ESG Bridge Report:(2317)Systena vol.1
 President & Representative Director Kenji Miura | Systena Corporation (2317) |
 |
Corporate Information
Exchange | TSE Prime |
Industry | Information and communications |
President & Representative Director | Kenji Miura |
Address | 14F・16FShiodome Building 1-2-20 Kaigan, Minato-ku, Tokyo |
Year-end | March |
URL |
Financial Information
Net Sales | Operating Income | Net Income | Total Assets | Net Assets | ROA | ROE |
76,940 million yen | 9,713 million yen | 7,232 million yen | 54,038 million yen | 38,601 million yen | 19.3% | 20.0% |
*Results in the fiscal year ended March 2024. Net income means net income attributable to shareholders of the parent company. ROA stands for return on assets. ROE stands for return on equity.
Table of Contents
1. Company Overview
2. Interview with the Top Executive
3. Challenges, material issues, and initiatives
4. Financial and non-financial data
<For Reference>
(1) Regarding ESG Bridge Report
(2) Regarding “Yanagi Model”
1. Company Overview
Systena Corporation was founded, when System Pro Corp. absorbed Katena Corp., which was an equity-method affiliate, on April 1, 2010. It is cultivating new domains by operating the business that fuses the former System Pro’s technologies, know-how, and open technologies for designing, developing, and testing mobile terminals and the financial knowledge and infrastructure technologies of the former Katena Corp. It forms a corporate group with 8 consolidated subsidiaries and 3 equity-method affiliates.
【1-1 Management Philosophy】
They uphold the following management philosophy (philosophy) and standards of conduct (value).
Management Philosophy (Philosophy)
Through heartfelt work, By loved by customers, Be family to society, And put the energy in Japan's future!
Systena Corporation will become an IT company, representing Japan and contribute to the development of the global economy.
We will become essential to our customers and society, and contribute to the development of the Japanese and the global economy.
Standards of conduct (Value)
Cultivate a spirit of hospitality, hone the skills of manufacturing and build a body to go the distance.
If I work hard, there will be people who will be happy.
Our conduct is governed by a desire to cultivate a spirit of treating important people with hospitality, honing the skills required to make high quality goods, building our bodies (our own bodies and that of the organization) to swiftly respond to customer needs,This is our approach to work.
【1-2. Management policy】
The management objective of the Systena Group is “to become one of Japan’s leading IT companies and support the Japanese economy from the ground up!” To achieve this, the Group embraces the basic policy of balanced management, controlling the conflicting qualities of “destruction and creation,” “stability and growth” and “maintenance and innovation” in the appropriate balance while continually placing the axis of management at the central point of the pendulum.
Their target management indicators are stable and high dividends, a high return on equity and a high ratio of operating profit to sales. To achieve these targets, it will aim to establish a high earnings structure consistent with a basic management policy.
【1-3. Business description】
The business of Systena Corporation is classified into the Solution Design Business, the Framework Design Business the IT Service Business, the Business Solution Business, the Cloud Business, the Overseas Business, and the Investment & Incubation Business. Involving all group companies, they offer comprehensive solution services for planning, designing, developing, installing, and maintaining systems and giving user support, including the development and quality check of software for automatic driving and in-vehicle systems, social infrastructure systems, online business systems, IoT-related systems, robots, AI, and mobile devices, the development of systems for financial institutions, system operation, help desk management, the sale of IT products, system integration, the provision of cloud services, and the development of game content.
◎Solution Design Business (accounting for 27.6% in FY 3/24)
The company concentrates its managerial resources on five business categories; “in-vehicle” items such as automatic driving technology and telematics where its know-how nurtured through the development of mobile terminals can be utilized, “social infrastructure” in the fields of electric power, transportation, aviation, space, defense, etc., “Internet business” for communications carriers, e-commerce, education, e-books, etc., “products,” including smartphones, home appliances, and robots, and “DX services,” including workflow and order receipt/placement systems. In every category, the company is swamped with inquiries about the development, testing of IoT-related systems and services. In addition, Systena Vietnam Co., Ltd., which is an overseas affiliate, functions as an offshore foothold for developing, testing, evaluating, maintaining, and operating software, handling all kinds of IT services, and so on. Clients include telecommunications carriers, telecom equipment manufacturers, automobile manufacturers, Internet business enterprises, etc.
◎Framework Design Business (accounting for 9.0% in FY 3/24)
Systena Corporation develops financial systems and foundational systems for not only life and non-life insurance companies, but also banks inside and outside Japan. As for life and non-life insurance tasks, the company has developed solutions for dealing with a broad range of tasks, including information management, contract management, insurance premium calculation, agency business, and sales management. In addition, the company has plentiful experiences of development, including the adaptation to the mainframe for banking business and the development of systems for sales offices and outward channels in the open system field. Previously, their tasks were mostly the development and operation of financial systems, but the projects for developing and operating public and corporate systems are increasing. They are promoting cross-selling to clients of two businesses through the linkage with the IT Service Business and the Business Solution Business, and pursuing financial systems and applying them to other fields through the linkage with the Solution Design Business for solutions for smartphone apps, web apps, etc. like the Solution Design Business section, Systena Vietnam Co., Ltd. is functioning as an offshore foothold.
◎IT Service Business (accounting for 23.8% in FY 3/24)
Systena Corporation operates and maintains systems and networks, and offers IT outsourcing services including help desk operation, user support, data inputting, and large-volume output. Clients are mainly electric-appliance manufacturers, financial institutions, foreign-affiliated enterprises, and public offices.
◎Business Solution Business (accounting for 37.0% in FY 3/24)
The company sells IT products including servers, PCs, peripheral devices, and software, to enterprises and integrates systems. The company is shifting business model from selling hardware to offering services. The company aims to expand its business and improve its added value by meeting the changing demands from ownership to usage (cloud, etc.) in cooperation with the IT Service Business section, etc. Clients are mainly electric-appliance manufacturers and foreign-affiliated enterprises.
◎Cloud Business (accounting for 2.7% in FY 3/24)
The company offers services ranging from the support for installation of cloud services to the provision of apps. For example, it offers cloud services of the Systena version of groupware combined with “Cloudstep,” which was developed jointly by the company and “Google Workspace”, “Canbus.,” a cloud database service, which was launched in May 2017, and “Web Shelter,” an anti-phishing solution for smartphones. It currently specializes in the public cloud, but it is also preparing for offering the private cloud service. “Cloudstep” is a collective term including business applications for improving the usability of cloud services, such as “Google Workspace”, and management tools for administrators. Clients include medium to large-sized companies that conduct general business, etc.
◎Overseas Business (accounting for 0.2% in FY 3/24)
The U.S. subsidiary operates two core businesses; one is the support for development and testing mobile and communications-related products, and the other is the researching on trends of the latest technologies and services and incubation in the U.S. The Vietnamese subsidiary is recognized as an offshore foothold that develops, tests, evaluates, maintains, and operates software, and handles all kinds of IT services. Clients include Japanese enterprises, American enterprises, telecommunications carriers, telecom equipment manufacturers, etc.
◎Investment & Incubation Business (accounting for 0.2% in FY 3/24)
GaYa Co., Ltd. develops game content for smartphones, offers the contents to leading SNS websites and undertakes the operation of video games developed and released by other companies.
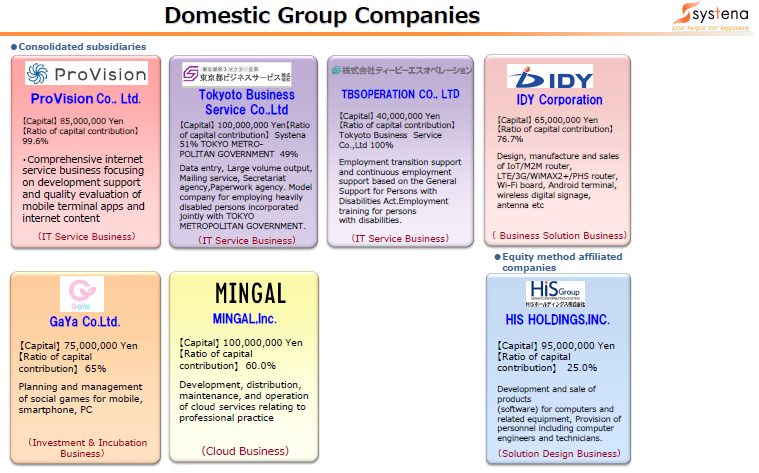
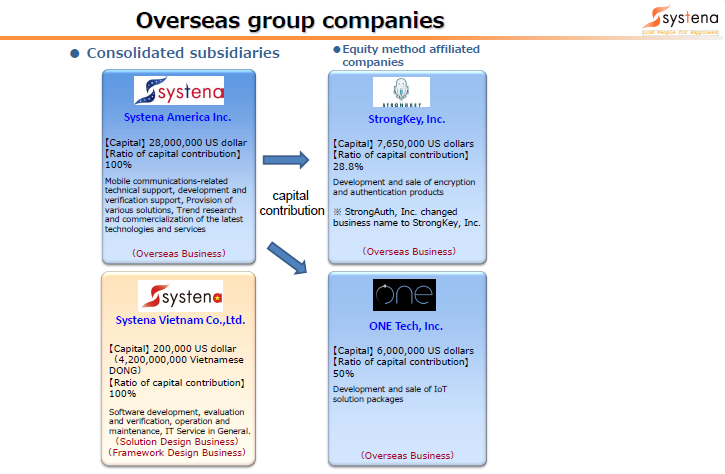
【1-4. Group companies】
The Systena Group is composed of 12 Systena Corporation, 8 consolidated subsidiaries (6 domestic and 2 overseas ones) and 3 equity-method affiliates (1 domestic and 2 overseas ones).
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
(Taken from the reference material of the company)
【1-5. Features, strengths, and measures for improving competitiveness】
As Systena operates a broad range of businesses, the following sections describe the features, strengths, competitive advantages, and measures for enhancing competitiveness of each major business.
(1) Solution Design Business
① Provision of solutions to a broad range of customers. Exertion of advantages of the proposing capability in cooperation with other business sections
By taking advantage of the know-how and experiences accumulated in long-term development of mobile terminals, the company develops and examines systems and services in various fields, including “in-vehicle devices” and “social infrastructure,” while utilizing IoT and AI. This business is highly evaluated by a broad range of clients, including about 100 large companies and about 300 small and medium-sized enterprises. Their capability of meeting diverse needs for the sale of IT devices, the development of systems, and maintenance & operation, which accompany the provision of solutions, in cooperation with other business divisions complements the advantage of the proposing capacity of the Solution Design Business department.
② For enhancing competitiveness
While executing the corporate social duty to create jobs, the company keeps recruiting new graduates stably in order to pass down and further foster their corporate culture.
The company actively conducts education for making employees fresh out of college competent, visualizes information on human resources by utilizing in-house tools for streamlining business operations, sets goals, evaluates personnel according to the degree of achievement, and carries out questionnaire surveys on the satisfaction level of employees to improve employees’ engagement and strengthen human capital. Other business sections, too, are considering the adoption of the in-house tools.
They aim to increase female employees at managerial positions, for developing a working environment in which female development engineers can work comfortably so that their meticulous trait can be utilized further.
(2) Framework Design Business
① Linkage between application development and infrastructure construction
In order to respond to complex needs and technological trends, they are enhancing the linkage between application development and infrastructure construction. Regarding application development, their forte lies in business knowledge and project management skills, which have been nurtured through over 40 years of mission-critical system development. Regarding infrastructure construction, their strength is the capability of using cutting-edge technologies in processes ranging from the establishment of a cloud environment to the designing of migration plans. By linking the strengths in the two fields and developing systems in a one-stop manner, the company earned high recognition among clients in not only the financial field, but also the public field and the corporate field.
② Operation of a DX lab
In order to train personnel and improve their skills to handle cutting-edge technologies, they operate a DX lab. The company’s engineers used to be dispatched to client companies and stationed there for developing systems in most cases, but remote work became common amid the COVID-19 pandemic, so the lab of the company is promoting team development with the aim of improving quality and accumulating know-how. This lab makes it possible to flexibly offer resources to clients and helps improve the productivity of each project by expanding the manageable range of leaders and enabling the mutual follow-up of engineers.
③ For enhancing competitiveness
They engage in active recruitment and the strengthening of their educational system. They concentrate on not only the improvement of technical skills, but also having engineers learn their principles of action through practical projects. In system development projects, the style of “co-creation” with clients became common, so the most important point for engineers is whether or not they can voluntarily think and take action. Senior employees serve as mentors, educating engineers to nurture the mindset as engineers. The young employees in the DX lab can receive well-designed follow-up programs easily. This improves retention rate, so half of employees fresh out of college belong to the lab.
(3) IT Service Business
① One of a few enterprises that offer support after installation
The number of enterprises that offer support after the development and installation of a system or the sale and delivery of equipment among system developers is limited. The IT management business department always supports around 200 client companies, and is highly evaluated by clients, because they can receive support even after installation on one-stop basis. In the fiscal year ended March 2024, the company received orders from about 50 new clients by the end of the third quarter, and about 10 clients out of them placed orders based on the introduction from other business departments. This indicates the synergy among businesses.
② Mainly female employees who do not have experience in the IT field attend to clients at a high level of quality.
This business department aims to “solve clients’ issues using employees with the spirit of hospitality.” The ratio of female employees as of the end of the fiscal year ended March 2024 was 70%, outstandingly high among all business departments, but about 90% of over 200 mid-career workers who joined the company in the fiscal year ended March 2024 have no experience in the IT field. The company recruits personnel who have acquired excellent interpersonal communication skills through the jobs of attending to customers or marketing in the fields of aviation, hotels, department stores, etc. and makes them obtain IT skills through effective training. With such personnel, the company offers high-level face-to-face customer services.
In April 2024, female employees were appointed as heads of the “IT infrastructure business department” and the “PMO service business department” for the first time.
③ For enhancing competitiveness
As digital transformation (DX) progressed, a variety of tools were released. Accordingly, they consider that it is necessary to strengthen the functions like a project management office (PMO), which is a system for supporting the management of each project in a cross-sectoral manner, in addition to conventional IT support. While continuing the above-mentioned high-level customer services, the company started recruiting personnel who aim to realize a PMO or flourish by utilizing more advanced IT technologies.
(4) Business Solution Business
① Organizational capabilities for attending to clients in a speedy manner
The Business Solution Business department sells about 2 million IT devices, etc. of about 1,200 makers and offers about 150 services to about 6,000 clients. Approximately the same number of assistants as marketing staff members belong to the company, to share the statuses and information of a broad range of clients as an organization. Assistants are not temporary workers whose employment period is limited, but all of them are full-time employees, so that knowledge can be shared.
According to the questionnaire survey on the customer satisfaction (CS) level, which is conducted every six months, many respondents highly evaluate “the speed of in-company response” and “swift proposals.” Such organizational capabilities increase the customer satisfaction level.
② For enhancing competitiveness
In the IT industry, which is becoming more complex, as the shift to cloud computing, etc. are progressing, it is forecast that marketing staff will need to have expertise of engineers, so they are developing an environment where employees can obtain qualifications and study new products and services through e-learning. In addition, they will concentrate on the cooperation with external business partners.
Assistants who take important roles in this business department are all female employees. The company has developed employment systems for maternity leave and childcare, with the aim of realizing a working environment where women can flourish. In addition, they have formed a creative sales promotion (CSP) team, which further backs up the work of assistants. For example, the CSP team manages the renewal of license contracts of clients, so that assistants can concentrate on customer services further, contributing to the improvement in quality of services.
【1-6. Flowchart of value creation】
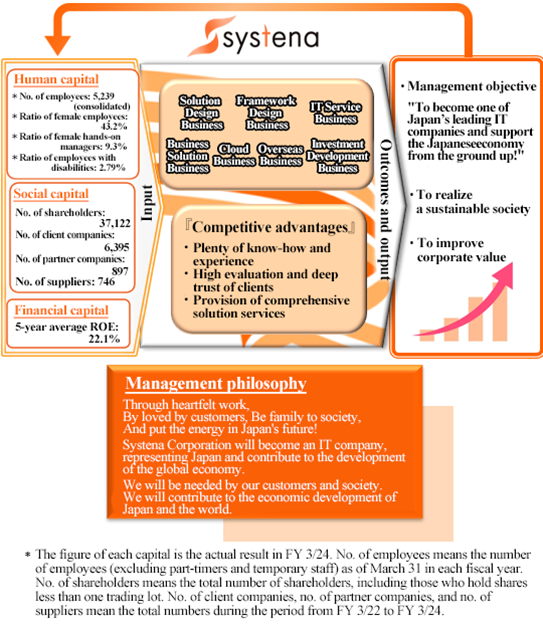
The Systena Group operates a broad range of businesses based on competitive advantages, such as “plenty of know-how and experience regarding ICT” and “high evaluation and deep trust of clients.” While upholding the management objective: “to become one of Japan’s leading IT companies and support the Japanese economy from the ground up !,” the company aims to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society and the increase in corporate value.
2. Interview with the Top Executive
●Social responsibility and the significance of social existence
Q. In recent years, as the entire society has been striving for sustainable growth, emphasis has been placed on the philosophy, mission, and significance of the social existence of each company, which is a key player in this endeavor.
To begin with, please tell us about your company's management philosophy and the significance of its social existence.
Our company's management philosophy is: “Through heartfelt work, By loved by customers, Be family to society, And put the energy in Japan's future! Systena Corporation will become an IT company, representing Japan and contribute to the development of the global economy.”
IT is an essential social infrastructure for the world. As an IT company, we strongly believe that the significance of our social existence lies in serving many customers in a wide range of industries and business categories, meeting their requests, and contributing to the development of not only the Japanese economy, but also the global economy. We are also strongly aware that our roles and responsibilities have been increasing in recent years.
●Business model, characteristics, strengths, and competitive advantages
Q. What are the characteristics, strengths, and competitive advantages of your company?
We are engaged in seven businesses centered on Solution Design, Framework Design, IT Services, and Business Solutions. I believe that we are the only independent, medium-sized corporate group that has been able to build such a diverse business portfolio.
In addition, each of our businesses has been entrusted with important projects by the Japanese government and has received orders for extremely high-level projects from top-ranking companies that are driving the Japanese economy. We believe that the fact that we have built deep and trusting relationships with first-class customers in a wide range of business domains is a significant competitive advantage for us.
●Initiatives for material issues
Q. This is the first time that your company has selected 10 material issues (see "3. Challenges, Material Issues, and Initiatives").
Among these, I would like to ask your opinion on the material issues that are particularly important for the sustainable growth of your company.
First, I would like to talk ask about “human capital.”
Could you please tell us again how important it is to "strengthen human capital" in order to improve your corporate value, and what initiatives you are taking to achieve this? In what ways has the strengthening of human capital been noticeable over the past few years?
Concept on human capital
Needless to say, employees and human capital are the most important resources for us as an IT company, and strengthening them will lead to the improvement of our corporate value and the resolution of social issues.
Since the company was established, we have considered our employees as family members and fellow employees who live together. Now that we have grown into a corporate group with approximately 6,000 employees, we are keenly aware of the importance of human capital and our wish to nurture employees with care. At the same time, we believe it is necessary to further refine our venture spirit, even though we have grown in size.
I always want my employees to become “people who can perform their duties.”
"People who can perform their duties" generally refers to people who are good at time management or who achieve high figures in sales; however, I believe it refers to people who can help others and are appreciated by those around them.
We want to be a group of people who receive comments such as “thank you” and “want to work with you again” from customers, partner companies, and colleagues. We send out such messages on various occasions.
Education and training in each business division are based on this concept.
Operation of a DX lab to strengthen human capital
As an example of how we are strengthening our human capital, I would like to talk about the operation of the DX Lab in the Framework Design Business.
The DX Lab is an initiative to develop human resources and improve technical capabilities for advanced technologies. Until now, system development has conducted mainly by visiting customers at their offices, but we are now promoting development by teams in the lab to improve quality and accumulate know-how. The operation of the lab enables us to provide flexible resources to our customers, expand the scope of leader management, and improve project-related productivity through mutual follow-up among engineers.
For younger employees, working in the lab makes it easier for them to receive in-depth follow-up from senior employees, which leads to a higher retention rate.
Our basic stance is to stay close to our customers and provide output that satisfies them. However, there are some employees who are highly skilled and excellent technicians, but are not good at communicating with customers. We will continue to focus on the operation of the DX Lab as a way of creating an environment where such employees can maximize their abilities.
Evaluation system
I have issued instructions to set up specialist positions in all business segments.
I think one of the reasons why I joined this company is the opportunity to participate in attractive projects unique to the company and exercise my skills. Some employees consider it more rewarding to be involved in projects on the ground than to be in a managerial position. Therefore, a system is needed to appropriately evaluate their contribution as specialists in such projects, even if they do not become managers.
We plan to create a system in about a year and then rebuild it to keep up with the ever-changing times.
Activities of Female Employees
Although the situation differs from division to division, the IT Management Division, which aims to "solve customer issues through employees with a spirit of hospitality," has the highest percentage of female employees among all divisions, which is 70% as of the end of March 2024. Female employees are particularly active in this division.
Under the Trainer Development Project, which trains certified trainers who provide training to external customers, the Design Management Promotion Office, whose general manager and assistant manager are both female employees, is responsible for the management and supervision of this project. Out of a total of 12 instructors, 11, including three leaders, are female.
Furthermore, in the Training Development Project, where certified trainers develop and commercialize training content and seminars customized to the needs of the training market, the general manager and leader are both women, and two out of the three development staff who actually run the courses are female employees.
With this groundwork laid for women to play an active role, the first female division heads were appointed in April 2024 in the “IT Infrastructure Services Division” and the “PMO Services Division.”
Approximately 90% of mid-career employees in this division have no experience in the IT industry. We recruit personnel with outstanding interpersonal communication skills who are engaged in customer service and sales in industries such as airlines, hotels, and department stores. We also provide high-level face-to-face customer support by helping them acquire IT skills through extensive training.
Both of the division managers were both mid-career recruits from different industries and were appointed as team leaders in about one year. After that, they spent five to six years working on projects and gradually accumulating on-the-ground experience as managers of larger teams. This time, each of them was given the important position of managing about 300 members.
With the progress of digitalization and the emergence of various tools, the Project Management Office (PMO), a system that provides cross-sectional support for the management of individual projects in addition to conventional IT support was newly established to strengthen the functions of the Project Management Division. The appointment of a female employee as General Manager of the PMO Service Division is an excellent example of the company's initiatives to strengthen human capital.
We offer a variety of educational and training programs. Of course, these programs are the foundation of their growth. However, more than that, the creation of an environment and a corporate culture that encourages them to think outside the box if it is something that makes customers happy is making a significant contribution.
The company has only prepared the stage; the rest is up to each individual's awareness and action, leading to results, which in turn motivates them to take the next action and achieve further results.
Both of them, who have become division managers, have expressed their happiness, saying, “We are grateful and blessed for the environment, and we would like to contribute as much as we can.”
This is truly a process of strengthening our human capital as a venture company.
Q. Next, what is your perception of the environmental challenges?
Based on our basic philosophy of contributing to the preservation of the global environment, we have established an "environmental policy" to reduce environmental impact. By implementing environmental preservation measures in accordance with ISO 14001 in-house, we are committed to making effective use of resources and reducing recycling. At the same time, we hope to contribute to resource and energy conservation at our customers' companies through business activities that promote the use of IT.
In the current fiscal year ending March 31, 2025, we will begin measuring emissions of greenhouse gases according to Scopes 1, 2, and 3. We plan to set a target for reducing emissions of greenhouse gases by the end of the next fiscal year, ending March 31, 2026, and start activities to achieve this target.
We are currently researching and examining specific initiatives to contribute to the realization of carbon neutrality by 2050, as announced by the Japanese government. Although we are still in the early stages, we will act with a strong awareness of our responsibility as a company.
Q:What are your thoughts and initiatives on corporate governance?
We aim to strengthen relationships of trust with all stakeholders and maximize profits for the company as a whole. At the same time, we will strengthen corporate governance to ensure sound management and thorough compliance.
At present, three of the nine directors are independent external directors. They are securities analysts, former bankers, and lawyers who provide advice and suggestions as external experts.
At present, the company has one female director. Keeping in mind the numerical target set by the Tokyo Stock Exchange to increase the ratio of female directors to 30% or higher by 2030, we will promote the establishment of a corporate governance system that places even greater emphasis on diversity both internally and externally within the company.
●Strategies for future growth
Q. Next, what are your directions, strategies, and challenges for future growth?
Since being listed on the stock exchange, we have been aiming to become a robust company and have focused our management on profit.
In the future, while continuing to focus on profitability, it is necessary to pursue value as well by creating new commercial products through upfront investment and incorporating services in areas we have not worked in before through M&As.
If All Systena is able to provide customers with new added value in areas that were not previously addressed from the perspective of profitability, I believe we will be able to please our customers even more than before and improve our corporate value. Therefore, I believe that the realization of synergies among the business divisions is an important theme.
For entering new areas, collaboration with the appropriate business partners is essential, we are considering investing in capital and business alliances.
One of the challenges in realizing the growth strategy is the development of human resources.
In particular, the level of requirements of Japan's top-runner customers is becoming increasingly sophisticated, so it is essential to have the ability to respond firmly to these requirements.
At the beginning, I said, "Our significance in social existence is to stand by our customers, respond to their needs, and contribute to the development of not only the Japanese economy, but also the global economy." However, we must clearly show our customers that we are true companions in the true sense of the term.
It will not be an easy challenge to not only improve the level of technology, but also reform the business structure and change the way employees think. However, we will achieve this by demonstrating our entrepreneurial spirit.
●Message to stakeholders.
Q. Thank you for sharing your various views. Finally, do you have a message for stakeholders?
I believe that Systena is now in the third stage of its history, following the first stage, at which the company was established and built up a strong corporate structure, and the second stage, at which it expanded its business domains through the merger with Catena.
At the same time as further strengthening what we have created so far, we will develop new products and services, as I mentioned earlier, despite the uncertain environment, and make ourselves a company that is more customer-focused than before.
IT has become an indispensable part of society and industries. Under such circumstances, we will reaffirm our social significance, improve corporate value, resolve social issues through business expansion, and aim to be a company that all stakeholders can say "thank you" to and would like to receive continued support from.
3.Challenges, material issues, and initiatives
The challenges and material issues Systena Corporation has identified so far are as follows. When identifying material issues, the company has also conducted interviews with external parties.
Challenges | Material Issues |
Environment | Various initiatives to solve environmental issues |
Social Capital | Security of data including customer information |
Social contribution | |
Human Capital | Improving employees’ job satisfaction, and building training and development programs |
Health and safety of employees | |
Diversity and involvement of employees | |
Business Models & Innovation | Initiatives and innovation to improve competitiveness |
Supply chain management | |
Risk Management and Governance | Expansion of the corporate governance system |
Risk management |
*Produced with reference to the SASB Materiality Map, etc.
[Basic understanding and promotion system for ESG challenges]
<Basic understanding>
The company’s management philosophy is to contribute to the development of the Japanese economy and thereby help create a spiritually rich society. Based on this management philosophy, the company aims to realize a sustainable society and increase its corporate value.
<Governance>
The company's corporate governance also includes its views on sustainability, and based on the basic policy on corporate governance, it is working on similar initiatives to promote ESG. In order to respond to rapid changes in the business environment and improve management efficiency, the company is promoting speedy management through quick decision-making. To achieve this, the director in charge reports directly to the President & Representative Director and carries out continuous improvement activities based on instructions received.
<Risk management>
The company has adopted the same system for sustainability risk management as for corporate governance risk management. The director in charge appropriately monitors the risk status across the entire group to ensure that the company's sustainability promotion activities are in line with the times, and works to develop and improve promotion systems and frameworks.
<Strategies, indicators and targets>
The company aims to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society by promoting business activities that continuously improve the satisfaction of three parties: customers, shareholders, and employees.
[3-1 Material issues regarding the “environment”]
◎Various initiatives to solve environmental issues
Based on its basic philosophy of contributing to global environmental conservation, the company has established an “environmental policy” to reduce and limit environmental impact, and is committed to the effective use of resources, conservation and recycling through the implementation of environmental conservation measures in accordance with ISO14001 within the company, while contributing to the conservation of resources and energy at client companies through business activities that promote IT.
<Environmental Policy>
Systena Corporation recognizes that the global environment is a shared asset of all humanity and an important gift borrowed from the future. Based on this recognition, we work to conserve and make effective use of resources, and reduce CO2 emissions.
Through our business of providing IT solutions, we contribute to reducing the amount of resources consumed by society and improving environmental efficiency.
1. | We will work continuously to reduce energy usage, save resources and reduce waste. |
2. | We will contribute to improving the environmental efficiency of society through the sale of IT products and provision of IT solutions. |
3. | We will set environmental objectives and goals, regularly review and revise our internal audit and environmental management systems, and work to make continuous improvements, prevent pollution and reduce CO2 emissions. |
4. | We will work to raise the environmental awareness of our employees through environmental education and awareness spreading activities, and enable individual employees to contribute to environmental conservation on an everyday basis. |
5. | We will comply with legal regulations, bylaws and other requirements. |
<Promotion System>
The company has established an “ISO Secretariat” to promote in-house education, awareness-raising activities, comprehension tests and other company-wide educational activities related to environmental management.
<Major initiatives>
①Initiatives to address climate change
The company plans to begin measuring greenhouse gas emissions of Scopes 1, 2, and 3* in the fiscal year ending March 2025, and to set greenhouse gas emission reduction targets by the end of the fiscal year ending March 2026 and begin activities accordingly.
* About Scopes 1, 2, and 3
Scope 1: Direct greenhouse gas emissions by the company
Scope 2: Indirect emissions from the use of electricity, heat, and steam supplied by other companies
Scope 3: Indirect emissions other than Scopes 1 and 2 (emissions by other companies associated with business activities)
②Initiatives through business
The IT solutions the company provides help its clients improve their work efficiency and save energy by reducing working hours. In addition, by supporting the digitization of clients' work environments, the company promotes paperless operations, thereby helping reduce waste and slow down global warming caused by deforestation.
③Internal initiatives
The company is working on reducing environmental impact based on the ISO 14001 environmental certification and shares the status of in-house reduction of power consumption, paper, and waste (including sorting).
<Major initiatives>
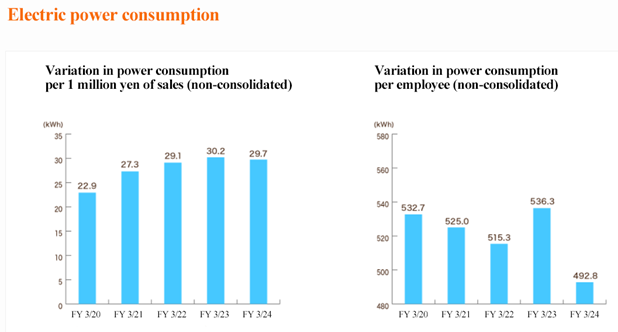
Electric power | Seeing the increase of employees, the company has taken energy-saving measures such as moving into an intelligent building with excellent environmental performance, installed high-performance, energy-efficient equipment such as multifunctional copiers and servers, encouraging employees to switch off lights and air conditioners when not in unoccupied areas and after using meeting rooms, setting air conditioners at energy-efficient temperatures, setting PC monitors to save power, and encouraging Cool-biz, which is casual business attire. |
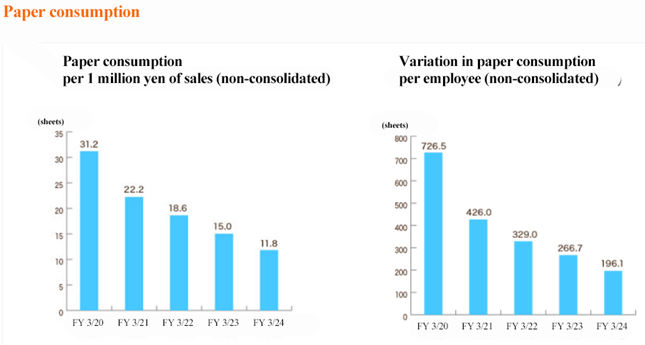
Paper | The company promotes the use of 2-in-1 and 4-in-1 printing for printed materials used within the company whenever possible and has installed projectors or monitors in meeting rooms to promote paperless operations. The company is promoting the computerization of internal procedures, and has developed and is using its own product, “Canbus. (Canbus dot).” The company is working to reduce paper consumption by continually digitizing internal approval documents. |
Waste | The company is working on green procurement, which prioritizes purchasing items that are recyclable or made from environmentally friendly materials. While the company is promoting computerization to reduce waste, waste generated is sorted and disposed of according to the sorting policy set by the building management company of the building in which the company is a tenant, in order to make recycling easier. |
(From the company website)
[3-2 Material issues regarding “social capital”]
(1)Security of data including customer information
The company is deeply involved in the planning, design, and development of new products and services as well as the creation of new technologies and know-how for its clients and is aware of the role it plays in their business strategies and in earning public trust. Based on this awareness, the company has established and complies with the “Basic Information Security Policy” and the “Personal Information Protection Policy” to prevent the leakage of information assets, including personal information and other information required to be protected by law, and to ensure thorough management of such assets.
<Basic Information Security Policy>
01.Compliance with Laws, Regulations and Company Regulations | Systena shall comply with laws, regulations and company regulations regarding information security in order to protect all information assets in its possession. |
02.Building an Information Security Management System | Systena shall appoint information security management supervisors and organize an information security committee in order to clarify responsibility for protection of information assets and manage information security constantly and assuredly. |
03.Establishment of Internal Regulations Regarding Information Security | Based on this policy, Systena shall establish company regulations that that reflect information security-related laws and regulations, display a clear policy regarding the handling of all information assets, and make its strict attitude toward information leaks, etc., thoroughly known. |
04.Information System Management | Systena shall establish an organization relating to information systems, and maintain and manage information systems to prevent the occurrence of incidents including unauthorized access, leaks, tampering, destruction, erasure, or interference with use of digital / electronic information assets. |
05.Development and Enhancement of Auditing System | In order to verify that this policy, company regulations and rules, etc., are being complied with, Systena shall prove compliance with this policy through the regular performance of internal audits. |
06.Information Security Training | In order to maintain and increase the level of information security, Systena shall continuously conduct necessary training to increase the level of awareness with regard to information security management, relevant laws, regulations and company regulations and ensure through compliance. |
07.Protection of Personal Information | Personal information is an extremely important form of information, and protecting it is an important social responsibility. Based on its understanding of this, Systena shall establish a separate Protection of Personal Information Policy and Protection of Personal Information Manual. |
08.Scope of Application | The scope of "information assets" to which this policy applies shall include all information learned by Systena in the course of business operations, and the policy shall also apply to all company officers, employees, and employees of affiliate companies and business process outsourcing partners who handle those information assets. |
09.Provision of Products | Systena shall provide IT solutions and IT-related products through methods that offer sufficient care, consideration and peace of mind for customers who use its information systems. |
10.Handling of Clients' Confidential and Personal Information | When engaging in business processes at a client's company premises, Systena shall take all possible measures to ensure compliance with the client's information security rules and appropriate handling of the client's confidential and personal information. |
(2)Social contribution
① Promoting employment of people with disabilities
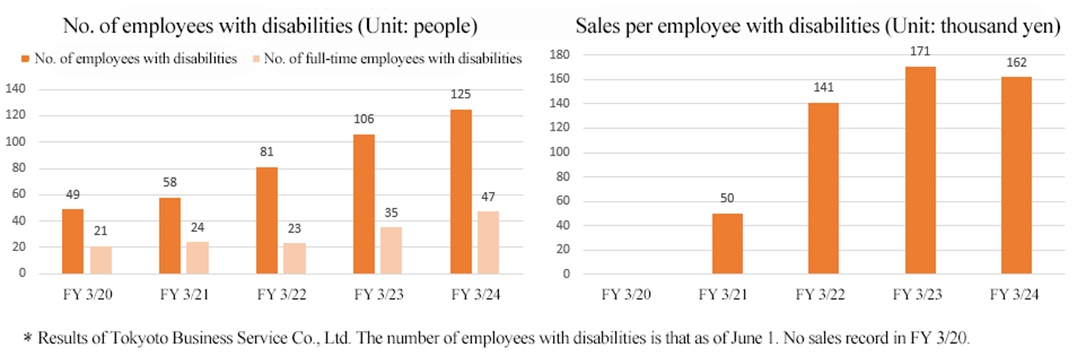
In 1986, a joint venture with the Tokyo Metropolitan Government established TOKYOTO BUSINESS SERVICE CO., LTD., as a model company for the employment of people with severe disabilities.
◎Overview of TOKYOTO BUSINESS SERVICE CO., LTD.
Established in | December 1986 |
Capital stock | 100 million yen |
Shareholders (investment ratio) | Systena Corporation (51%), Tokyo Metropolitan Government (49%) |
Number of employees (as of June 1, 2024) | 585 (including 125 people with disabilities) (consolidated) |
*Main business activities
“BPO Services,” which includes enclosing and shipping, campaign secretariats, scanning solutions, data entry, printing solutions, and marketing research; “IT Support & Services,” which use a variety of administrative and IT skills to predict clients' business needs and provide support to address issues and achieve results that exceed expectations; “Development Solutions,” which solve clients' business issues with solutions using IT technology, such as system construction and introduction of business support tools; and “Employment Consulting Services for People with Disabilities,” which provide comprehensive consulting, recruitment support and training for people with disabilities in order to expand their employment opportunities.
In the area of “Employment Consulting Services for People with Disabilities,” the company provides high-quality consulting services as a leading company in the field of employment of people with disabilities, aiming to create a society in which the active participation of people with disabilities has become the standard, so that the term “active participation of people with disabilities” will no longer exist.
*Business environment
The information and communications industry ranks the lowest among all industries in terms of the actual employment rate of people with disabilities and the percentage of companies that have achieved their targets.
*Currently, the statutory employment rate for private companies is set at 2.5% under Article 43, Paragraph 1 of the Act to Facilitate the Employment of Persons with Disabilities. Employers with 40.0 or more employees must employ at least one person with a disability.
On the other hand, following the revision of the Act for Facilitating the Employment of Persons with Disabilities, the statutory employment rate is expected to rise from the current 2.5% to 2.7% in July 2026. In addition, due to the inclusion of extremely short-time work, restrictions on employment agency services (restrictions on employment agency businesses such as agriculture that only aim to achieve the specified number of disabled employees not involved in the core business), the enactment of the Act for Eliminating Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities, and increased social awareness of CSR and ESG, the playing field for special subsidiaries that are the main employers of persons with disabilities is expected to improve significantly, and the company believes that new action is necessary.
*Basic policy and ideal state
In this environment, the company has set a target of employing 146 people with disabilities in April 2025. In addition, in order to comply with the statutory employment rate and expand opportunities for people with disabilities, the company is working on “recruitment,” “growth,” and “active roles” for people with disabilities from the perspective of “DE&I*.
Field | Target | KPI | |
Recruitment | Diversity | Responding to changes in policies and society, such as higher employment rates, abolition of exclusion rates, and very short working hours | Number of people employed |
Growth | Equity | Creation of added value by developing growth and development opportunities for motivated people with disabilities | Sales per person with disabilities |
Participation | Inclusion | Promotion of activities through a system that makes the most of their strengths and undertake diverse tasks | Number of full-time employees |
* Abbreviation for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion. A state in which differences in gender, age, place of origin, and values are recognized, and each individual is able to maximize his or her abilities.
The company is focusing not only on recruiting talented people with disabilities by disseminating examples of in-house initiatives, but also on expanding sales of consulting services for the success of people with disabilities outside the company, thereby developing a system that can contribute to the realization of DE&I in the entire society.
②Support for sports activities and sports promotion activities
ProVision Inc. has been hiring athlete employees and supports athletes in various sports, including lacrosse, para-alpine skiing, soccer (football), field hockey, and e-sports. The company also supports sports promotion activities as an official partner of Vissel Kobe (soccer [football]) and an official sponsor of Fukuoka Softbank Hawks (professional baseball).
③Other
The company supports the activities of the Japan Guide Dog Association and has continuously supported its guide dog training projects since 2002.
【3‐3 Material issues regarding “human capital”】
<Fundamental recognition>
The company respects the human rights, other rights, and values of all people, prohibits unjust discrimination against based on race, religion, gender, age, sexual orientation, disability, nationality, etc., observes laws and regulations regarding labor, prevents harassment, and engages in the development of a safe, comfortable, people-friendly environment. In addition, they pursue sound business development and appropriate business administration to create new jobs based on regular employment, and provide all employees with opportunities to receive education, undergo training, get promoted, and advance in their careers to produce independent personnel as members of society.
Due to its business structure, the increase of employees is an important matter closely related to business development, so indicators regarding the variations in sales, operating income, and the number of employees are shown in “5. Financial and non-financial data” written below.
(1) Systems for fostering the awareness of employees, promoting them to feel that their jobs are worthwhile, educating and training them
The company has original career path and training systems, so that employees can hone their skills. Considering that it is necessary to have a cycle of learning knowledge through lectures and putting the knowledge into practice, the company holds many high-quality training sessions, including new employee training, study sessions, and lectures on the basics of IT, technologies, novice leaders, management, qualifications, and human skills.
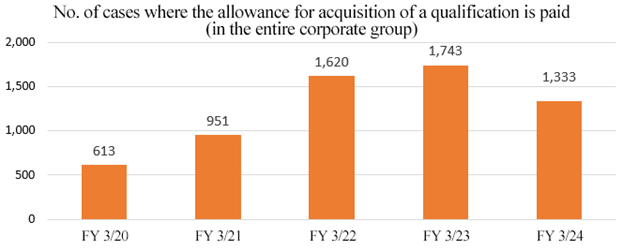
In addition, as a system for supporting personal development, they pay “exam fees and an allowance for qualifications” to employees who have obtained a qualification for supporting the acquisition of necessary knowledge and skills for business, to develop an environment in which employees can maintain their motivation and engage in personal development.
<Concrete measures>
The company operates an optimal education and training system for each business department.
①System for supporting the acquisition of qualifications
For the purpose of supporting the improvement in skills required for business operations, they pay “exam fees and an allowance for qualifications” to employees when they have obtained a designated qualification.
The company operates for each business department.
(Designated qualifications)
Business department | Overview |
IT Management Business department | 250 qualifications, such as qualifications recognized by vendors, including Oracle, Microsoft, Google, and AWS, the certification of the capability of programming with the C language, TOEIC, and Bookkeeping and Accounting Test for International Communication (BATIC) |
Solution Design department | 207 qualifications, such as the certification for information processing engineers, the certification for open technology engineers, qualifications recognized by vendors, including Salesforce, AWS, Microsoft, and Google, and TOEIC |
Framework Design Business department | 80 qualifications, such as qualifications recognized by vendors, including Oracle, Microsoft, Google, and AWS, and the certification for information processing engineers |
Business Solution Business department | 162 qualifications, such as qualifications recognized by vendors, including Oracle, Microsoft, Google, and AWS, and the certification for information processing engineers |
*As of Jan. 25, 2024
The total number of cases of payment of an allowance for qualifications in the corporate group has been increasing steadily.
②Personnel development system
The following sections introduce the “personnel development project” of the IT Management Business department, the “study session” and “preview” of the Business Solution Business department, and the “project for dealing with complaints” in each department.
◎ “Personnel development project”
The IT Management Business department engages in personnel development and the creation of services in a cross-sectoral manner. All processes of the “course for developing trainers” who offer training as a lecturer for external clients have been terminated, and employees who have acquired necessary skills are recognized as “trainers certified by Systena.” Certified employees receive a certificate, and can indicate the title “IT trainer certified by Systena” in their business cards. There are a “project for developing trainers” and a “project for developing training programs.”
(Outline of the project)
*Purposes
・To increase and further develop certified trainers, plan and commercialize new services, expanding the lineup of training services, improve the customer satisfaction level, and grow sales revenue
・To improve the awareness and skills of existing certified trainers
・To improve their technological skills and driving force by utilizing certified trainers
*Details and goals of courses
In the “project for developing trainers,” the company holds training for producing certified trainers for about 8 months. The goal is to enable trainers to flourish as staff representing Systena in a cross-sectoral manner after passing the final certification test and acquire management skills through the development project.
In the “training program development project,” trainers certified by Systena develop and commercialize training programs and seminars according to market needs. The goal is to develop programs and seminars according to needs, catch up on issues from the viewpoints of trainers and planning, and acquire abilities to give proposals and solve issues.
(Outcomes of the projects)
The total number of certified trainers is 113, and 32 trainers out of them have been promoted to managerial posts. In the fiscal year ended March 2024, 23 employees were certified as trainers. Eight new programs have been released.
(Project systems)
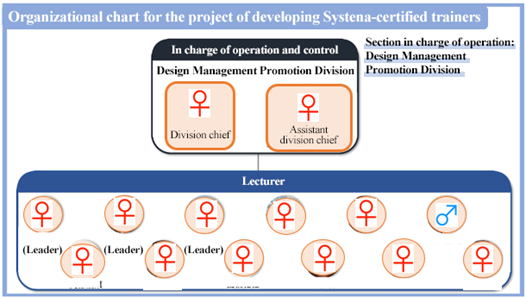
“Trainer development project”
The design management promotion division (whose chief and team leader are female employees) is in charge of operation and management. Twelve staff members (including 11 female ones), including three female leaders, operate the course as a lecturer.
“Training program development project”
Under the supervision of a female manager and a female team leader, three staff members (including two female ones) in charge of development operate the course.
 |
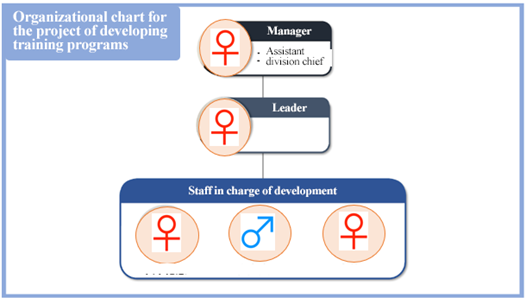 |
The IT management business department has the highest ratio of female employees among business departments, and the female employees in this department show remarkable performance.
(The records are all as of the end of March 2024.)
◎ “Study sessions” and “previews”
The Business Solution Business department holds “study sessions” and “previews” as education for each job category and each issue. “Study sessions” and “previews” are both managed by mainly the sales support division. When new products or services are released, they hold a preview for makers and service vendors inside and outside Japan, and hold a study session to deepen marketing staff’s knowledge of products and share effective methods for giving proposals to clients. In the fiscal year ended March 2024, they held about 90 “study sessions” or “previews.”
◎ “Project for dealing with complaints”
In this project, the company proactively asks clients about their requests to grasp potential requirements and deal with possible complaints before they are made based on the results of interviews. Based on the results of questionnaire surveys on the customer satisfaction level, they appropriately deal with the items that could not satisfy customers enough and complaints written in questionnaire sheets. The Business Solution Business department holds a survey twice a month while the department head organizes it and section chiefs and their superiors participate in it.
(2) Health and safety of employees
An environment in which employees can work healthily is indispensable for establishing an important business foundation so that they can contribute to customers and society through business activities and achieve continuous improvements that would satisfy three parties: customers, shareholders, and employees. Accordingly, they issued “Systena Corporation’s Declaration of Health” and have been promoting measures for maintaining or enhancing the health of employees in cooperation with Systena Health Insurance Society and industrial doctors. The results of these activities were highly evaluated, and the company received the certification of “Excellent Corporations with Health-oriented Business Administration (large-scale business establishments)-White 500,” which was initiated by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, for 4 consecutive years until 2024. In addition, for the purpose of invigorating in-company communication and enhancing solidarity, the company started holding “an interdepartmental tug-of-war” involving over 1,000 employees in 2013, and actively holds a variety of events, supports club activities, and distributes information on exercise. As these initiatives were highly evaluated, Japan Sports Agency recognized the company as “Sports Yell Company 2024” for the fourth consecutive year.
“Systena Health Declaration”
*Improving the health awareness of each and every employee
Aiming to build healthier bodies, we seek to improve the health awareness of each and every employee, such as through anti-smoking activities, activation of exercise-related circle groups and other events, regular communication of information from the company, and linking these efforts on to activities that actively maintain and improve health.
*Improving health through qualitative and quantitative assessments
Systena uses comprehensive health checks, stress checks, questionnaire surveys and other methods to monitor health at both the individual and organizational levels, and leads the way in making suitable improvements.
*Fostering an easy-to-work workplace environment
Systena reduces incidents are inhibiting to health and encourage early response by increasing the awareness and skills of management personnel with regard to the health and care for members of their line. We also work with back-office personnel to promote the creation of sounder, healthier workplace environments by developing conditions that enable casual consultations and consideration of response measures.
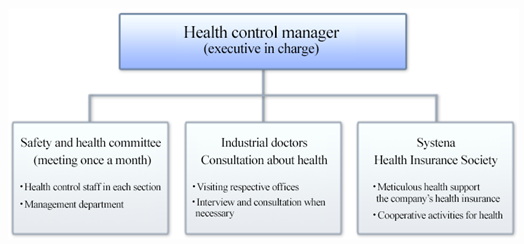
(Health improvement system)
Health-oriented management is promoted by four parties: the executive in charge, who serves as a health control manager, the safety and health committee, which holds a monthly meeting, industrial doctors who receive inquiries about health, and Systena Health Insurance Society, which offers health support.
(Taken from the website of the company)
(Major initiatives for health-oriented management)
・Holding of meetings of the safety and health committee
・To have all employees undergo a health checkup
・Involvement of industrial doctors to increase the ratio of employees who keep a desirable weight (goal: up 10% from the previous year)
・Promotion of specific health guidance
・Immunization against influenza (target immunization rate: 50% or higher)
・Stress check, group analysis, and measures (target stress check rate: 100%; ratio of employees with high stress levels: down 10% from the previous year)
・Improvement in health literacy through regular distribution of health information
・Mental health education for managers
・Enhancement of engagement in work through the streamlining of communication (goal: up 10% from the previous year)
・Regular education for mastering self-care (Target presenteeism rate: down 10% from the previous year)
・To reduce employees on temporary retirement by early finding those who are in bad shape (Target absenteeism rate: down 10% from the previous year)
・Abstention from smoking
・Promotion of sports club activities
・Holding of events, such as tugs-of-war and barbeque parties
・Enhancement of measures, such as the provision of healthy dishes via an in-house storage of healthy foods (Office Okan)
Stress checks are effective for preventing mental disorder. The company makes efforts to develop an environment in which employees can work healthily by having them recognize the status of their stress and sharing reference material on self-care. While the average rate of stress check implementation in the information and telecommunication field is 91.3%, the rate of stress check implementation in the Systena Group is 96%, exceeding the average.
Events are held for all employees, to invigorate communication at workplaces and realize a comfortable working environment. This is highly evaluated by employees.
(3) Diversity and participation of employees
To promote diversity, the company actively recruit personnel and promote them to managerial posts regardless of attributes, such as gender, age, race, nationality, and whether they are new graduates or mid-career workers, so that all employees are provided with equal opportunities to receive education and training, advance in their careers, and get promoted, receive performance-based treatment, and are assigned to an appropriate section. Regarding their initiatives for promoting female employees to flourish, “the ratios of jobs to applicants for men and women,” “retention rate,” “workstyles, including working hours,” “ratio of managers,” “diverse career paths,” etc. were highly evaluated, so the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare gave the three-star “Eruboshi” certification to the company, in accordance with the Act on the Promotion of Women's Active Engagement in Professional Life in 2020.
The non-consolidated goals they aim to achieve by the end of March 2025 and their progress are as follows.
Goal | Progress |
Goal 1: To increase the ratio of female employees to 40% | It has been increased to 43.2% as of the end of March 2024. They will continue recruitment activities for attaining the management objective of increasing the ratio of female hires at the time of recruitment of new graduates and mid-career workers to 50%. |
Goal 2: To increase the ratio of employees who have taken paid leave to 65% or higher, to foster a good balance between private and business life and enhance employees’ engagement | It reached 85.4% in the fiscal year ended March 2024. They will make continuous efforts to attain the goal by specifying anniversary holidays, dates for promoting employees to take paid leave, etc. |
Goal 3: To develop an environment in which employees can work from home at least once a week | They achieved this goal earlier than scheduled, thanks to the measures for preventing COVID-19. |
As of now, the field of their core business is inside Japan, so there are no non-Japanese managers, but the number of non-Japanese managers is expected to increase as their business expands in overseas markets.
【3‐4 Material issues regarding “business models and innovation”】
(1) Initiatives and innovation for enhancing competitiveness
(2) Supply chain management
The company prohibits improper transactions, unfair competition, and the abuse of a dominant position, and built appropriate partnerships with customers and suppliers.
The company produced “a purchase policy,” including “reasonable selection of business partners and provision of fair competition opportunities,” “compliance with laws and regulations and establishment of partnership,” “purchase conscious of the environment and society,” “management of confidential information,” “prohibition of pursuit of personal profit,” and “collection and analysis of corporate information.” Under the recognition that in order to realize a sustainable society, it is indispensable to conduct measures for fulfilling social responsibilities in the entire supply chain, including business partners, “requests toward business partners” are mentioned in the website.
Requests toward business partners (excerpts)
☆Human rights and labor | |
Eradication of discrimination | Not to discriminate employees on the basis of race, religion, gender, age, sexual orientation, disability, nationality, or the like in recruitment, promotion, remuneration, wage, or the like |
Prevention of inhumane treatment and harassment | To prevent all kinds of inhuman acts and harassment, such as power harassment, sexual harassment, corporal punishment, mental or physical oppression, and verbal abuse |
☆Compliance | |
Compliance with laws and regulations | To comply with all applicable laws and regulations |
Prohibition of abuse of a dominant position | To maintain appropriate relationships with stakeholders without abusing a dominant position |
☆Environment conservation | |
Environmental activities | To engage in activities for conserving the earth environment |
Promotion of the efficient use of energy | To strive to implement energy-saving measures for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in business activities |
Purchase policy and requests to business partners
https://www.systena.co.jp/ir/management/procure.html
【3‐5 Material issues regarding risk control and governance】
(1) Corporate Governance
<Basic policy>
The Company intends to enhance corporate governance with the aim of responding to rapid changes in the business climate, to promote management emphasizing speed based on promote decision-making to increase management efficiency, to work toward sustainable growth of the business, increasing shareholder value and continuous shareholder returns, to harmonize the interests of shareholders, customers, business partners, employees, local communities and other stakeholders (interested parties) and to maximize general benefits as a whole while endeavoring to secure soundness in management and full regulatory compliance.
To achieve this, the Company intends to take very seriously the advice and suggestions of the external experts (audit corporation, lead-managing securities companies, lawyers, labor and social security attorneys, judicial scriveners, etc.) and stakeholders and will work to enhance the fairness and transparency of management, to build systems appropriate to the size of the Company using its inherent mobility, to further promote self-improvement as a listed company in full awareness of stakeholders, to enhance corporate governance and to disclose information in a timely and appropriate manner.
<System for corporate governance>
While comprehensively considering speedy management based on swift decision making, business scale, the appropriateness of the function to oversee them, etc., the company adopted the auditor system, in which the board of directors and the board of auditors oversee and audit business executions.
*Organization type, and the composition of directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with corporate auditors |
Directors | 9 directors, including 3 outside ones. (including 3 independent executives) |
Auditors | 4 auditors, including 4 outside ones. (including 3 independent executives) |
◎Corporate Governance Report
Updated on April 1, 2024
<Reason for not following the principles of the Corporate Governance Code (excerpt)>
Written based on the Code revised in June 2021.
Principles | Disclosure contents |
【Supplementary Principle 2-4-(1) Ensuring Diversity in the Promotion of Core human Resources, etc.】 | The Company promotes employees to management positions regardless of attributes such as gender, age, race, nationality or whether they were hired mid-career or as a new graduate. The Company’s policy is to treat employees according to their abilities and to assign the right people to the right positions. For details, please refer to the following website. diversityhttps://www.systena.co.jp/sustainability/esg_society/# |
【Supplementary Principle 3-1-3 Approaches to Sustainability】 | The Company’s initiatives on sustainability are described on the webpage below. Here, the Company explains its disclosures based on the TCFD recommendations or an equivalent framework, which is mandatory only for companies listed on the Prime Market. The Company engages in the business of providing IT service, and does not operate any business with high environmental impact, such as the manufacturing of goods. Accordingly, at present the climate change problem is not expected to affect the Company’s business significantly. However, the Company began to acquire ISO 140001 certification in 2004 and has since been striving to reduce resource consumption and waste emissions based on its understanding that the global environment is an asset held by all of mankind that is valuable and must be preserved for future generations. In addition, all IT-related climate change measures taken by companies are in the Company’s business domain. The increase of the Company’s helps increase the efficiency of customers' business and leads to their reduction of resources they consume and the waste they emit, which contributes to the protection of the global environment. Therefore, the Company believes that its growth leads to the ability to control climate change. Based on the above ideas, the Company has yet to disclose information based on the TCFD recommendations or an equivalent framework at present. The Company will consider the matter where necessary in the future. The Company’s environmental initiatives are described on the webpage below. The Company’s sustainability initiatives https://www.systena.co.jp/sustainability/ The Company’s environmental initiatives https://www.systena.co.jp/sustainability/esg_environment.html |
<Disclosure pursuant to the principles of the Corporate Governance Code (excerpt)>
Written based on the Code revised in June 2021.
Principles | Disclosure contents |
【Principle 1-4 Strategically held shares】 | Our company does not and will not hold listed shares strategically. |
【Principle 5-1 Policy on Constructive Dialogue with Shareholders】 | The Company establishes and discloses a disclosure policy to encourage constructive dialogue with shareholders. Please refer to the Company’s website for further details. https://www.systena.co.jp/ir/management/disclosure.html Please refer to "2. Status of IR Activities" in "III. Implementation Status of Measures for Shareholders and Other Stakeholders" in this Report for information about the development of a framework and initiatives for this. |
(2) Risk control
Regarding important legal affairs and compliance, the staff of the business administration division conduct necessary discussions and receive legal advice from corporate lawyers. This system is aimed at appropriately dealing with various latent risks and preventing illegal and unlawful acts, etc.
4.Financial and non-financial data
(1) Financial data
◎ BS/PL
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
Sales | 64,552 | 60,781 | 65,272 | 74,526 | 76,940 |
Ordinary income | 7,871 | 7,507 | 8,578 | 9,955 | 9,942 |
Net income | 5,471 | 4,974 | 5,992 | 7,317 | 7,232 |
EPS [yen] | 14.05 | 12.84 | 15.47 | 18.89 | 18.67 |
ROE [%] | 25.5 | 20.6 | 21.6 | 22.9 | 20.0 |
Total assets | 35,956 | 38,886 | 43,477 | 48,879 | 54,038 |
Net assets | 22,955 | 25,996 | 30,173 | 34,650 | 38,601 |
Equity ratio [%] | 63.0 | 65.9 | 68.5 | 69.9 | 70.5 |
*Unit: million yen. Net income means net income attributable to owners of the parent.
◎ CF
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
Operating CF | 4,831 | 7,205 | 5,544 | 7,648 | 9,036 |
Investment CF | -640 | -1,562 | -559 | -2,016 | -251 |
Free CF | 4,191 | 5,643 | 4,985 | 5,632 | 8,785 |
Financial CF | -3,145 | -1,983 | -1,905 | -2,854 | -3,504 |
Cash and cash equivalents | 15,221 | 18,875 | 21,964 | 24,792 | 30,092 |
*Unit: million yen
(2) Non-financial data
① Social capital-related
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
Number of shareholders | 11,178 | 8,433 | 10,406 | 15,700 | 37,122 |
*Total number of shareholders, including shareholders holding shares less than one trading lot
② Human capital-related
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
No. of employees (consolidated) | 3,278 | 3,754 | 4,293 | 4,832 | 5,239 |
No. of employees (non-consolidated) | 2,565 | 2,900 | 3,456 | 4,117 | 4,506 |
No. of male employees | 1,714 | 1,813 | 2,036 | 2,365 | 2,559 |
Ratio of male employees [%] | 66.8 | 62.5 | 58.9 | 57.4 | 56.8 |
No. of female employees | 851 | 1,087 | 1,420 | 1,752 | 1,947 |
Ratio of female employees [%] | 33.2 | 37.5 | 41.1 | 42.6 | 43.2 |
*Unit: people. No. of employees (excluding part-time workers and temporary staff) as of March 31 in each fiscal year
◎ Recruitment-related
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
No. of new graduates recruited (non-consolidated) | 162 | 363 | 577 | 808 | 798 |
No. of male ones | 114 | 256 | 303 | 503 | 498 |
No. of female ones | 48 | 107 | 274 | 305 | 300 |
No. of mid-career workers recruited (non-consolidated) | 248 | 240 | 280 | 281 | 284 |
No. of male ones | 118 | 63 | 76 | 84 | 87 |
No. of female ones | 130 | 177 | 204 | 197 | 197 |
*Unit: people
◎ Diversity-related
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
No. of managers | 190 | 192 | 217 | 205 | 161 |
No. of male hands-on managers | 176 | 179 | 200 | 187 | 146 |
Ratio of male hands-on managers [%] | 92.6 | 93.2 | 92.2 | 91.2 | 90.7 |
No. of female hands-on managers | 14 | 13 | 17 | 18 | 15 |
Ratio of female hands-on managers [%] | 7.4 | 6.8 | 7.8 | 8.8 | 9.3 |
No. of non-Japanese employees | 53 | 55 | 65 | 87 | 102 |
No. of employees with disabilities | 72 | 68 | 92 | 116 | 146 |
Ratio of employees with disabilities [%] | 2.20 | 1.81 | 2.14 | 2.40 | 2.79 |
*Unit: people. No. of managers means the number of managers, that is, section chiefs and managers at higher positions as of April 1 in each fiscal year. The ratio of employees with disabilities means the ratio to the total number of employees of the Systena Group.
◎ Work-life balance-related
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
Average overtime hours per month | 20 | 13.5 | 12.6 | 10.8 | 9.3 |
Ratio of employees who have taken paid leave [%] | 63.0 | 62.1 | 65.2 | 75.6 | 85.4 |
No. of employees who have taken childcare leave | 83 | 92 | 113 | 134 | 158 |
No. of male ones | 7 | 7 | 8 | 15 | 17 |
Ratio of male ones | 6.7 | 11.6 | 13.3 | 28.2 | 33.3 |
No. of female ones | 76 | 85 | 105 | 119 | 141 |
Ratio of female ones [%] | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
No. of employees working for short hours | 67 | 82 | 91 | 100 | 110 |
No. of male ones | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
No. of female ones | 66 | 79 | 90 | 99 | 109 |
No. of employees who have taken leave for spouse’s childbirth | 39 | 22 | 25 | 15 | 20 |
No. of employees who have taken leave for nursing a child | 16 | 9 | 14 | 18 | 17 |
*Unit: people. The unit of the average overtime hours per month is hours/month.
◎ Wage gap between male and female employees
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
All laborers [%] | - | - | - | 80.0 | 80.1 |
Full-time employees [%] | - | - | - | 80.1 | 80.2 |
Fixed-term employees [%] | - | - | - | 83.1 | 83.2 |
◎ Health-oriented management-related
| FY 3/20 | FY 3/21 | FY 3/22 | FY 3/23 | FY 3/24 |
Ratio of employees who maintain a desirable weight | - | 61.0 | 58.2 | 57.7 | 57.6 |
Rate of implementation of specific health guidance | - | - | - | - | 23.1 |
Rate of undergoing a stress check | - | 94.1 | 95.5 | 97.2 | 98 |
Ratio of employees with high stress levels | - | 16.7 | 13.9 | 13.9 | 14 |
Absenteeism*1 | - | - | - | - | 1.9 |
Presenteeism*2 | - | - | - | - | 75.1 |
Engagement in work [scores]*3 | - | - | 2.98 | 2.76 | 2.75 |
Ratio of employees who have an exercise habit*4 | - | 13.8 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 20.2 |
Ratio of employees who sleep enough*5 | - | 46.8 | 56.3 | 54.3 | 53.1 |
Cigarette smoking rate | - | 28.5 | 26.6 | 26.6 | 25.2 |
Ratio of employees who have a drinking habit*6 | - | 16.4 | 14.1 | 11.5 | 13.5 |
*Unit: %
*1: Ratio of employees who have taken 4 or more days off in a row due to mental or physical disorder, taken from the attendance data of all employees
*2: Measured with a Single-Item Presenteeism Question (SPQ) developed by the University of Tokyo. Average of performance level in the past 4 weeks under the assumption that the performance made when there is no illness or injury is 100%.
*3: Average of Utrecht Work Engagement Scale for questions about vigor and ardor
*4: Ratio of employees who exercise for 30 minutes or longer twice a week
*5: Ratio of employees who can get restful sleep
*6: Ratio of employees who drink sometimes or everyday with the amount of alcohol intake being equivalent to 360 ml of refined sake per day
<For reference>
For publishing ESG Bridge Report, the company enlisted significant cooperation from Mr. Ryohei Yanagi (PhD. in economics from Kyoto University, and a visiting professor of Graduate School of Accountancy, Waseda University).
This section mentions the purpose of publishing ESG Bridge Report and outlines the “Yanagi model” proposed by Mr. Yanagi, while citing a passage from his literature “CFO Policy 2nd ed.”
(1) Regarding ESG Bridge Report
While ESG investment became mainstream, investors demand that Japanese companies disclose ESG information proactively. Accordingly, an increasing number of companies produce integrated reports.
However, the production of integrated reports requires the understanding and involvement of executives, some human resources and some budgets. Accordingly, many companies still cannot produce integrated reports.
Also, for producing integrated reports, it is necessary to take many steps, including the summarization of various data, the identification of materiality, and the setting of indicators and goals. It seems that many companies are not prepared enough, so they are reluctant.
However, Mr. Yanagi mentioned, in “CFO Policy 2nd ed,” that “if Japanese enterprises shed light on their potential ESG value, their PBR will probably be at least the same level (around 2x) as that of companies in the UK” and “by actualizing Yanagi model, it is possible to double the value of Japanese companies, probably improving investment, employment, and pensions and maximizing national wealth, which have a high probability.” Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. considers that the provision of ESG information of Japanese companies is meaningful for the entire Japan and should be promoted actively.
Under these circumstances, for companies who deeply recognize the necessity to disclose ESG information although they still cannot produce integrated reports, our company cooperatively produces “ESG Bridge Report” based on currently available data and resources, to provide investors with ESG information as needed by investors as much as possible.
Japan Exchange Group actively encourages Japanese companies to disclose EGS information, and published “Practical Handbook for ESG Disclosure.” Page 6 of this handbook mentions “We do not mean that you cannot disclose information unless all of the elements mentioned here are covered. We expect that this handbook will provide you with some clues when you start with what you can do while considering your situation for disclosing ESG information to communicate with investors and proceed with more initiatives.” We believe that “ESG Bridge Report” is a tool for “starting with what you can do for disclosing ESG information.”
Mr. Yanagi mentioned that in order to achieve full-scale Yanagi model, it is necessary to conduct empirical research indicating positive correlation between ESG and corporate value and disclose concrete cases in which companies’ contribution to society helps increase long-term economic value. Accordingly, the actual hurdle is high, but we would like to explicitly describe how ESG initiatives of each company lead to the improvement in corporate value.
Based on the feedback from many investors who have read our reports, we would like to improve the quality of our reports. We would appreciate your candid opinions.
Kaoru Hosaka
Representative Director and Chairperson
Investment Bridge Co., Ltd.
k-hosaka@cyber-ir.co.jp
(2) Regarding “Yanagi Model”
(Increasing value of non-financial capital, rapid increase of ESG investment, and production of a conceptual framework for connecting ESG and corporate value)
Recently, many empirical studies have verified the increase of importance of non-financial information in corporate value evaluation, and it can be inferred that invisible value (intangible assets) and non-financial capital value account for about 80% of corporate value.
In addition, it can be considered, from the results of many empirical studies on the relation between non-financial information and corporate value, that ESG may be positively correlated with corporate value.
On the other hand, as ESG investment is becoming mainstream globally, Japanese enterprises, whose PBR is less than one or stagnant in many cases although they have latent ESG value, need to transform non-financial capital into future financial capital with the “Yanagi model” for raising PBR, or produce and disclose a conceptual framework for connecting ESG and corporate value.
(Overview of the “Yanagi Model”)
Out of shareholder value, the book value of shareholders’ equity, which corresponds to “the part where PBR = 1,” is composed of current financial capital and financial value.
On the other hand, out of shareholder value, market value added, which corresponds to “the part where PBR exceeds 1,” is composed of non-financial capital (which can be said to be future financial capital), and the sum of current value of cash flow of equity spread (= ROE – Cost of shareholders’ equity) in the residual profit model.
Therefore, Mr. Yanagi proposed “the synchronization model of non-financial capital and equity spread” = “Yanagi Model” as a conceptual framework for synchronizing ESG and corporate value, as a result of non-financial strategy.
In the “Yanagi Model,” non-financial capital has a mutually complementary relation with equity spread, which is the sum of current value of residual profit through “market value added.” Namely, the value creation with equity spread is consistent in the long term because of the delay, via the creation of value of non-financial capital, including ESG, and market value added.
Therefore, ESG management can be synchronized with long-term investors, who demand capital efficiency, via marked value added, and cooperation is possible.
According to Mr. Yanagi’s survey on investors for supporting the model, many investors around the world demand that “the relation between ESG and ROE values is explained” and answered that “100% or a significant proportion of the value of ESG is taken into account in PBR.” It can be considered that the “Yanagi model” is supported directly or indirectly by most of long-term investors.
(For details about his “Yanagi Model,” refer to “CFO Policy 2nd ed.” authored by Ryohei Yanagi, CHUOKEIZAI-SHA (2020).)
This report is not intended for soliciting or promoting investment activities or offering any advice on investment or the like, but for providing information only. The information included in this report was taken from sources considered reliable by our company. Our company will not guarantee the accuracy, integrity, or appropriateness of information or opinions in this report. Our company will not assume any responsibility for expenses, damages or the like arising out of the use of this report or information obtained from this report. All kinds of rights related to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. The contents, etc. of this report may be revised without notice. Please make an investment decision on your own judgment. Copyright(C) Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |



