | 27,716 | 33,413 | 10,569 | 31,101 |
EPS (JPY) | 92.4 | 126.7 | 153.2 | 49.9 | 147.2 |
DPS (JPY) | 21.00 | 22.00 | 28.00 | 36.00 | 40.00 |
Total assets | 405,131 | 448,821 | 484,660 | 522,868 | 532,254 |
Net assets | 260,358 | 298,246 | 321,836 | 339,308 | 363,729 |
Interest bearing liabilities | 20,960 | 18,960 | 8,960 | 27,960 | 27,960 |
Capital expenditures | 29,088 | 19,645 | 22,902 | 34,045 | 32,135 |
Depreciation & Amortization | 17,448 | 18,154 | 21,469 | 20,382 | 20,123 |
Research and Development Expenses | 15,274 | 14,258 | 15,869 | 17,580 | 18,233 |
<Financial Summary>
|
|
|
|
| (%) |
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
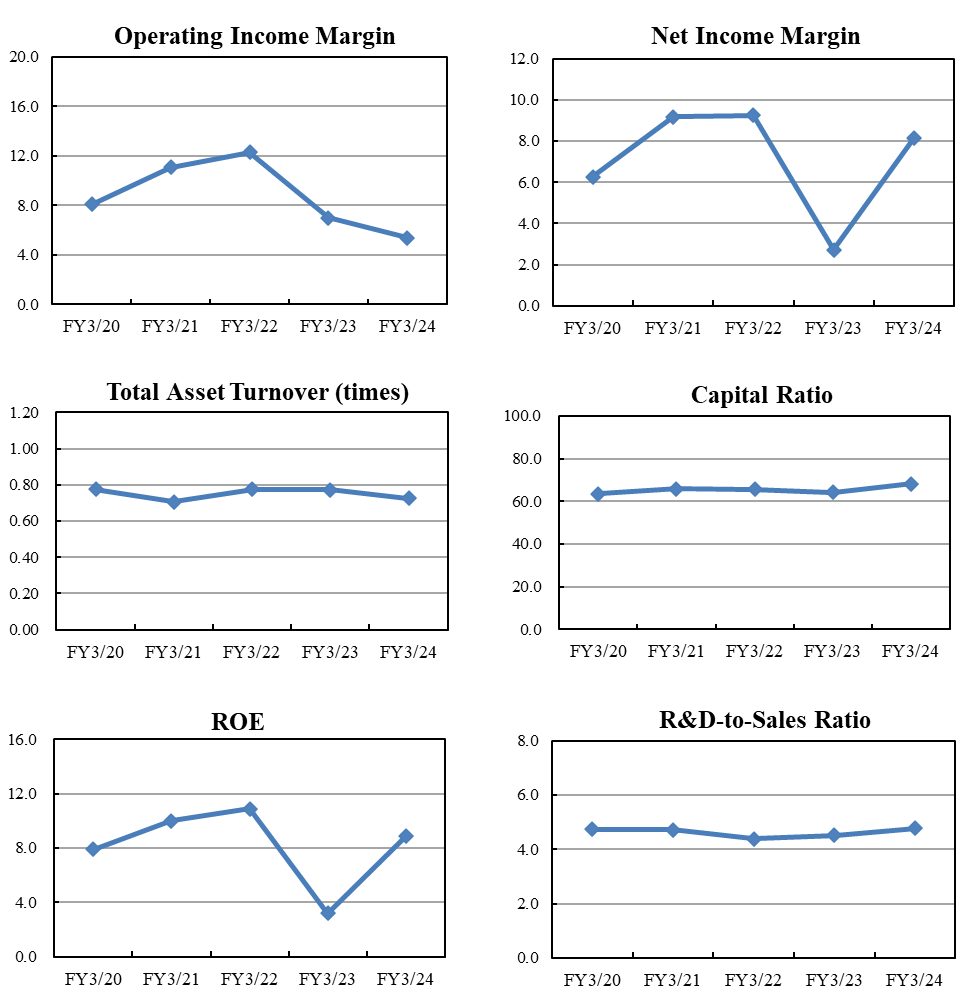
Operating Income Margin | 8.1 | 11.1 | 12.3 | 7.0 | 5.4 |
Net Income Margin | 6.3 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 2.7 | 8.1 |
Total Asset Turnover (times) | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.72 |
Capital Ratio | 63.5 | 65.8 | 65.7 | 64.3 | 68.1 |
ROE | 7.9 | 10.0 | 10.9 | 3.2 | 8.9 |
R&D-to-Sales Ratio | 4.7 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.8 |
<Segment Information>
(Units: Million Yen)
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
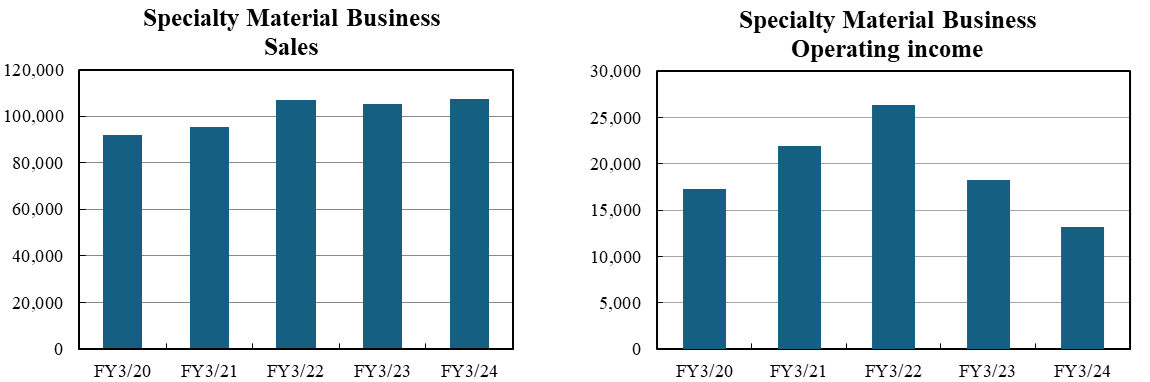
Specialty Materials Business | 91,749 | 95,465 | 106,791 | 105,356 | 107,373 |
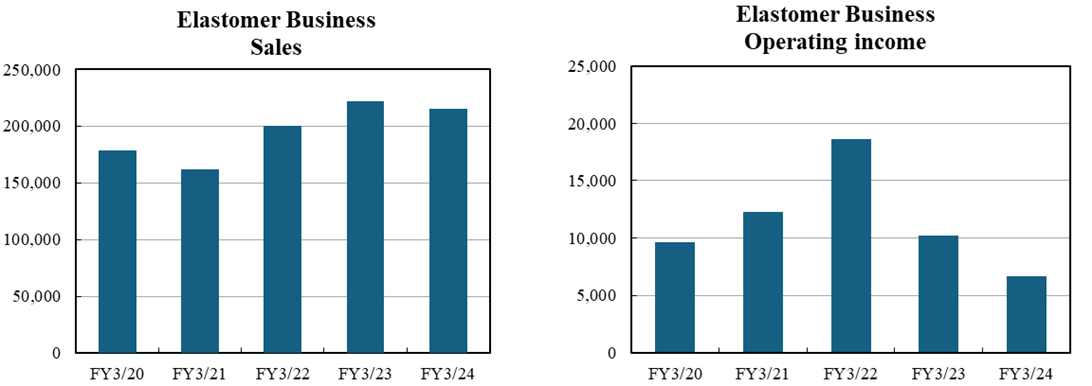
Elastomer Business | 178,847 | 161,626 | 200,566 | 222,230 | 215,286 |
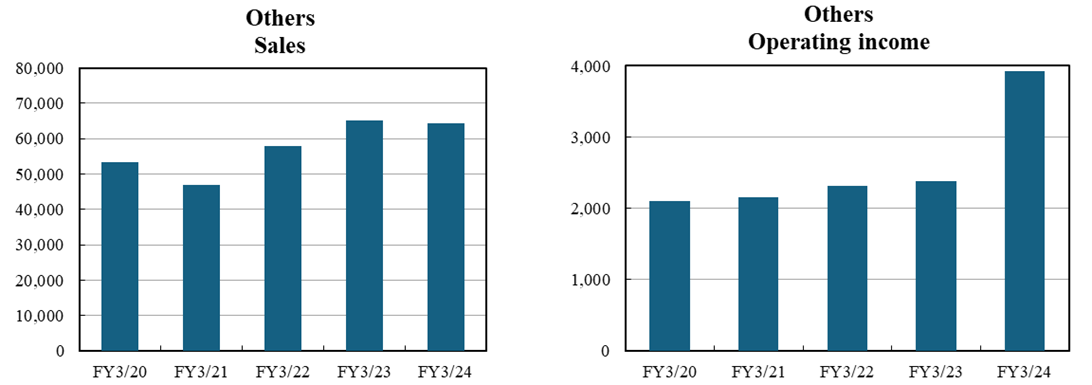
Others | 53,473 | 46,977 | 57,822 | 65,270 | 64,339 |
Eliminations and corporate assets | -2,103 | -2,107 | -3,449 | -4,242 | -4,720 |
Consolidated | 321,966 | 301,961 | 361,730 | 388,614 | 382,279 |
Operating income |
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 17,311 | 21,960 | 26,360 | 18,296 | 13,241 |
Elastomer Business | 9,642 | 12,283 | 18,623 | 10,184 | 6,635 |
Others | 2,098 | 2,156 | 2,318 | 2,381 | 3,927 |
Eliminations and corporate assets | -2,948 | -2,991 | -2,868 | -3,682 | -3,303 |
Consolidated | 26,104 | 33,408 | 44,432 | 27,179 | 20,500 |
Total assets |
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 101,425 | 118,840 | 118,724 | 134,490 | 143,563 |
Elastomer Business | 189,618 | 195,856 | 223,375 | 234,261 | 233,233 |
Others | 31,193 | 30,006 | 42,008 | 41,778 | 49,468 |
Eliminations and corporate assets | 82,895 | 104,119 | 100,553 | 112,339 | 105,992 |
Consolidated | 405,131 | 448,821 | 484,660 | 522,868 | 532,254 |
Depreciation & Amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 6,089 | 7,362 | 10,208 | 9,574 | 10,631 |
Elastomer Business | 8,432 | 8,211 | 8,846 | 8,475 | 7,385 |
Others | 312 | 263 | 243 | 268 | 171 |
Eliminations and corporate assets | 2,616 | 2,318 | 2,170 | 2,065 | 1,935 |
Consolidated | 17,448 | 18,154 | 21,469 | 20,382 | 20,123 |
Capital Expenditure |
|
|
|
|
|
Specialty Materials Business | 17,965 | 10,111 | 10,596 | 18,220 | 16,382 |
Elastomer Business | 7,792 | 7,440 | 9,493 | 8,527 | 12,013 |
Others | 95 | 47 | 291 | 764 | 436 |
Eliminations and corporate assets | 3,236 | 2,047 | 2,521 | 6,534 | 3,304 |
Consolidated | 29,088 | 19,645 | 22,902 | 34,045 | 32,135 |